Wheels/Rims
White Masterbatch
White Masterbatch is a concentrated mixture of titanium dioxide (TiO₂), a polymer carrier resin, and various additives designed to provide whiteness, brightness, and opacity in plastic products. It is widely used in different plastic manufacturing processes to enhance aesthetic appeal, opacity, and UV resistance.
Structure of White Masterbatch
White masterbatch consists of a high concentration of titanium dioxide (TiO₂) dispersed in a polymer carrier, which imparts opacity, brightness, and whiteness to plastic products. The main component, TiO₂, is uniformly distributed within carrier resins such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS), or other compatible polymers to ensure even dispersion during processing.
In addition, additives such as dispersing agents, processing aids, and stabilizers may be included to improve pigment dispersion, enhance processability, and increase resistance to heat and UV radiation.
The formulation of white masterbatch is designed to ensure easy handling and consistent color performance, making it an essential component in industries such as packaging, automotive, textiles, and consumer goods.
Key Properties of White Masterbatch
White masterbatch possesses several critical properties that make it ideal for use in the plastics industry:
-
High opacity and brightness due to the presence of titanium dioxide (TiO₂).
-
Excellent whiteness and coverage performance.
-
Uniform color dispersion with no streaking or spotting.
-
Good thermal stability, resistant to degradation during high-temperature processing.
-
Strong UV resistance to prevent discoloration and surface degradation under sunlight.
-
Enhanced mechanical strength and durability of the final product.
-
Moisture resistance and excellent compatibility with various polymer types.
-
Easy to blend and process across different production methods.
Applications of White Masterbatch
-
Packaging materials such as films, bottles, and containers for food, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods.
-
Automotive components, both interior and exterior plastic parts.
-
Household appliances, furniture, and electronic housings for aesthetic and protective purposes.
-
Textiles and fibers to achieve whiteness and UV protection.
-
Construction materials including PVC pipes, window profiles, and roofing sheets.
-
Agricultural films, mulching sheets, and irrigation pipes.
Advantages of White Masterbatch
-
High opacity and brightness, improving product appearance.
-
Excellent dispersion of TiO₂, preventing streaks or uneven coloration.
-
Increased UV resistance, protecting against color fading and degradation.
-
Enhanced mechanical properties, improving strength and durability.
-
Thermal stability suitable for high-temperature processing.
-
Compatible with a wide range of base polymers for versatile applications.
-
Available in customized formulations tailored to specific industrial needs.
Disadvantages of White Masterbatch
-
High TiO₂ content increases production costs.
-
Possible incompatibility with certain polymers if not properly formulated.
-
Overuse may reduce mechanical strength, causing brittleness.
-
May require additional additives to optimize dispersion and processing performance.
-
Excessive use can increase material consumption and negatively affect environmental goals.
Types of Masterbatch
Black Masterbatch
Contains carbon black and is commonly used in cable, pipe, automotive, and packaging industries. It provides excellent UV resistance, high coverage, and thermal conductivity.
Purple Masterbatch
Used in various industries to achieve specific aesthetic effects by introducing violet tones, often combined with other colors such as yellow or green.
Yellow Masterbatch
Formulated with organic or inorganic pigments for decorative, packaging, household, toy, and industrial applications requiring vibrant coloration.
Green Masterbatch
Similar in use to yellow masterbatch, it is applied in consumer goods, household products, and industrial components.
Blue-White Masterbatch
A white masterbatch with a bluish tint that provides enhanced visual brightness and clarity, ideal for premium packaging and decorative products.
Refrigerator White Masterbatch
Specially formulated for refrigerator and household appliance parts, producing a clean, cool-toned white appearance.
White Masterbatch Price Factors
As many manufacturers know, the price of white masterbatch is a key consideration in industries such as plastics, packaging, household goods, and automotive manufacturing.
While it offers strong opacity, high brightness, and excellent light resistance, the final price depends on several factors:
-
Titanium dioxide concentration and quality.
-
Type of carrier resin used.
-
Level of dispersion and processing technology.
-
Additives for UV, heat, or moisture resistance.
-
Custom formulation and color matching requirements.
-
Global TiO₂ market fluctuations and raw material costs.
Understanding these factors helps manufacturers make informed and cost-effective purchasing decisions while maintaining product quality and performance.
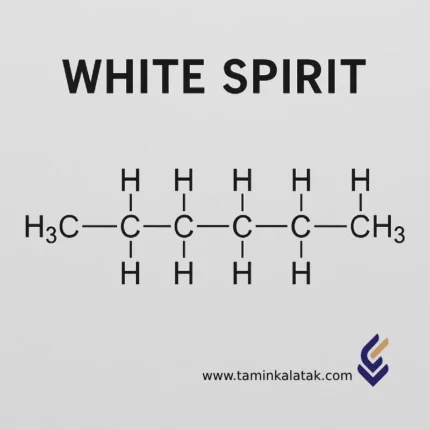
White Spirit
White Spirit, also known as industrial kerosene, mineral spirits, or light naphtha, is a light aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbon mixture obtained through fractional distillation of crude oil. It is a colorless, transparent, volatile, and flammable liquid, widely used as a solvent in various industries such as paints and coatings, degreasing, automotive, and woodworking.
Chemical Structure of White Spirit
-
General Formula: A mixture of n-alkanes, iso-alkanes, cycloalkanes, and a small proportion of aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene
-
Chemical Composition: Primarily composed of C₇–C₁₂ hydrocarbons, depending on the grade
-
Molecular Structure: A combination of linear and branched saturated hydrocarbon chains with a minor aromatic fraction
-
CAS Number: 8052-41-3 (for White Spirit Type 1)
Physical and Chemical Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical State | Colorless, clear, and volatile liquid |
| Odor | Mild petroleum-like odor |
| Boiling Point | 130–230 °C |
| Flash Point | 38–55 °C (depending on the type) |
| Viscosity (at 40 °C) | Approximately 1–2 cSt |
| Refractive Index | 1.43–1.46 |
| Water Solubility | Practically insoluble |
| Log P (Partition Coefficient) | Around 3.5 – indicating lipophilicity and high affinity for organic phases |
Applications of White Spirit
Paints and Thinners Industry
-
Solvent for oil-based, alkyd, and resin paints
-
Viscosity regulator in the production of thinners and varnishes
-
Used in solvent-based coatings to ensure uniform film formation and drying
Degreasing and Cleaning
-
Removes grease and oils from industrial machinery and tools
-
Cleans metal parts prior to painting or coating
-
Applied in dry degreasing processes in metalworking and fabrication lines
Printing and Automotive Industries
-
Solvent for petroleum-based printing inks (e.g., flexographic and gravure inks)
-
Used for cleaning mechanical parts, engines, and tools
Wood and Furniture Industry
-
Diluent for wood varnishes, polishes, and waxes
-
Removes excess oils and grease before painting or finishing
-
Used in final polishing to improve surface smoothness and uniformity
Advantages of White Spirit
-
High solvency power for oils, resins, and oil-based paints
-
Moderate volatility, allowing optimal drying without overly fast evaporation
-
Safer alternative compared to harsher solvents such as acetone or xylene, especially on wooden surfaces
-
Economical and widely available for industrial use
-
Stable under standard storage and handling conditions
Disadvantages of White Spirit
-
Highly flammable, requiring strict safety precautions in enclosed spaces
-
Irritating to eyes and skin upon direct contact
-
Inhalation of vapors may cause dizziness, nausea, or headaches
-
Unpleasant odor at high concentrations
-
Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents such as permanganates or peroxides
Safety and Storage Guidelines
- According to GHS Classification, White Spirit is labeled with:
- H226: Flammable liquid and vapor
- H304: May be fatal if swallowed and enters airways
- H336: May cause drowsiness or dizziness
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Nitrile gloves, half-face respirator with organic vapor filters, and safety goggles are required.
- Ventilation: Adequate ventilation is essential (preferably local exhaust or mechanical ventilation).
- Storage: Keep in tightly sealed, solvent-resistant containers, away from heat, open flames, and direct sunlight.
- Transportation: Classified under UN 1300 with flammable liquid labeling required on all containers.
xylene
Xylene is an aromatic hydrocarbon compound with the chemical formula C₆H₄(CH₃)₂ (or C₈H₁₀), consisting of a benzene ring substituted with two methyl (–CH₃) groups.
It exists in three structural isomers — ortho-xylene, meta-xylene, and para-xylene — as well as in the form of mixed xylene, which contains a mixture of these isomers along with a certain amount of ethylbenzene.
Due to its distinct physical and chemical properties, xylene is widely used across various industrial sectors.
Structure of Xylene
Xylene is an aromatic compound with the chemical formula C₆H₄(CH₃)₂.
It consists of a benzene ring (a six-membered ring with alternating double bonds) with two methyl groups attached at different positions.
Xylene exists in the following three isomeric forms:
-
Ortho-xylene (o-xylene): Methyl groups at positions 1 and 2 on the benzene ring.
-
Meta-xylene (m-xylene): Methyl groups at positions 1 and 3.
-
Para-xylene (p-xylene): Methyl groups at positions 1 and 4.
Each isomer exhibits distinct physical properties and industrial applications due to the positional differences of the methyl groups.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Xylene
-
Chemical Formula: C₆H₄(CH₃)₂
-
Appearance: Colorless liquid with a sweet, characteristic odor (similar to toluene)
-
Boiling Point: Approximately 138–144°C, depending on the isomer
-
Solubility: Slightly soluble in water (<20 mg/L), but highly soluble in organic solvents such as alcohol, ether, and benzene
-
Chemical Stability: Highly stable under normal conditions due to its aromatic structure
-
Flammability: Flash point around 27–30°C — highly flammable material
Applications of Xylene
-
Petrochemical Industry: Para-xylene is a key raw material for producing purified terephthalic acid (PTA), which is used in polyethylene terephthalate (PET) manufacturing.
-
Industrial Solvent: Used as a powerful solvent in paints, resins, adhesives, and coatings.
-
Plastics Industry: Para-xylene is used to produce plastic bottles and polyester fibers.
-
Pharmaceuticals: Utilized in the synthesis of certain chemical intermediates and active ingredients.
-
Printing Industry: Employed as a solvent in printing inks.
-
Laboratory Use: Commonly used for cleaning equipment and in chemical analysis.
Advantages of Xylene
-
Excellent Solvency: Capable of dissolving a wide range of organic compounds.
-
High Stability: Aromatic structure provides strong resistance to chemical degradation.
-
Isomeric Versatility: Multiple isomer forms enable diverse industrial applications.
-
Economic Production & Availability: A by-product of petroleum refining and catalytic reforming processes, making it widely accessible.
Disadvantages of Xylene
-
Toxicity: Prolonged exposure to xylene vapors may cause central nervous system, liver, and kidney damage.
-
Fire Hazard: Highly flammable liquid with vapors heavier than air.
-
Environmental Impact: Low biodegradability and potential for soil and groundwater contamination.
-
Health Limitations: Requires purification and FDA/EMA approval for use in food or pharmaceutical industries.
Safety and Handling of Xylene
-
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Use chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and suitable respiratory protection in enclosed areas.
-
Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in industrial workplaces to prevent vapor accumulation.
-
Storage Conditions: Store in tightly sealed containers, away from heat, sparks, and open flames.
-
Hazardous Contact Points: Eyes, skin, and respiratory system. In case of contact, rinse immediately with water.
Occupational Exposure Limits (OSHA / NIOSH)
-
Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL): 100 ppm (TWA)
-
Recommended Exposure Limit (REL): 100 ppm (TWA), 150 ppm (STEL)
Zinc Nitrate
PropertiesAppearance: Colorless crystals Chemical formula: Zn(NO3)2 Solubility: Soluble in water Compound type: Inorganic compound
Applications Zinc NitrateAgriculture: Nitrogen fertilizer: Used as a source of zinc and nitrogen for plants, which helps increase plant growth and health. Electronics: Electronic components production: Used in the manufacture of electronic components and batteries. Pharmaceuticals: Drug production: Used as an additive in the production of drugs and dietary supplements. Chemical industry: Paint and coating production: Used as a raw material in the production of industrial paints and coatings.
BenefitsIncrease plant growth: The zinc in Zinc Nitrate increases plant growth and development. Wide applications: Used in various industries due to its multifunctional properties. High solubility: Easily dissolves in water, which makes it easy to use in various solutions.
Zinc Stearate
Zinc stearate propertiesHydrophobicity: Zinc stearate is hydrophobic and therefore prevents materials from sticking to each other. Lubricity: This substance acts as a lubricant and reduces friction between particles. Anti-sticking: Zinc stearate is used as an anti-sticking agent in various industries. Thermal stability: This substance is stable against heat.
Zinc stearate applicationsPlastics industries: Lubricant: Used to improve the flowability of plastic materials in the production process. Releasing agent: Prevents plastic materials from sticking to molds. Rubber industry: Lubricant: Used in rubber production to improve the production process and reduce friction. Activating agent: Plays an important role in the rubber vulcanization process. Cosmetic industry: Lubricant: Used in the production of cosmetics such as lipstick and eye shadow. Anti-sticking: Prevents cosmetics from sticking to packaging. Paint and coating industry: Anti-staining: Prevents paint from settling. Lubricant: Used in paint production to improve flow properties. Pharmaceutical industry: Lubricant: Used in the production of tablets and capsules to improve the flowability of powders. Food industry: Anti-sticking: Used in the production of food such as chocolate powders and flour.