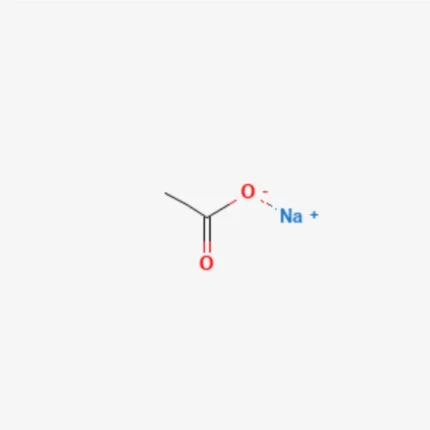
Sodium acetate
Sodium Acetate, with the chemical formula CH₃COONa, is the sodium salt of acetic acid. It appears as a white crystalline powder, odorless or with a mild vinegar-like smell (especially when heated). Sodium acetate is moderately hygroscopic, particularly in its anhydrous form. It is available in two forms: anhydrous and hydrated (commonly the trihydrate form, CH₃COONa·3H₂O).
Structure of Sodium Acetate
Sodium acetate is an ionic compound composed of a sodium cation (Na⁺) and an acetate anion (CH₃COO⁻). The acetate ion consists of a methyl group (CH₃) bonded to a carboxylate group (COO⁻). In the carboxylate group, the double bond between carbon and oxygen exhibits resonance, meaning the negative charge is delocalized over the two oxygen atoms.
Chemical Formula: CH₃COONa
Resonance Structure: O=C–O⁻ ⇄ ⁻O–C=O
Properties of Sodium Acetate
-
Appearance: White crystalline powder
-
Odor: Odorless; may release a vinegar-like smell when heated
-
Solubility: Highly soluble in water; moderately soluble in ethanol (~1.4 g/100 mL)
-
Hygroscopicity: Anhydrous form absorbs moisture from the air
-
Basic Nature: As the salt of a weak acid and strong base (NaOH), its aqueous solution is slightly alkaline (pH ~8–9 for a 0.1 M solution)
-
Melting Point: Anhydrous form decomposes around 324°C; trihydrate melts at ~58°C, releasing water of crystallization
-
Buffering Properties: In combination with acetic acid, it forms a buffer solution effective within a pH range of 4 to 6.5
-
Chemical Behavior: Can release gases such as acetic acid or CO₂ when in contact with strong acids or oxidizing agents
Applications of Sodium Acetate
Food Industry
-
Used as a food additive (E262) for pH regulation, providing a salty/sour taste, and as a preservative
-
Acts as an antibacterial and antifungal agent in some food formulations
Pharmaceutical and Medical
-
Serves as a sodium source in IV injections or dialysis solutions
-
Functions as a buffer component in drug formulations and biological reactions
Textile Industry
-
Used in dye baths to control pH and aid in dye uptake
-
Neutralizes residual acids like H₂SO₄
-
Helps prevent static electricity buildup
Construction Industry
-
Acts as an additive to control pH and improve freeze resistance in concrete (e.g., in sealants)
Laboratory Use
-
Employed in buffer preparation (especially in biochemistry and DNA extraction)
-
Used as a carbon source in bacterial culture media
-
Forms part of extraction buffers in molecular biology
Hand Warmers and Heating Pads
-
Utilizes supersaturated sodium acetate trihydrate solution that releases latent heat (~264–289 kJ/kg) upon sudden crystallization
Other Uses
-
Delays curing in chloroprene rubber production
-
Used in leather tanning and dye manufacturing
Advantages of Sodium Acetate
-
Generally safe for food use as approved by the FDA in regulated amounts
-
Effective buffering capacity
-
Highly compatible with industrial processes
-
Low cost
-
Preservative effect (antimicrobial)
-
Useful in phase-change thermal storage systems
Disadvantages of Sodium Acetate
-
Moderately hygroscopic (especially in anhydrous form) → requires airtight storage
-
Irritant to eyes and skin upon contact
-
Dust inhalation may cause respiratory irritation
-
Ingestion in high amounts may lead to digestive upset or hypernatremia
-
Thermal decomposition at high temperatures may release irritating vapors
-
Caution in patients with kidney or heart issues due to electrolyte imbalances
-
Pharmaceutical forms may contain aluminum or other excipients; special care is needed in premature infants or patients with renal insufficiency
Sodium Acetate Trihydrate
Properties of Sodium Acetate TrihydrateHigh solubility in water: Sodium acetate trihydrate dissolves easily in water and its aqueous solutions are neutral. Moisture-absorbing property: This compound acts as a moisture-absorbing agent and can absorb moisture from the environment. Low melting point: Sodium acetate trihydrate melts at a relatively low temperature and releases heat when solidified. Odorless and colorless: This compound exists in the form of colorless and odorless crystals.
Sodium Acetate Trihydrate ApplicationsFood Industry: Food Additive: It is used as a food additive to adjust pH and improve the taste of foods. Preservative: Acts as a natural preservative in some foods. Chemical industry: Buffer: Used as a buffer in chemical reactions. Catalyst: Acts as a catalyst in some chemical reactions. Textile industry: Dye fixation: Used to fix colors in fabrics. Construction industry: Antifreeze: Used in some antifreeze mixtures. Heating industry: Hand warmers: The exothermic properties of this compound are used in hand warmers. Laboratories: Melting point determination: Used in laboratories to determine the melting point of other substances.
Sodium acid pyrophosphate
Sodium Acid Pyrophosphate
Sodium acid pyrophosphate propertiesBuffering property: SAPP can reduce pH changes in solutions and act as a buffer. Chelating agent: SAPP can form complexes with metal ions and hence is used as a chelating agent in various industries. Anti-oxidation: SAPP can act as an anti-oxidation agent and prevent oxidation of food and other products.
Sodium acid pyrophosphate applicationsFood industry: pH adjuster: Used to adjust pH in food products such as cheese, soft drinks and processed meats. Emulsifying agent: Acts as an emulsifier in the production of dairy products and ice cream. Anti-caking agent: Used in washing powders and other powdered products. Color controller: Used in meat products to maintain the red color of meat. Pharmaceutical industry: Drug carrier: Used as a drug carrier in some formulations. pH regulator: Used to adjust the pH in pharmaceutical products. Detergent industry: Water softener: Used in detergents to soften hard water. Foam builder: Helps produce foam in detergents. Advantages of using sodium acid pyrophosphate High solubility: Easily dissolves in water. Buffering property: Helps maintain pH stability. Chelating agent: Forms complexes with metal ions. Antioxidant: Prevents oxidation of materials. Wide applications: Used in various industries.
Important points in using sodium acid pyrophosphateSkin and eye contact: Causes irritation if it comes into contact with skin and eyes. Inhalation: Inhalation of dust from this material can cause respiratory problems. Storage: Store in closed containers in a cool, dry place.
Sodium alpha olefin sulfonate / AOS
Product SpecificationsAppearance Clear yellow liquid Active substance 28-32 Color (Colour) Max 50 pH 9.0-11.0 Molecular mass 341
Applications- Due to its creamy state, it is used in creams, lotions, toilet liquid, etc. - Due to its good foaming power, PADAFIN is used in the textile, petrochemical, industrial detergents, etc. - In fire-fighting foam as a foaming agent. - As a concrete volume modifier - Emulsifier and wetting agent in pesticides"
Features and Benefits- High wetting, foaming, detergency and emulsifying properties - Environmentally biodegradable - Resistant to water hardness - Low sensitivity to hand skin - High solubility in water and easy rinsing - High stability - Good compatibility with other types of surfactants
PropertiesIt has high wetting, foaming, detergency and emulsification. The most important properties of sodium alpha olefin sulfonate: Appearance of sodium alpha olefin sulfonate » Clear yellow liquid Molecular mass of sodium alpha olefin sulfonate » 341 Active ingredient sodium alpha olefin sulfonate » 28-32
Sodium Bicarbonate
Sodium Bicarbonate, also known as Baking Soda, Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate, or NaHCO₃, is a white, odorless, crystalline, and mildly hygroscopic inorganic compound. It has a wide range of applications in the food, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, agricultural, detergent, petrochemical, firefighting, and water treatment industries. It functions as a pH regulator, buffering agent, antacid, mild cleanser, flame retardant, and deodorizing agent.
Chemical Structure of Sodium Bicarbonate
-
Chemical Formula: NaHCO₃
-
IUPAC Name: Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate
-
Molecular Structure: Ionic (Na⁺ + HCO₃⁻)
-
CAS Number: 144-55-8
-
3D Structure: The hydrogen carbonate ion (HCO₃⁻) is planar and forms a stable ionic crystal lattice with sodium ions in the solid state.
-
Molecular Weight: 84.01 g/mol
-
Natural Source: Found naturally in deposits such as Nahcolite.
Physical and Chemical Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical State | White crystalline or powdery solid |
| Taste and Odor | Odorless, slightly alkaline taste |
| Decomposition Temperature | Approximately 270 °C |
| pH (1% aqueous solution) | Between 8.2 and 8.6 |
| Viscosity | Not applicable (solid material) |
| Chemical Stability | Stable under normal conditions; decomposes upon heating to CO₂, Na₂CO₃, and H₂O |
Applications of Sodium Bicarbonate
Food Industry (Food Grade – E500)
-
Leavening agent in bread, cakes, and baked goods
-
pH regulator in processed foods
-
Antacid component in carbonated drinks and instant beverage powders
Pharmaceutical Industry
-
Antacid for treatment of heartburn and acid reflux
-
Active ingredient in mouthwash, nasal rinse, and contact lens solutions
-
Buffering agent in effervescent tablets, injectables, and syrups
Detergent and Cleaning Industry
-
Mild cleaning and natural deodorizing agent
-
Water softener in detergent powders
-
Odor absorber in refrigerators and footwear
Firefighting
-
Primary component of dry chemical fire extinguishers
-
Neutralizing agent for acid spills in chemical emergencies
Agriculture and Animal Husbandry
-
Soil pH balancer for acidic soils
-
pH regulator in animal feed formulations
-
Antifungal treatment for plant leaves
Water and Wastewater Treatment
-
pH adjustment in industrial effluents
-
Neutralization of dissolved metal ions
Advantages of Sodium Bicarbonate
-
Non-toxic, biocompatible, and environmentally degradable
-
Available in food, pharmaceutical, and industrial grades
-
Safe for humans and the environment under permitted doses
-
Multi-functional and cost-effective
-
Chemically stable during long-term storage under proper conditions
-
Compatible with many other chemical substances
Disadvantages of Sodium Bicarbonate
-
Moisture-sensitive – loses effectiveness in humid environments
-
Decomposes at high temperatures, unsuitable for direct thermal processes
-
Excessive use may cause over-alkalization of the medium
-
Requires high purity grades for specific uses (e.g., pharmaceutical, food)
-
Not suitable for closed pressurized systems due to CO₂ generation during decomposition
Safety and Handling
-
GHS Classification: Not classified as hazardous
-
Oral Toxicity: Non-toxic at dietary levels (GRAS – Generally Recognized as Safe by FDA)
-
Inhalation: Low hazard; excessive dust exposure may irritate respiratory passages
-
Skin and Eye Contact: Generally safe; prolonged exposure may cause dryness of skin
-
Reactivity: Stable; decomposes upon heating to form Na₂CO₃, CO₂, and H₂O
Safety Precautions
-
Use a respiratory mask in dusty industrial environments
-
Wear protective gloves when handling large quantities
-
Use safety goggles in powder-handling areas
-
Ensure adequate ventilation in storage or enclosed spaces
-
Avoid direct contact with acids (reacts vigorously with effervescence)
Storage Conditions
| Parameter | Recommended Condition |
|---|---|
| Storage Temperature | Between 15 °C and 30 °C |
| Humidity | Dry, low-humidity environment (moisture causes caking) |
| Light Exposure | Store away from direct sunlight |
| Packaging | Multi-layer polypropylene or kraft paper bags with moisture barrier |
| Storage Area | Covered, ventilated warehouse away from acids |
| Labeling | Clear and standardized labeling (production date, grade, safety warnings, storage conditions) |
Sodium carbonate
Sodium Carbonate, commonly known as Soda Ash, Washing Soda, or Soda Crystal, is a white, odorless, inorganic compound that appears as a fine powder or granular solid.
It is one of the most widely used basic chemicals in the world and is supplied in three main grades: Light Soda Ash, Dense Soda Ash, and High-Purity Grade.
Chemical Structure
-
Chemical Name: Sodium Carbonate
-
Chemical Formula: Na₂CO₃
-
Structure Type: Ionic, containing two Na⁺ ions and one CO₃²⁻ ion
-
CAS Number: 497-19-8
-
Molecular Weight: 105.99 g/mol
-
Crystal Structure: Monoclinic (Anhydrous form)
-
EC Number: 207-838-8
Physical and Chemical Properties
| Property | Description / Value |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White powder or granules |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density (20°C) | 2.53 g/cm³ |
| Bulk Density: | |
| – Light Grade | 0.50 – 0.60 g/cm³ |
| – Dense Grade | 0.90 – 1.10 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 851°C (decomposes to Na₂O and CO₂ at higher temperatures) |
| Boiling Point | Not applicable – decomposes before boiling |
| pH (1% solution, 25°C) | ~11.6 |
| Viscosity | Not applicable (solid) |
| Solubility in Water (20°C) | 215 g/L |
| Solubility in Ethanol | Very low (~0.1 g/100 mL) |
| Vapor Pressure | Zero (non-volatile) |
Applications of Sodium Carbonate
1. Glass Manufacturing
-
The largest global application of sodium carbonate.
-
Reduces the melting temperature of silica (SiO₂) and improves the flow of molten glass.
-
Essential raw material in flat glass, container glass, and fiberglass production.
2. Detergents and Cleaning Products
-
Acts as a strong alkaline builder in powdered and liquid detergents.
-
Helps remove hardness ions (Ca²⁺ and Mg²⁺) and enhances surfactant performance.
-
Used in industrial cleaning agents and laundry formulations.
3. Water Treatment
-
Used to raise water pH and remove temporary hardness by precipitating calcium and magnesium ions.
-
Applied in municipal, industrial, and boiler water treatment systems.
4. Food Industry (E500)
-
Approved as Food Additive E500 (Sodium Carbonate).
-
Used as a pH regulator, anti-caking agent, and leavening agent.
-
Helps control acidity in carbonated beverages and acts similarly to sodium acid pyrophosphate in food formulations.
5. Metallurgy
-
Used to desulfurize iron ore and assist in alumina extraction and copper refining processes.
-
Acts as a fluxing and purifying agent in metal smelting.
6. Other Industries
-
Leather tanning – pH control and neutralization
-
Textiles – dyeing and finishing operations
-
Pulp and Paper – delignification and pH control
-
Paints and Coatings – pH buffer and pigment dispersion
-
Petrochemical Processes – neutralizing and refining applications
Advantages of Sodium Carbonate
✅ Widely available and cost-effective
✅ Chemically stable under normal storage and handling conditions
✅ Environmentally friendly in permitted grades
✅ Non-toxic and safe to transport
✅ Efficient alkaline source for pH adjustment
✅ Suitable replacement for Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) in many applications
Limitations
⚠️ Irritating to skin and eyes upon direct contact with aqueous solutions
⚠️ Absorbs CO₂ from air over time, forming sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃)
⚠️ Hygroscopic – tends to absorb moisture and form lumps during humid storage
⚠️ Limited use in processes sensitive to sodium ion contamination
Safety and Storage
-
GHS Classification:
Skin Irritant (Category 2); Eye Irritant (Category 2); STOT SE 3 (Respiratory Irritant) -
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, dust mask or respirator -
Inhalation:
May cause irritation of respiratory passages at high concentrations -
Skin/Eye Contact:
Rinse immediately with plenty of cold water for at least 15 minutes -
Packaging:
25 kg or 50 kg polypropylene bags, palletized, moisture-resistant -
Storage Conditions:
Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from moisture -
Chemical Incompatibility:
Avoid contact with strong acids (CO₂ evolution) and high humidity environments
Summary
Sodium Carbonate (Na₂CO₃) is an essential alkaline raw material used globally in glass manufacturing, detergents, water treatment, and numerous industrial processes.
With its strong basicity, high stability, and versatility, it remains one of the most important and cost-effective inorganic compounds in the chemical industry.
Sodium Carbonate (Light- Heavy Soda)
Difference between light and heavy sodium carbonateThe only main difference between light and heavy sodium carbonate is their particle size and density. Light sodium carbonate: It has finer particles and lower density. For this reason, it dissolves easily in water and is used in the detergent, textile and water purification industries. Heavy sodium carbonate: It has coarser particles and higher density. For this reason, it is used in the glass, paper and leather industries.
Properties of sodium carbonateAlkalinity: Sodium carbonate is an alkaline substance and creates an alkaline solution in water. Solubility in water: Both light and heavy types of sodium carbonate dissolve in water. Moisture absorption: Sodium carbonate absorbs moisture from the air. Thermal stability: It is stable at high temperatures.
Sodium carbonate applicationsDetergent industry: Production of laundry detergents, dishwashing detergents and household cleaners Textile industry: Dyeing, bleaching and pH adjustment processes Food industry: pH adjustment, texture improvement and increase in food shelf life Glass industry: Glass production Paper industry: Paper bleaching and recycling processes Leather industry: Leather tanning Water treatment: Water softening and removal of impurities Agriculture: Soil pH adjustment and pest control Pharmaceutical industry: Production of some drugs Safety tips Sodium carbonate is an alkaline substance and its contact with skin and eyes can cause irritation and burns. Use gloves and safety glasses when working with sodium carbonate. Store sodium carbonate in a cool, dry place.
Sodium Citrate
Properties of Sodium CitrateHigh solubility in water: Sodium citrate dissolves easily in water and its aqueous solutions are neutral. Mild taste: Sodium citrate tastes slightly salty and sour. Buffering property: Sodium citrate acts as a buffer and can reduce pH changes in solutions. Anticoagulant property: Sodium citrate combines with calcium ions and prevents blood clotting.
Sodium Citrate ApplicationsFood industries: Food additive: It is used as a food additive to adjust pH, improve taste, and increase the shelf life of foods. Emulsifier: It acts as an emulsifier in the production of some food products such as cheese. Canning: Used in the canning process of food to prevent discoloration and maintain quality. Pharmaceutical industry: Anticoagulant: Used in laboratories and blood banks to prevent blood clotting. Antacids: Used to treat indigestion and acid reflux. Injectable solutions: Used as an ingredient in injectable solutions. Detergent industry: Water softener: Used to soften hard water and increase the effectiveness of detergents. Cosmetic industry: Creams and lotions: Used as a moisturizing agent in creams and lotions. Photographic industry: Image fixer: Used in the process of developing photographic films.
Benefits of using sodium citrateSafety: Sodium citrate is generally safe and has few side effects when used correctly. High efficiency: Sodium citrate performs very well in many applications. Availability: Sodium citrate is readily available and reasonably priced.
Sodium Diacetate
Sodium Diacetate (NaH(C₂H₃O₂)₂) is a double salt composed of sodium acetate and acetic acid, widely recognized as a versatile food additive. Registered under CAS No. 126-96-5, it appears as a white crystalline powder with a mild vinegar-like odor. Sodium diacetate exhibits antimicrobial properties and serves as an acidity regulator, making it highly useful in the food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries.
Chemical Structure of Sodium Diacetate
-
Chemical formula: NaH(C₂H₃O₂)₂
-
Composition: Formed by the reaction of sodium acetate and acetic acid
-
Functional group: Double salt of acetic acid
-
Appearance: White crystalline solid with a faint acetic acid odor
-
Solubility: Soluble in water and stable under ambient conditions
The structure allows sodium diacetate to act not only as a buffering agent but also as a slow-release source of acetic acid.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Sodium Diacetate
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White crystalline powder with mild acetic acid odor |
| Melting Point | 150–160 °C |
| Solubility | Freely soluble in water |
| pH (1% aqueous solution) | 4.5 – 5.0 |
| Stability | Stable under cool, dry conditions |
| Taste | Slightly salty with a vinegar-like flavor |
Grades of Sodium Diacetate
1. Food Grade Sodium Diacetate
-
Approved food additive (E262(ii))
-
Functions as an acidity regulator, antimicrobial, and preservative
-
Widely used in bakery, meat, and dairy industries
2. Pharmaceutical Grade Sodium Diacetate
-
Used as an excipient in pharmaceutical formulations
-
Provides antimicrobial protection and pH control in drug manufacturing
3. Industrial Grade Sodium Diacetate
-
Used in chemical processes, animal feed, and odor control
-
Exhibits antifungal and antimicrobial effects in non-food applications
Applications of Sodium Diacetate
1. Food Industry
-
Preservative and Antimicrobial Agent: Prevents mold and bacterial growth in bread, cakes, and baked goods.
-
Acidity Regulator: Controls pH in sauces, dressings, and beverages.
-
Flavor Enhancer: Imparts a mild vinegar-like taste to snacks, chips, and processed foods.
-
Shelf-life Extension: Widely used as food additive E262(ii) to extend product freshness.
2. Pharmaceutical Industry
-
Used in antiseptic formulations and personal care products.
-
Contributes to microbial control in pharmaceutical compositions.
3. Animal Feed
-
Acts as an antimicrobial additive in livestock and poultry feed.
-
Enhances feed safety and prevents spoilage.
4. Chemical Industry
-
Serves as a deodorizing and antifungal agent in various products.
-
Applied in specialized chemical formulations.
Advantages of Sodium Diacetate
✅ High safety for food and pharmaceutical uses (approved by FDA and EFSA)
✅ Multifunctional — applicable across food, pharmaceutical, and industrial sectors
✅ Strong antimicrobial activity against molds and bacteria
✅ Enhances food shelf life and reduces waste
✅ Improves flavor with a mild vinegar profile
Disadvantages of Sodium Diacetate
⚠️ Excessive use can result in an overly strong or unpleasant flavor
⚠️ High concentrations may cause gastric irritation
⚠️ Hygroscopic — readily absorbs moisture in humid environments
Safety and Storage Guidelines
-
Store in airtight, moisture-resistant containers
-
Keep away from direct sunlight, in a cool, dry environment
-
Use protective gloves and goggles in industrial handling
-
Follow approved dosage limits for food applications (E262 standard)
Sodium Diacetate Production Process
-
Step 1 – Sodium Acetate Production:
Reaction of acetic acid with sodium carbonate or sodium hydroxide. -
Step 2 – Addition of Extra Acetic Acid:
Sodium acetate reacts with excess acetic acid to form the double salt (sodium diacetate). -
Step 3 – Cooling and Crystallization:
The resulting solution is cooled, allowing sodium diacetate crystals to form. -
Step 4 – Drying and Packaging:
The dried crystals are processed into a fine white powder and packaged for commercial use.
Technical Specifications of Sodium Diacetate
| Parameter | Approximate Value |
|---|---|
| Chemical Name | Sodium Diacetate |
| Chemical Formula | NaH(C₂H₃O₂)₂ |
| CAS Number | 126-96-5 |
| Appearance | White powder with mild acetic acid odor |
| Melting Point | 150–160 °C |
| Solubility in Water | High |
| Grades | Food, Pharmaceutical, Industrial |
| Food Additive Code | E262(ii) |
Purchasing Sodium Diacetate
To purchase high-quality sodium diacetate and get the best pricing, it’s important to choose a reliable supplier.
Tamin Kala Tak Co., with years of experience in supplying raw materials for the food, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries, offers sodium diacetate in multiple grades.
Contact our experts today for orders and price inquiries.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions Sodium Diacetate
1. What is Sodium Diacetate?
A double salt of sodium acetate and acetic acid, used as a food additive, antimicrobial, and acidity regulator.
2. What’s the difference between Sodium Acetate and Sodium Diacetate?
Sodium acetate is a simple salt of acetic acid, while sodium diacetate contains additional acetic acid, providing stronger antimicrobial properties and a vinegar-like flavor.
3. Is Sodium Diacetate safe for consumption?
Yes. Food-grade sodium diacetate (E262(ii)) is approved by both the FDA and EFSA as safe for use in food.
4. What industries use Sodium Diacetate?
It’s used in food (bakery, meat, snacks), pharmaceutical, animal feed, and chemical industries.
5. How is the price of Sodium Diacetate determined?
Pricing varies based on grade, purity, supplier, and market conditions.