formic acid
- Agriculture Pesticides Textile and Leather Industry Dye Fixation Chemical Industries Cleaning Agents Fuel Cells
Full-automatic Rubber Crumb Produc…
Full-circle Retread Vulcanizer
General Purpose PolyStyrene (GPPS)
General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS) is produced through the polymerization of styrene monomer via a suspension process. The product is obtained as a solid material and compressed into granules to manufacture a wide range of plastic products. GPPS is characterized by its excellent clarity and high transparency. It is a hard, crystal-clear thermoplastic polymer that is versatile and easy to process. GPPS exhibits excellent electrical insulation, low density, and good dimensional stability. It is widely used in applications such as packaging, household goods, and office equipment.
Structure of GPPS
GPPS is a thermoplastic polymer derived from styrene monomer. The chemical structure of GPPS granules consists of linear chains of styrene monomer units connected by covalent bonds. The properties of GPPS can be modified through copolymerization with other monomers such as acrylonitrile, butadiene, zinc, or methyl methacrylate.
Properties of General Purpose Polystyrene
GPPS has high moisture resistance and excellent electrical insulation properties. However, it is brittle and exhibits low impact strength. Its tensile strength is about 50–60 MPa, and its flexural modulus ranges between 2200–2500 MPa.
The glass transition temperature (Tg) is approximately 85–105 °C, and its melting point (Tm) ranges between 200–240 °C. The heat deflection temperature (HDT) under a load of 0.45 MPa is typically 70–80 °C.
Applications of GPPS
1. Packaging
GPPS is a popular choice for packaging materials due to its excellent clarity, rigidity, and moldability. It is used in the production of food containers, disposable utensils, and CD cases. It is also utilized in blister packaging, commonly used for pharmaceutical products.
2. Consumer Products
Because of its excellent electrical insulation, lightweight, and dimensional stability, GPPS is used in the manufacture of various consumer goods, such as toys, cosmetic packaging, hangers, trays, and household organizers.
3. Construction Industry
GPPS, particularly grade 1540, is used in construction due to its outstanding insulation properties, low weight, and dimensional stability. It is employed in foam insulation boards, window frames, and lighting fixtures.
4. Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, GPPS is used for producing components such as instrument panels, door panels, and radiator parts because of its moldability and dimensional accuracy.
5. Standard Polystyrene Foam
Standard GPPS foam is a hard, transparent polymer with good thermal and electrical insulation and lightweight properties. Although less impact-resistant than HIPS, it is still widely used across various industries.
Advantages of GPPS
✅ Excellent moldability
✅ Good thermal and electrical insulation
✅ Cost-effective and versatile
✅ High transparency and optical clarity
✅ Stable dimensions
Disadvantages of GPPS
❌ Low impact resistance
❌ Limited thermal stability
❌ Non-biodegradable
GPPS Market Price
The price of GPPS in the market varies depending on brand, delivery location, and market conditions. Due to frequent price fluctuations, it is recommended to consult industry experts for up-to-date pricing information before purchase to ensure a cost-effective buying experience.
GPPS Grades
GPPS 1540
GPPS 1540 is one of the most widely used grades due to its high transparency, easy processability, and glossy surface finish. It is ideal for packaging, household appliances, and laboratory equipment. With its excellent melt flow index (MFI), it is suitable for injection molding and extrusion applications.
GPPS 1551
GPPS 1551 is a rigid, transparent thermoplastic designed for injection molding and component manufacturing. This grade offers high MFI and good thermal resistance, making it ideal for construction, packaging, and household products.
GPPS MP08
GPPS MP08 is a black-colored, UV-stabilized grade suitable for injection and blow molding processes. It contains an optimized carbon black content that enhances surface quality and durability. The supplier ensures consistent quality and long-term reliability for customers.
Production Process of GPPS
1. Styrene Monomer Preparation
Styrene monomer (C₈H₈) is obtained from refining units and purified through fractional distillation to remove organic and gaseous impurities. The industrial-grade styrene must have a purity of over 99% to prevent discoloration and mechanical weakness in the final polymer.
Key steps include:
-
Maintaining distillation temperature between 144–146 °C
-
Testing acid number and oil color index
-
Adding antioxidants (e.g., 4-tert-butylcatechol) to prevent premature polymerization
2. Suspension Polymerization
In this process, styrene monomer droplets are suspended in water with stabilizers and initiators. The main components include:
-
Styrene monomer: 30–40 wt%
-
Deionized water (carrier phase)
-
Suspension agent: gelatin or polyvinyl alcohol
-
Peroxide initiators: benzoyl peroxide or AIBN
Reaction temperature: 60–90 °C under near-atmospheric pressure.
Careful control of temperature, agitation speed, and composition ensures uniform bead size and targeted molecular weight.
3. Separation, Washing, and Drying
After polymerization:
-
Filtration: beads are separated from the aqueous phase
-
Washing: several rinses with deionized water to remove initiator residues
-
Drying: in rotary or fluid-bed dryers at 110–120 °C to achieve <0.1% moisture content
These steps ensure low moisture and high purity, resulting in an easily processable polymer.
Difference Between GPPS and HIPS
Although both belong to the polystyrene family, they differ fundamentally in structure and performance.
GPPS (General Purpose Polystyrene)
A pure homopolymer consisting only of styrene monomer units. It is amorphous, allowing light to pass through easily, giving it excellent clarity. However, it is brittle and has low impact resistance.
HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene)
A copolymer produced by polymerizing styrene in the presence of polybutadiene rubber. The rubber particles act as microscopic shock absorbers, greatly improving impact resistance (5–10× higher) than GPPS.
However, the inclusion of rubber reduces transparency, making HIPS opaque and milky white.
✅ Choose GPPS when clarity and rigidity are priorities.
✅ Choose HIPS when impact resistance and toughness are more important.
Comparison Table: GPPS vs. HIPS
| Property | GPPS (General Purpose Polystyrene) | HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene) |
|---|---|---|
| Alternative Name | Crystal Polystyrene | High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) |
| Impact Strength | Very Low | High to Very High |
| Transparency | Excellent (up to 90%) | Opaque / Milky |
| Brittleness | High | Low |
| Surface Hardness | High | Medium |
| Flexibility | Very Low | Moderate |
| Softening Temperature | Slightly Higher | Slightly Lower |
| Price | Slightly Cheaper | Slightly More Expensive |
FAQ – GPPS
1. What is GPPS and what are its main properties?
GPPS (General Purpose Polystyrene) is a clear, rigid thermoplastic made by the polymerization of styrene monomer. It features smooth surface, high clarity, easy moldability, and cost efficiency, making it suitable for packaging and consumer products.
2. What is the difference between GPPS and HIPS?
GPPS is transparent but brittle, while HIPS is impact-resistant but opaque, containing rubber additives (polybutadiene) for toughness.
3. In which industries is GPPS used?
GPPS is widely used in:
-
Food packaging and disposable containers
-
Electronic and office equipment
-
Advertising and display materials
-
Laboratory and medical devices requiring transparency
Glycerin
Properties of GlycerinHumectant: Glycerin attracts and retains moisture, making it a popular ingredient in skincare products. Solvent: It's a good solvent for many substances, including dyes, flavors, and drugs. Sweetener: Glycerin is often used as a sugar substitute in low-calorie foods and beverages. Non-toxic: It's safe for human consumption and topical use. Applications of Glycerin Cosmetics and Personal Care: Moisturizer: Glycerin is a common ingredient in moisturizers, lotions, and creams. Skin care products: It's used in soaps, cleansers, and toners. Hair care products: It's used in shampoos, conditioners, and hair styling products. Food Industry: Sweetener: It's used as a sugar substitute in low-calorie foods and beverages. Humectant: It helps retain moisture in food products. Texture agent: It's used to improve the texture of various food products. Pharmaceutical Industry: Medicine delivery: It's used as a solvent and carrier for drugs. Skin care products: It's used in topical medications and ointments. Other Industries: Antifreeze: It's used as a non-toxic antifreeze in various applications. Industrial lubricants: It's used as a lubricant in various industrial processes. Safety Considerations Glycerin is generally safe for use in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical products. However, excessive ingestion can lead to digestive issues.
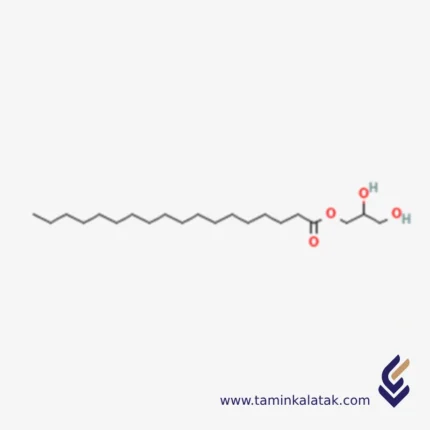
Glycerin MonoStearate
Glycerol Monostearate, commonly known as GMS, is a type of monoglyceride widely used as an emulsifier, thickening agent, and stabilizer in food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
It appears as a white, odorless, slightly sweet powder with mild hygroscopic properties. Chemically, it is an ester formed from glycerol and stearic acid.
GMS is also often incorporated into hydration and energy supplement formulations used in sports and fitness products.
Glycerol Monostearate 90% (GMS 90)
GMS 90% is a high-purity grade of glycerol monostearate, providing superior emulsifying performance in both food and personal care applications.
Its higher active monoglyceride content ensures improved emulsion stability, smoother texture in bakery products, and a rich, creamy mouthfeel in ice creams and dairy items.
Due to its efficiency and performance, GMS 90 is the preferred choice for manufacturers seeking premium quality with lower usage levels.
Chemical Structure
-
Chemical Name: Glycerol Monostearate
-
Molecular Formula: C₂₁H₄₂O₄
-
IUPAC Name: 1-Monoctadecanoyl-rac-glycerol
-
Structure: A glycerol backbone (propane-1,2,3-triol) with one hydroxyl group esterified with stearic acid (C18 fatty acid), leaving two free hydroxyl groups.
-
This makes GMS a monoglyceride exhibiting both hydrophilic and lipophilic properties.
Physical & Chemical Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White, odorless, waxy powder or flakes with a slightly sweet taste |
| Melting Point | 55–65 °C |
| Hygroscopicity | Moisture-absorbing |
| Solubility | Insoluble in cold water, dispersible in hot water; soluble in oils and organic solvents |
| pH (5% Dispersion) | Neutral to slightly acidic |
| Amphiphilic Nature | Possesses both hydrophilic and lipophilic groups, allowing effective emulsification |
| Functionality | Emulsifier, thickener, anti-caking agent, humectant, and stabilizer |
GMS helps enhance texture, extend shelf life, and prevent drying across a wide range of food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic formulations.
Applications of Glycerol Monostearate
Food Industry
Glycerol Monostearate is a versatile ingredient with multiple functionalities:
-
Acts as an emulsifier in bakery products, margarine, and dairy formulations, preventing oil-water separation.
-
Improves texture, softness, and moisture retention in bread, cakes, and pastries.
-
Used in ice creams and frozen desserts to inhibit ice crystal formation and enhance creaminess.
-
Serves as an anti-staling agent in baked goods, extending shelf life.
Pharmaceutical Industry
-
Used as a stabilizer in tablet formulations to maintain consistency.
-
Acts as a controlled-release agent in drug delivery systems.
-
Improves solubility and absorption in capsule and coating formulations.
Cosmetics & Personal Care
-
Serves as a thickener and emollient in lotions, creams, and moisturizers, improving product texture.
-
Enhances smoothness and hydration in hair care formulations.
-
Functions as a moisturizing agent in facial care products to prevent dryness.
Sports Nutrition & Health Supplements
-
Included in hydration powders and energy drinks to enhance water absorption.
-
Helps maintain muscle hydration and prevents dehydration during intense physical activity.
Industrial Uses
-
Used as a lubricant and antistatic agent in plastic and polymer processing.
-
Enhances consistency and shine in waxes and polishes.
-
Functions as a defoaming agent in certain industrial processes.
For optimal coating performance in titanium dioxide formulations, GMS is often blended with compatible binders such as resins and adjusted with suitable solvents to achieve the desired viscosity.
Purchasing Glycerol Monostearate
For both food and industrial applications, high-purity GMS offers an excellent balance of performance and cost efficiency.
It serves as an emulsifier, stabilizer, and anti-foaming agent in food, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and plastic industries.
When purchasing GMS, it’s important to consider purity grade, source of manufacture, and standard packaging to ensure consistent quality.
Price Factors
The price of Glycerol Monostearate (GMS) depends on several variables including:
-
Product grade (Food, Cosmetic, Pharmaceutical, Industrial)
-
Purity level
-
Manufacturer brand
-
Global raw material market fluctuations
-
Transportation costs and currency exchange rates
For the latest GMS pricing and grade selection assistance, our technical team is ready to provide expert guidance and rapid supply based on your production needs.
Advantages of Glycerol Monostearate
✅ Enhanced Texture & Stability: Improves product consistency and uniformity in both food and cosmetic applications.
✅ Excellent Emulsifying Power: Effectively combines water and oil in creams, lotions, and margarines.
✅ Extended Shelf Life: Its mild antioxidant properties help prevent early product spoilage.
✅ Multi-Industry Usability: Widely applicable in food, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and plastic sectors.
✅ Good Thermal Stability: Withstands heat well and performs reliably in industrial manufacturing processes.
Limitations of Glycerol Monostearate
⚠️ Dose Sensitivity: Overuse can affect texture or taste in food products.
⚠️ Quality Control Required: Lower grades may contain impurities affecting end-product performance.
⚠️ Compatibility Issues: May interact with certain active ingredients in complex formulations.
⚠️ Restrictions in Natural/Organic Lines: Some natural brands may limit or exclude its use despite safety approval.
Safety & Storage Guidelines
Glycerol Monostearate (GMS) is one of the most widely used safe and non-toxic emulsifiers, recognized by global authorities such as FDA and EFSA as GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe).
However, proper handling and storage are essential to maintain quality and performance.
Recommended Storage Conditions
-
Temperature: Store between 15–30 °C (59–86 °F).
-
Humidity: Keep in a dry, moisture-free environment to prevent caking or reduced emulsifying power.
-
Light & Ventilation: Avoid direct sunlight and ensure adequate ventilation.
-
Packaging: Supplied in multi-layer 25 kg bags with an inner polyethylene liner. Reseal tightly after opening.
-
Shelf Life: Up to 24 months under recommended conditions.
-
Transportation: Use intact, sealed packaging. Avoid contact with strong acids, alkalis, or reactive chemicals.
Glycerol Monostearate vs. Glycerol Tri-stearate
Both GMS (Mono) and GTS (Tri) are esters of glycerol and stearic acid, but they differ structurally and functionally:
-
GMS contains one stearic acid molecule → emulsifying and stabilizing properties.
-
GTS contains three stearic acid molecules → more hydrophobic, used mainly as a lubricant or opacifier in plastics and cosmetics.
Comparison: GMS 40 vs. GMS 90
| Technical Feature | GMS 40 | GMS 90 |
|---|---|---|
| Full Product Name | Glycerol Monostearate 40% | Glycerol Monostearate 90% |
| Monoglyceride Content | ~40% | ~90% |
| Di- & Triglycerides | ~60% | <10% |
| Appearance | Off-white, soft, waxy powder | Pure white, dry crystalline powder |
| Melting Point | 55–60 °C | 65–70 °C |
| Density (20 °C) | ~0.98 g/cm³ | ~0.95 g/cm³ |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble, dispersible in warm water | Insoluble, highly emulsifiable in hot water |
| Acid Value | ≤5 | ≤3 |
| Saponification Value | 145–165 | 155–175 |
| Thermal Stability | Suitable for low–medium temperatures | Excellent stability at high temperatures |
| Main Applications | Texture improvement in cakes, ice cream, and bread | Strong emulsifier in creams, lotions, and sensitive food/pharma formulations |
| Emulsifying Power | Moderate | Very high |
| Moisture Content | ≤2% | <1% |
| Available Grades (turkish Market) | Food, Industrial | Food, Pharmaceutical, Cosmetic |
| Standard Packaging | 25 kg multilayer bags | 25 kg multilayer bags |
FAQs about Glycerol Monostearate
1️⃣ Is GMS compatible with other emulsifiers?
Yes. GMS is highly compatible with other surfactants such as polysorbates, sorbitan stearate, stearic acid, and propylene glycol, ensuring excellent emulsion stability in oil-in-water (O/W) systems.
2️⃣ What are the recommended storage and safety conditions?
GMS is non-toxic, non-corrosive, and biodegradable, approved under E471 for food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic use.
-
Store in a cool, dry, shaded area (15–30 °C).
-
Keep sealed to prevent moisture absorption.
-
Shelf life: up to 24 months under proper storage.
3️⃣ What is the difference between GMS 40 and GMS 90?
The key difference lies in monoglyceride purity:
-
GMS 40: ~40% monoglyceride content — ideal for general food applications (cakes, breads, biscuits).
-
GMS 90: ~90% monoglyceride — superior emulsifying power for dairy, cream, chocolate, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic uses.
Glycerin USP
Properties of Glycerin USPStrong humectant: Glycerin USP has the ability to absorb and retain moisture, and for this reason it is used as an effective moisturizer in skin and hair care products. Solvent: This compound can dissolve many substances and is used as a solvent in the production of medicines and cosmetic products. Natural sweetener: Glycerin USP has a mild sweet taste and is used as a natural sweetener in food products. Natural antifreeze: Due to its low freezing point, Glycerin USP is used as an antifreeze in some products. Preservative: Glycerin USP can act as a preservative against the growth of microorganisms.
USP Glycerin ApplicationsPharmaceutical Industries: As a solvent in the production of liquid medicines As a softener in the production of tablets and capsules As an ingredient in the production of syrups and drops As a moisturizer in skin products Cosmetic and health industries: In the production of lotions, creams, soaps and shampoos As a skin and hair softener and moisturizer As a solvent in the production of perfumes and colognes Food industries: As a sweetener in food products As a solvent in the production of extracts and flavors As a softener in baked goods
Benefits of using USP GlycerinHigh purity: USP Glycerin has a high purity and is pharmaceutically safe. Skin compatibility: USP Glycerin rarely causes skin sensitization or irritation. Mild Taste: The mild sweet taste of USP glycerin makes it palatable in food products. Wide Applications: USP glycerin is used in a variety of industries and is a very versatile raw material. USP Standards USP standards ensure that USP glycerin is pure, free from harmful impurities, and of high quality. These standards include physicochemical, microbiological, and other tests necessary to ensure product quality.
Glycolic acid
- Cosmetics and Skincare
- Industrial Uses
- Medical Applications
- cleaning agents
- pharmaceutical
Grinder
Handcart/Trolley Tires
HDPE Film Compound
Structure HDPE Film Compound
The structure of an HDPE film compound consists of a high-density polyethylene base resin combined with various additives to enhance its properties and performance. The HDPE resin itself is composed of long, linear polymer chains with minimal branching, which contributes to its high strength, stiffness, and resistance to moisture and chemicals. To improve processability and functionality, the compound may include antioxidants to prevent thermal degradation during extrusion, UV stabilizers to protect against sunlight exposure, and slip or anti-block agents to reduce friction and prevent films from sticking together. Processing aids are often added to ensure smooth extrusion and reduce defects, while colorants or pigments can be incorporated for aesthetic or identification purposes. The resulting compound is designed to produce films with excellent mechanical properties, making them suitable for applications such as packaging, agriculture, and industrial protection. The specific formulation of an HDPE film compound can be tailored depending on the desired balance of flexibility, toughness, and barrier properties required for a given application.Properties HDPE Film Compound
HDPE film compound exhibits a combination of properties that make it highly suitable for various applications. It has a high strength-to-density ratio, providing excellent durability while maintaining lightweight characteristics. The material offers outstanding moisture resistance, making it ideal for packaging applications where barrier protection is required. It also has good chemical resistance, allowing it to withstand exposure to a wide range of substances without degrading. HDPE film compounds demonstrate excellent flexibility while retaining sufficient rigidity, enabling ease of handling and processing. The material is resistant to environmental stress cracking, ensuring longevity in demanding conditions. Additionally, it can be formulated with UV stabilizers for outdoor use, slip and anti-block agents for improved processing, and other additives to enhance specific properties. With its ease of extrusion and recyclability, HDPE film compound is a versatile and sustainable choice for industries such as packaging, agriculture, and construction.Applications HDPE Film Compound
- Packaging films for food, consumer goods, and industrial use
- Shopping bags, grocery bags, and T-shirt bags
- Agricultural films such as mulch films and greenhouse covers
- Industrial liners and heavy-duty sacks
- Shrink wraps and stretch films for packaging and palletizing
- Protective films for construction and medical applications
- Lamination films for enhancing strength and barrier properties
Advantages HDPE Film Compound
- High strength-to-density ratio, offering durability while remaining lightweight
- Excellent moisture and chemical resistance, making it ideal for packaging
- Good flexibility with sufficient rigidity for easy handling and processing
- Environmental stress cracking resistance, ensuring longevity in tough conditions
- Can be customized with additives for UV protection, anti-blocking, and slip properties
- Suitable for food contact and compliant with safety regulations
- Easy to process through extrusion, including blown and cast film methods
- Fully recyclable, contributing to environmental sustainability
Disadvantages HDPE Film Compound
- Lower transparency compared to some other film materials like LDPE or PET
- Susceptible to degradation under prolonged UV exposure without stabilizers
- Can be prone to wrinkling or shrinkage during processing if not properly controlled
- Less stretchability compared to LLDPE films, which may limit some applications