Chromic acid
Citric acid
Citric acid monohydrate
- Key Applications
- Food and Beverage Industry
- Pharmaceuticals
- Cosmetics and Personal Care
- Cleaning Agents
- Industrial Applications
Clarifying Masterbatch
Structure
The structure of clarifying masterbatch consists of a polymer carrier resin, typically polypropylene (PP), combined with a clarifying agent such as sorbitol-based compounds, phosphate esters, or nucleating agents. The clarifying agent works by modifying the crystallization behavior of semi-crystalline polymers, reducing the size of spherulites formed during cooling, which enhances transparency and gloss. The masterbatch is formulated with a precise concentration of additives to ensure uniform dispersion within the polymer matrix. In addition to the clarifying agent, the formulation may include processing aids, stabilizers, and dispersants to improve compatibility, flowability, and thermal stability. The overall structure ensures that when mixed with raw polymer during processing, the masterbatch effectively enhances optical properties while maintaining mechanical strength and process efficiency.Properties
Clarifying masterbatch possesses several key properties that enhance the optical and mechanical performance of polypropylene and other semi-crystalline polymers. It improves transparency by reducing haze and increasing light transmission, giving the final product a glass-like appearance. The masterbatch also enhances surface gloss, making the material more visually appealing. In addition to optical benefits, it increases stiffness and impact resistance, ensuring that the material remains durable while maintaining flexibility. It also optimizes processing by lowering the melting temperature, reducing cycle times, and improving mold release, which enhances production efficiency. Furthermore, clarifying masterbatch is thermally stable, ensuring long-term performance without degradation, and is often formulated to comply with FDA and food-grade safety standards, making it suitable for food packaging and medical applications. Applications of Clarifying Masterbatch:- Food Packaging – Used in transparent containers, trays, and beverage cups.
- Household Products – Applied in storage boxes, kitchenware, and organizers.
- Medical Devices – Used in syringes, vials, IV components, and lab equipment.
- Automotive Components – Enhances clarity in light housings and interior parts.
- Thin-Wall Injection Molding – Improves transparency in cosmetic packaging and electronic casings.
- Blow Molding and Extrusion – Used in clear bottles, films, and thermoformed sheets.
- Enhances Transparency – Reduces haze and increases clarity in polypropylene.
- Improves Gloss and Aesthetic Appeal – Provides a smooth, shiny surface.
- Increases Stiffness and Strength – Enhances mechanical properties without brittleness.
- Optimizes Processing Efficiency – Lowers processing temperature and cycle time.
- Compatible with Food and Medical Applications – Often FDA-approved for safety.
- Reduces Material Costs – Allows for thinner wall sections while maintaining strength.
- Limited Compatibility – Mainly effective for polypropylene, with minimal impact on other polymers.
- Processing Sensitivity – Requires precise temperature control to achieve maximum clarity.
- Potential Cost Increase – Higher-quality clarifying agents may raise material costs.
- Aging and Performance Stability – Some clarifying agents may degrade over time, reducing effectiveness.
Coagulators/Gellants/ Heat-sensiti
cocamide
Cocamide is a nonionic amide compound produced by the reaction of fatty acids from coconut oil with amines, such as ethanolamine or diethanolamine (DEA).
The most common commercial form is:
Cocamide DEA
Diethanolamide derived from coconut fatty acids
General Chemical Formula:
R–CO–N(CH₂CH₂OH)₂
(R represents a C₁₂–C₁₈ alkyl chain from coconut oil fatty acids)
Typical Properties of Cocamide
| Property | Value / Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Light brownish-yellow viscous liquid |
| Odor | Mild, fatty, soap-like odor |
| Density (25°C) | 0.98 – 1.01 g/cm³ |
| Boiling Point | > 250°C (decomposes before boiling) |
| Viscosity (25°C) | 2,000 – 3,000 cP |
| pH (10% aqueous solution) | 9.5 – 10.5 |
| Solubility in Water | Partially soluble – stable in emulsions |
| pH Stability Range | Stable between pH 4 – 11 |
| Compatibility | Compatible with anionic, nonionic, and cationic surfactants |
Applications of Cocamide
Personal Care Products
-
Used in shampoos, liquid soaps, shower gels, and facial cleansers
-
Acts as a foam booster and viscosity enhancer
-
Functions as a skin and hair conditioning agent
Household and Industrial Cleaners
-
Used in dishwashing liquids, multi-purpose cleaners, and surface detergents
-
Serves as a foam stabilizer and thickening agent
Industrial Uses
-
Emulsifying agent in industrial lubricants
-
Antistatic additive in textile processing
Advantages
-
Biodegradable and plant-based (derived from coconut oil)
-
Mild pH and skin-compatible
-
Effective in hard water conditions
-
Enhances foam stability and product smoothness
-
Suitable for sulfate-free formulations
Limitations
-
May form nitrosamines when combined with nitrite-containing materials
-
Can oxidize or discolor under high temperature or unstable pH conditions
-
High concentrations may cause irritation to sensitive skin
Safety and Handling
| Safety Aspect | Guideline |
|---|---|
| Skin contact | Safe at normal use levels; gloves recommended for prolonged handling |
| Eye contact | May cause mild irritation; rinse immediately with plenty of water |
| Inhalation | Non-volatile; no vapor hazard under normal conditions |
| Flash Point | > 200°C |
| Storage | Store in HDPE drums or coated steel barrels, in a cool, dry, and shaded area |
| Chemical Compatibility | Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents |
| Environmental Stability | Biodegradable; low environmental hazard |
| Recommended Shelf Life | 12 – 18 months under proper storage conditions |
Summary
Cocamide DEA is a versatile nonionic surfactant and thickener derived from renewable coconut oil fatty acids.
It provides foam enhancement, viscosity control, and conditioning in a wide range of personal care, household, and industrial cleaning formulations.
Due to its biodegradability and natural origin, Cocamide DEA remains one of the most widely used secondary surfactants in mild detergent systems.
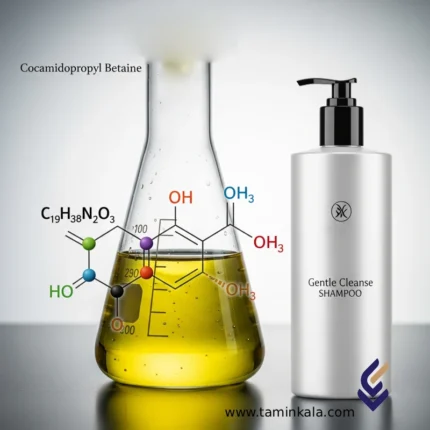
Cocamidopropyl betaine
Cocamidopropyl Betaine (CAPB) is an amphoteric surfactant primarily derived from fatty acids of coconut oil and dimethylaminopropionic acid.
It is widely used in personal care and cleaning formulations as a foaming agent, cleanser, and conditioning additive.
Chemical Structure
General Formula:
R–CO–NH–(CH₂)₃–N⁺(CH₃)₂–CH₂–COO⁻
Where represents a fatty alkyl chain (mainly C₁₂ and C₁₄, with smaller fractions of C₁₆ and C₁₈).
Cocamidopropyl betaine contains both hydrophilic (betaine group) and hydrophobic (alkyl chain) segments.
It behaves as a cationic surfactant in acidic media and as an anionic surfactant in alkaline conditions, giving it its amphoteric nature.
Typical Physical and Chemical Properties
| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Clear to pale yellow, viscous liquid |
| Odor | Mild, characteristic coconut-like odor |
| Density (25°C) | 1.045 – 1.085 g/cm³ (per Sigma-Aldrich) |
| pH (10% solution) | 4.5 – 6.5 (depending on purity and formulation) |
| Active Matter | 28 – 32% |
| Solubility | Fully soluble in water |
| Hard Water Stability | Excellent |
| Chemical Compatibility | Compatible with anionic, cationic, nonionic, and amphoteric surfactants |
Applications of Cocamidopropyl Betaine
Personal Care and Cosmetic Products
-
Mild and baby shampoos
-
Liquid hand soaps and shower gels
-
Facial cleansers and gentle laundry detergents
Functional Roles
-
Foam booster and foam stabilizer
-
Viscosity enhancer in surfactant blends
-
Skin and hair conditioner, providing softness and moisture
Advantages
-
Mild to skin and eyes (per OECD 404 and 405 testing)
-
Compatible with all major surfactant types
-
Stable over a wide pH range
-
Readily biodegradable and environmentally safe (complies with OECD 301)
-
Sulfate-free (SLS/SLES-free) with low irritation profile
Limitations & Safety Considerations
-
May cause contact sensitization in rare cases — typically due to trace impurities such as Dimethylaminopropylamine (DMAPA) or amidoamine residues.
-
Possible nitrosamine formation in the presence of nitrites under certain conditions.
-
Slightly higher cost compared to conventional synthetic surfactants like SLES.
Safety & Handling Information
| Aspect | Guideline |
|---|---|
| Skin and eye contact | Low irritation potential; rinse with water after prolonged contact |
| Inhalation | Non-volatile; no vapor hazards under normal conditions |
| Flash Point | > 100°C |
| Storage Conditions | Store in tightly sealed containers, in a cool, dry area away from direct sunlight and strong oxidizers |
| Environmental Stability | Biodegradable and low toxicity to aquatic organisms |
Summary
Cocamidopropyl Betaine is a mild, multifunctional amphoteric surfactant valued for its excellent foaming, cleansing, and conditioning properties.
Its biodegradability, low irritation potential, and broad compatibility make it an essential ingredient in modern personal care and household formulations, particularly in sulfate-free systems.
Coconut fatty acid
Coconut Fatty Acid is a natural mixture of saturated fatty acids with short to medium carbon chains, obtained through the hydrolysis or saponification of coconut oil. Due to its unique molecular structure, it has wide applications across various industries, particularly in cosmetics, personal care, and detergents. Over 90% of its composition consists of saturated fatty acids, with the main components being:
-
Lauric acid (C12:0): ~45–52%
-
Myristic acid (C14:0): ~16–21%
-
Capric acid (C10:0): ~4–8%
-
Caprylic acid (C8:0): ~5–10%
Minor amounts of Palmitic acid (C16:0) and Stearic acid (C18:0) are also present.
Chemical Structure of Coconut Fatty Acid
The structure of coconut fatty acids consists of saturated alkyl chains (C8–C18) with a carboxyl group (-COOH) at the end of each chain. This structure provides the following properties:
-
Short to medium carbon chains (C8–C14)
-
High saturation: strong resistance to oxidation
-
High reactivity: suitable for producing soaps, esters, and amides
Properties of Coconut Fatty Acid
Physical state: Solid or semi-solid at room temperature
Odor: Mild, natural coconut scent
Iodine value: Low (indicating high saturation)
High surface activity:
-
Capable of reducing surface tension, making it ideal for surfactant production
-
Plays a crucial role in emulsification in cosmetic, detergent, and pharmaceutical products
Thermal and chemical stability:
-
More resistant to oxidation compared to oils containing unsaturated fatty acids
-
Stable under moderate heat and alkaline conditions
High biodegradability:
-
Eco-friendly and biodegradable composition
-
Excellent for sustainable product formulations
Plant-based and renewable origin:
-
Derived from natural, renewable coconut oil sources
High skin compatibility:
-
Non-toxic and gentle on skin, suitable for personal care formulations
-
Antibacterial properties, especially due to Lauric acid
Applications of Coconut Fatty Acid
Detergent and Hygiene Industries
-
Production of plant-based, transparent, and handmade soaps
-
Used in shampoos, conditioners, body washes, and shower gels
-
Raw material for foam boosters and mild surfactants such as Cocamide DEA/MEA
Cosmetic Industry
-
Used in moisturizing creams, lotions, lip balms, and hair oils
-
Ideal for formulations targeting dry and sensitive skin
Food Industry
-
Source of MCTs (Medium Chain Triglycerides) in therapeutic diets
-
Used as an anti-foaming agent or emulsifier in food processing
Industrial and Chemical Applications
-
Production of amides, esters, surfactants, and resins
-
Additive in plastics, coatings, lubricants, and adhesives
-
Bio-based feedstock for biodiesel, epoxides, and bio-lubricants
Advantages of Coconut Fatty Acid
-
Natural and renewable plant-based source
-
Biodegradable and environmentally friendly
-
High foaming capability in soap formulations
-
Excellent thermal and light stability
-
Skin-friendly, non-irritating even for sensitive skin
-
Suitable for MCT oil production in ketogenic and therapeutic diets
Disadvantages of Coconut Fatty Acid
-
Higher cost compared to animal- or petroleum-based fatty acids
-
Potential for mild allergic reactions in individuals with extremely sensitive skin
-
In dietary use, high saturated fat content requires moderate consumption
-
Solidifies at low temperatures, which may affect product appearance
Price of Coconut Fatty Acid
Due to its broad range of applications, coconut fatty acid is one of the most widely used plant-based fatty acids in various industries. Its price fluctuates depending on factors such as purity level, country of origin, coconut oil market volatility, shipping and import costs, and exchange rate variations.
In the turkish market, it is commonly supplied in barrels or bulk containers by various suppliers. Industrial buyers are advised to review technical specifications—including Lauric acid content, iodine index, and melting point—before purchasing. For optimal quality and pricing, it is essential to evaluate the supplier source, product analysis, and transportation conditions.
Safety and Storage of Coconut Fatty Acid
| Category | Details and Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Hazard Classification | Generally non-hazardous under GHS for cosmetic and industrial grades |
| Skin Contact | Concentrated or unrefined forms may cause dryness or mild irritation — gloves recommended |
| Eye Contact | Direct exposure may cause stinging or redness — rinse immediately with plenty of water |
| Inhalation of Vapors/Particles | Not hazardous, but ensure adequate ventilation during melting or heating |
| Accidental Ingestion | Industrial grades are not for ingestion; food-grade is safe within regulated limits |
Coconut Fatty Acid
Properties of coconut fatty acidChemical composition: Coconut fatty acid is mainly composed of lauric acid, which is a medium-chain saturated fatty acid. Physical state: At room temperature, it is a white solid with a strong and characteristic odor. Antimicrobial property: Lauric acid in coconut fatty acid has strong antibacterial and antifungal properties. Foaming property: Coconut fatty acid is used in the production of soaps and detergents due to its high foaming property. Softening property: This substance is used as a softener in the production of cosmetic and health products.
Applications of coconut fatty acidCosmetic and health industry: It is used in the production of soaps, shampoos, lotions, creams and other skin and hair care products. Food industry: Used as an emulsifier, softener, and antimicrobial agent in food production. Detergent industry: Used in the production of household and industrial detergents. Pharmaceutical industry: Used in the production of some drugs and dietary supplements. Textile industry: Used as a softener and water repellent in the textile industry.
Benefits of using coconut fatty acidNatural and biodegradable: Coconut fatty acid is a natural and biodegradable material and does not harm the environment. Antimicrobial properties: Effective against bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Skin and hair softening: Helps make skin and hair soft and supple. Inflammation reduction: Effective in reducing inflammation and skin inflammation. Safety tips Skin irritation: Direct contact with coconut fatty acid may cause skin irritation. Inhalation: Inhaling coconut fatty acid vapors can cause respiratory tract irritation. Storage: Store coconut fatty acid in closed containers in a cool, dry place.
Coconut Fatty Acid Diethanolamide
Coconut Fatty Acid is a natural mixture of saturated short- to medium-chain fatty acids obtained through the hydrolysis or saponification of coconut oil (Cocos Nucifera Oil).
Due to its unique molecular composition, it is widely used in cosmetic, personal care, detergent, and chemical industries.
Over 90% of its composition consists of saturated fatty acids, primarily:
| Component | Typical Content (%) |
|---|---|
| Lauric Acid (C12:0) | 45 – 52% |
| Myristic Acid (C14:0) | 16 – 21% |
| Capric Acid (C10:0) | 4 – 8% |
| Caprylic Acid (C8:0) | 5 – 10% |
| Palmitic Acid (C16:0) | Minor |
| Stearic Acid (C18:0) | Minor |
Chemical Structure
Coconut fatty acids are composed of saturated alkyl chains (C8–C18) terminated by a carboxylic acid group (-COOH).
This molecular structure gives rise to several key properties:
-
Short to medium carbon chains (C8–C14) for excellent surface activity
-
High saturation, ensuring strong oxidative stability
-
High reactivity, suitable for synthesis of soaps, esters, and amides
Physical and Chemical Properties
| Property | Typical Description |
|---|---|
| Physical State | Solid or semi-solid at room temperature |
| Odor | Mild, characteristic coconut scent |
| Iodine Value | Low (indicating high saturation) |
| Thermal & Chemical Stability | Stable under moderate heat and alkaline conditions |
| Biodegradability | Readily biodegradable; environmentally friendly |
| Origin | 100% plant-based, renewable (from coconut oil) |
| Skin Compatibility | Mild, non-toxic, suitable for sensitive skin |
| Antibacterial Properties | Naturally effective, mainly due to lauric acid content |
Functional Characteristics
-
High Surface Activity: Reduces surface tension effectively — ideal for surfactant production
-
Excellent Emulsification: Useful in personal care, detergents, and pharmaceutical formulations
-
Thermal and Oxidative Stability: More stable than unsaturated fatty acids under normal processing conditions
-
Eco-Friendly Profile: Fully biodegradable and derived from renewable resources
Applications
1. Detergent and Personal Care Industry
-
Production of natural and transparent soaps
-
Used in shampoos, conditioners, body washes, and shower gels
-
Raw material for foam boosters and mild surfactants (e.g., Cocamide DEA / MEA)
2. Cosmetic Industry
-
Ingredient in moisturizing creams, lotions, lip balms, and hair oils
-
Ideal for dry and sensitive skin formulations
3. Food Industry
-
Source of MCTs (Medium-Chain Triglycerides) used in nutritional and medical diets
-
Employed as antifoaming or emulsifying agent in food processing
4. Industrial and Chemical Applications
-
Intermediate for amide, ester, resin, and surfactant synthesis
-
Additive for plastics, coatings, lubricants, and adhesives
-
Bio-based raw material for biodiesel, epoxides, and bio-lubricants
Advantages
-
100% natural and renewable plant-based origin
-
Biodegradable and environmentally safe
-
High foaming performance in soap formulations
-
Excellent stability against heat and light
-
Gentle on skin, suitable for sensitive skin care products
-
Usable in MCT oil production for ketogenic and therapeutic applications
Limitations
-
Higher cost compared to animal- or petrochemical-derived fatty acids
-
May cause mild irritation in ultra-sensitive individuals
-
High saturated fat content requires controlled intake in food use
-
Solidification at low temperatures may affect appearance in some formulations
Market Information
Coconut fatty acid is one of the most widely used plant-based fatty acids due to its broad applicability and mild, stable nature.
Market price depends on factors such as purity, lauric acid content, country of origin, coconut oil price fluctuations, import costs, and currency exchange rates.
In the turkish market, it is available in bulk or drum packaging from various suppliers.
Industrial buyers are advised to review technical specifications (e.g., lauric acid percentage, iodine value, and melting point) before purchase to ensure product quality and performance.
Safety and Handling
| Aspect | Guidelines |
|---|---|
| Hazard Classification (GHS) | Generally non-hazardous in cosmetic and industrial grades |
| Skin Contact | May cause dryness or mild irritation in concentrated form – gloves recommended |
| Eye Contact | Direct contact may cause irritation – rinse thoroughly with water |
| Inhalation | No significant risk; ensure ventilation during melting or heating processes |
| Ingestion | Not suitable for ingestion in industrial grade; food-grade is safe within regulated limits |
| Storage Conditions | Keep in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area; avoid direct sunlight and moisture |
Summary
Coconut Fatty Acid is a versatile, renewable, and eco-friendly ingredient derived from natural coconut oil, offering excellent surface activity, stability, and skin compatibility.
It serves as a key raw material in soaps, surfactants, cosmetics, and bio-based industrial formulations, combining performance, sustainability, and safety in one solution.
Coconut fatty acid propylaminodimethylamine
Coconut Fatty Acid Propylamino Dimethylamine is an amine-based amide derived from the natural fatty acids of coconut oil. In this compound, coconut fatty acid (mainly lauric acid) reacts with dimethylaminopropylamine (DMAPA) to form an amide linkage. It acts as an effective cationic or amphoteric surfactant in formulations for personal care, cleansing, cosmetic, and hair care products.
Chemical Structure
-
Base structure: Coconut fatty acid (C12–C14, primarily lauric acid)
-
Functional group: Propylamino dimethylamine (containing both an amide group and a tertiary amine)
-
Type of bond: Amide linkage between the carboxylic group of the fatty acid and the amine group
-
Structural behavior: In acidic environments, the molecule becomes protonated and carries a positive charge, acting as an effective cationic surfactant. In some formulations, it may also behave as an amphoteric surfactant.
Physical and Chemical Properties
-
Physical state: Clear to pale yellow viscous liquid
-
pH (1% solution): Approximately 9–10
-
Odor: Mild, with a light amine scent
-
Ionic nature: Amphoteric at neutral pH; cationic under acidic conditions
-
Surfactant properties: Yes — moderate foaming ability with excellent conditioning effects
-
Molecular formula: Approx. C17H36N2O (varies depending on fatty acid composition)
Applications of Coconut Fatty Acid Propylamino Dimethylamine
In Shampoos and Conditioners
-
Provides antistatic properties
-
Enhances softness, shine, and combability of hair
-
Compatible with low-pH formulations — ideal for damaged hair
In Body and Facial Cleansers
-
Suitable for sensitive skin
-
Improves foam stability and skin smoothness
In Makeup Removers and Cleansing Products
-
Skin-friendly with low irritation potential
-
Helps emulsify oily residues for better cleansing performance
In Pet Care Products
-
Mild yet effective on animal skin and fur
-
Non-irritating to thin or delicate skin
✅ Advantages
-
Mild and low-irritation: Suitable for sensitive skin
-
Cationic nature: Ideal for hair conditioning and softness
-
Acidic pH compatibility: Superior to typical anionic surfactants
-
Natural origin: Derived from coconut oil
-
Highly biodegradable: Eco-friendly and sustainable
-
Affinity to hair keratin: Forms a smooth, soft film on hair for lasting conditioning
❌ Disadvantages
-
Relatively high cost compared to conventional anionic surfactants
-
Reduced performance in strongly alkaline environments (high pH)
-
Potential for mild skin sensitivity at high concentrations or with frequent exposure
-
Possible contamination with amidoamine (a known irritant) in raw materials, which must be removed during quality control
Coconut Oil
Coconut Oil PropertiesAntimicrobial Properties: Coconut oil has strong antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral properties due to its lauric acid content and can be effective in treating some infections. Moisturizer for Skin and Hair: Coconut oil, as a natural emollient, moisturizes the skin and hair and prevents them from drying out. Hair Strengthener: Coconut oil helps strengthen hair roots and reduce hair loss. Treatment of Some Skin Diseases: Coconut oil is effective in treating some skin diseases such as eczema and psoriasis. Reduce Inflammation: Coconut oil has anti-inflammatory properties and can be effective in reducing inflammation of the skin and joints. Boost Immunity: The lauric acid in coconut oil can help strengthen the immune system.
Coconut Oil applicationsSkin: Coconut oil is used as a moisturizer, emollient, makeup remover, natural sunscreen, and treatment of some skin diseases. Hair: Coconut oil is used to strengthen hair, reduce split ends, soften hair, and protect hair from heat. Cooking: Coconut oil is used as a cooking oil, in preparing salads and desserts. Oral health: Oil pulling with coconut oil is beneficial for oral health.
Types of coconut oilRefined coconut oil: This type of oil has a mild odor and taste and is used more in industrial applications. Virgin coconut oil: This type of oil is extracted using natural methods and has the natural aroma and flavor of coconut. Organic coconut oil: This type of oil is produced from organically grown coconuts without the use of chemical pesticides. Important points in using coconut oil Allergy: Some people may be allergic to coconut oil. Oral consumption: Excessive consumption of coconut oil can cause weight gain due to its high calories. Heat: Coconut oil is solid at low temperatures and becomes liquid at high temperatures.