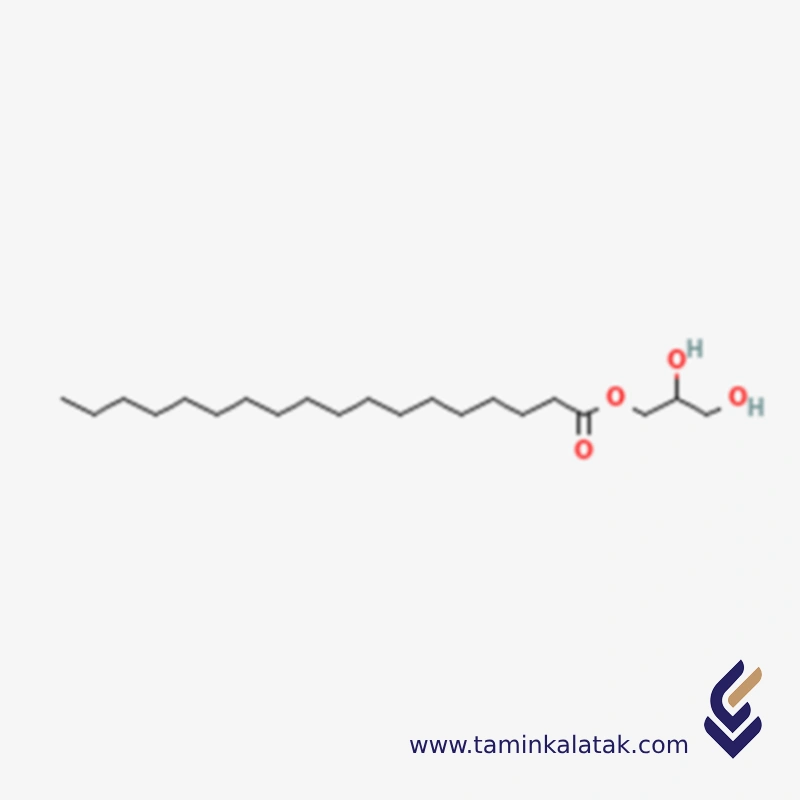
Glycerin MonoStearate
Glycerol Monostearate, commonly known as GMS, is a type of monoglyceride widely used as an emulsifier, thickening agent, and stabilizer in food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
It appears as a white, odorless, slightly sweet powder with mild hygroscopic properties. Chemically, it is an ester formed from glycerol and stearic acid.
GMS is also often incorporated into hydration and energy supplement formulations used in sports and fitness products.
Glycerol Monostearate 90% (GMS 90)
GMS 90% is a high-purity grade of glycerol monostearate, providing superior emulsifying performance in both food and personal care applications.
Its higher active monoglyceride content ensures improved emulsion stability, smoother texture in bakery products, and a rich, creamy mouthfeel in ice creams and dairy items.
Due to its efficiency and performance, GMS 90 is the preferred choice for manufacturers seeking premium quality with lower usage levels.
Chemical Structure
-
Chemical Name: Glycerol Monostearate
-
Molecular Formula: C₂₁H₄₂O₄
-
IUPAC Name: 1-Monoctadecanoyl-rac-glycerol
-
Structure: A glycerol backbone (propane-1,2,3-triol) with one hydroxyl group esterified with stearic acid (C18 fatty acid), leaving two free hydroxyl groups.
-
This makes GMS a monoglyceride exhibiting both hydrophilic and lipophilic properties.
Physical & Chemical Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White, odorless, waxy powder or flakes with a slightly sweet taste |
| Melting Point | 55–65 °C |
| Hygroscopicity | Moisture-absorbing |
| Solubility | Insoluble in cold water, dispersible in hot water; soluble in oils and organic solvents |
| pH (5% Dispersion) | Neutral to slightly acidic |
| Amphiphilic Nature | Possesses both hydrophilic and lipophilic groups, allowing effective emulsification |
| Functionality | Emulsifier, thickener, anti-caking agent, humectant, and stabilizer |
GMS helps enhance texture, extend shelf life, and prevent drying across a wide range of food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic formulations.
Applications of Glycerol Monostearate
Food Industry
Glycerol Monostearate is a versatile ingredient with multiple functionalities:
-
Acts as an emulsifier in bakery products, margarine, and dairy formulations, preventing oil-water separation.
-
Improves texture, softness, and moisture retention in bread, cakes, and pastries.
-
Used in ice creams and frozen desserts to inhibit ice crystal formation and enhance creaminess.
-
Serves as an anti-staling agent in baked goods, extending shelf life.
Pharmaceutical Industry
-
Used as a stabilizer in tablet formulations to maintain consistency.
-
Acts as a controlled-release agent in drug delivery systems.
-
Improves solubility and absorption in capsule and coating formulations.
Cosmetics & Personal Care
-
Serves as a thickener and emollient in lotions, creams, and moisturizers, improving product texture.
-
Enhances smoothness and hydration in hair care formulations.
-
Functions as a moisturizing agent in facial care products to prevent dryness.
Sports Nutrition & Health Supplements
-
Included in hydration powders and energy drinks to enhance water absorption.
-
Helps maintain muscle hydration and prevents dehydration during intense physical activity.
Industrial Uses
-
Used as a lubricant and antistatic agent in plastic and polymer processing.
-
Enhances consistency and shine in waxes and polishes.
-
Functions as a defoaming agent in certain industrial processes.
For optimal coating performance in titanium dioxide formulations, GMS is often blended with compatible binders such as resins and adjusted with suitable solvents to achieve the desired viscosity.
Purchasing Glycerol Monostearate
For both food and industrial applications, high-purity GMS offers an excellent balance of performance and cost efficiency.
It serves as an emulsifier, stabilizer, and anti-foaming agent in food, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and plastic industries.
When purchasing GMS, it’s important to consider purity grade, source of manufacture, and standard packaging to ensure consistent quality.
Price Factors
The price of Glycerol Monostearate (GMS) depends on several variables including:
-
Product grade (Food, Cosmetic, Pharmaceutical, Industrial)
-
Purity level
-
Manufacturer brand
-
Global raw material market fluctuations
-
Transportation costs and currency exchange rates
For the latest GMS pricing and grade selection assistance, our technical team is ready to provide expert guidance and rapid supply based on your production needs.
Advantages of Glycerol Monostearate
✅ Enhanced Texture & Stability: Improves product consistency and uniformity in both food and cosmetic applications.
✅ Excellent Emulsifying Power: Effectively combines water and oil in creams, lotions, and margarines.
✅ Extended Shelf Life: Its mild antioxidant properties help prevent early product spoilage.
✅ Multi-Industry Usability: Widely applicable in food, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and plastic sectors.
✅ Good Thermal Stability: Withstands heat well and performs reliably in industrial manufacturing processes.
Limitations of Glycerol Monostearate
⚠️ Dose Sensitivity: Overuse can affect texture or taste in food products.
⚠️ Quality Control Required: Lower grades may contain impurities affecting end-product performance.
⚠️ Compatibility Issues: May interact with certain active ingredients in complex formulations.
⚠️ Restrictions in Natural/Organic Lines: Some natural brands may limit or exclude its use despite safety approval.
Safety & Storage Guidelines
Glycerol Monostearate (GMS) is one of the most widely used safe and non-toxic emulsifiers, recognized by global authorities such as FDA and EFSA as GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe).
However, proper handling and storage are essential to maintain quality and performance.
Recommended Storage Conditions
-
Temperature: Store between 15–30 °C (59–86 °F).
-
Humidity: Keep in a dry, moisture-free environment to prevent caking or reduced emulsifying power.
-
Light & Ventilation: Avoid direct sunlight and ensure adequate ventilation.
-
Packaging: Supplied in multi-layer 25 kg bags with an inner polyethylene liner. Reseal tightly after opening.
-
Shelf Life: Up to 24 months under recommended conditions.
-
Transportation: Use intact, sealed packaging. Avoid contact with strong acids, alkalis, or reactive chemicals.
Glycerol Monostearate vs. Glycerol Tri-stearate
Both GMS (Mono) and GTS (Tri) are esters of glycerol and stearic acid, but they differ structurally and functionally:
-
GMS contains one stearic acid molecule → emulsifying and stabilizing properties.
-
GTS contains three stearic acid molecules → more hydrophobic, used mainly as a lubricant or opacifier in plastics and cosmetics.
Comparison: GMS 40 vs. GMS 90
| Technical Feature | GMS 40 | GMS 90 |
|---|---|---|
| Full Product Name | Glycerol Monostearate 40% | Glycerol Monostearate 90% |
| Monoglyceride Content | ~40% | ~90% |
| Di- & Triglycerides | ~60% | <10% |
| Appearance | Off-white, soft, waxy powder | Pure white, dry crystalline powder |
| Melting Point | 55–60 °C | 65–70 °C |
| Density (20 °C) | ~0.98 g/cm³ | ~0.95 g/cm³ |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble, dispersible in warm water | Insoluble, highly emulsifiable in hot water |
| Acid Value | ≤5 | ≤3 |
| Saponification Value | 145–165 | 155–175 |
| Thermal Stability | Suitable for low–medium temperatures | Excellent stability at high temperatures |
| Main Applications | Texture improvement in cakes, ice cream, and bread | Strong emulsifier in creams, lotions, and sensitive food/pharma formulations |
| Emulsifying Power | Moderate | Very high |
| Moisture Content | ≤2% | <1% |
| Available Grades (turkish Market) | Food, Industrial | Food, Pharmaceutical, Cosmetic |
| Standard Packaging | 25 kg multilayer bags | 25 kg multilayer bags |
FAQs about Glycerol Monostearate
1️⃣ Is GMS compatible with other emulsifiers?
Yes. GMS is highly compatible with other surfactants such as polysorbates, sorbitan stearate, stearic acid, and propylene glycol, ensuring excellent emulsion stability in oil-in-water (O/W) systems.
2️⃣ What are the recommended storage and safety conditions?
GMS is non-toxic, non-corrosive, and biodegradable, approved under E471 for food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic use.
-
Store in a cool, dry, shaded area (15–30 °C).
-
Keep sealed to prevent moisture absorption.
-
Shelf life: up to 24 months under proper storage.
3️⃣ What is the difference between GMS 40 and GMS 90?
The key difference lies in monoglyceride purity:
-
GMS 40: ~40% monoglyceride content — ideal for general food applications (cakes, breads, biscuits).
-
GMS 90: ~90% monoglyceride — superior emulsifying power for dairy, cream, chocolate, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic uses.
Applications
| Applications | , , , |
|---|
Glycerin monostearate
| Products | Melting point | Density (g/cm3) | Viscosity | Applications | Data Sheet | MSDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glycerin monostearate | 55–65°C | 0.97–1.03 | 50–200 cP | Food Industry,Pharmaceutical Industry, Cosmetics & SkincareSports & Health Supplements,Industrial Applications |