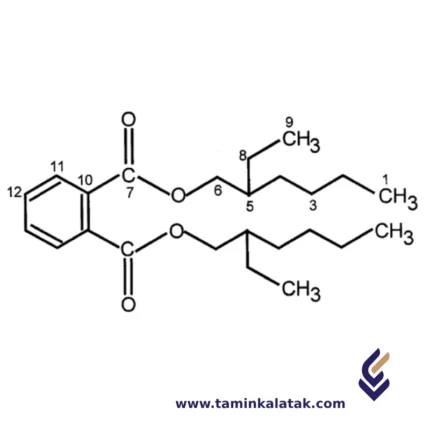
Mixed xylene
Mixed xylene is an aromatic organic compound composed of three main xylene isomers — ortho-xylene (o-xylene), meta-xylene (m-xylene), and para-xylene (p-xylene) — along with a significant proportion (approximately 10–20%) of ethylbenzene.
This chemical is primarily used as a solvent in various industries and, due to its moderate volatility and chemical stability, is one of the most widely used solvents in the petrochemical, paint and resin, printing, and adhesive industries.
Structure of Mixed Xylene
Mixed xylene consists of the following three isomers:
-
Ortho-xylene (o-xylene)
-
Meta-xylene (m-xylene)
-
Para-xylene (p-xylene)
together with about 10–20% ethylbenzene.
General Chemical Formula: C₈H₁₀
Structure: A benzene ring with two methyl (–CH₃) groups attached at different positions.
Properties of Mixed Xylene
-
Chemical Formula: C₆H₄(CH₃)₂
-
Appearance: Colorless, clear liquid with a sweet, characteristic odor
-
Boiling Point: Approximately 138–144°C
-
Flash Point: About 27–30°C (highly flammable)
-
Solubility: Insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, and acetone
Applications of Mixed Xylene
Mixed xylene has a wide range of applications, including:
-
As a solvent in the manufacture of paints, varnishes, inks, and thinners
-
In adhesive and resin formulations
-
In the petrochemical industry for producing para-xylene, a raw material for polyesters and PET bottles
-
As an extraction agent in laboratories
-
In the production of plastics, synthetic fibers (such as polyester), detergents, and pesticides
-
As a cleaning and degreasing agent in the metal and electronics industries
Advantages of Mixed Xylene
-
High solvency power for a wide range of organic compounds
-
Readily available and cost-effective
-
Excellent compatibility with industrial and chemical processes
-
Good chemical stability in various industrial applications
Disadvantages of Mixed Xylene
-
Highly flammable: Must be stored in a safe environment away from heat sources
-
Toxic vapors: Prolonged inhalation can cause headaches, dizziness, drowsiness, central nervous system damage, and respiratory issues
-
Environmental hazards: Leakage can contaminate groundwater and soil
-
Skin and eye irritation: Direct contact may cause dryness, inflammation, and irritation
Safety and Handling of Mixed Xylene
When handling mixed xylene, the following safety precautions should be observed:
-
Wear chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and an appropriate respirator
-
Store in tightly sealed, solvent-resistant containers
-
Keep away from heat, sparks, and open flames
-
Work in a well-ventilated area to prevent vapor accumulation
-
In case of a spill, absorb with non-combustible materials (such as clay or sand) and dispose of according to environmental regulations
Modifier
- Impact Modifiers – Improve toughness and reduce brittleness (e.g., ABS, MBS, rubber-based modifiers).
- Plasticizers – Increase flexibility and reduce stiffness (e.g., phthalates, adipates).
- Processing Aids – Enhance melt flow and ease of processing (e.g., acrylic copolymers).
- Stabilizers – Protect polymers from degradation due to heat, UV, or oxidation (e.g., UV stabilizers, antioxidants).
- Flame Retardants – Reduce flammability (e.g., halogenated compounds, phosphorus-based additives).
- Fillers & Reinforcements – Improve mechanical strength (e.g., glass fibers, carbon black, silica).
- Compatibilizers – Improve miscibility of polymer blends (e.g., maleic anhydride grafted polymers).
StructureA plasticizer modifier typically consists of a small, flexible organic molecule containing both polar and nonpolar regions. These molecules insert themselves between polymer chains, reducing intermolecular forces and increasing flexibility. Most plasticizers have a core structure with ester, ether, or phosphate functional groups, which enhance compatibility with polymers. Phthalates, such as di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP), are among the most common plasticizers, featuring a benzene ring with ester-linked alkyl chains. Adipates, like di(2-ethylhexyl) adipate (DEHA), have a linear aliphatic backbone, making them suitable for low-temperature applications. Trimellitates, such as tri(2-ethylhexyl) trimellitate (TOTM), offer high-temperature resistance due to their aromatic core with three ester groups. Additionally, phosphate esters, such as triphenyl phosphate (TPP), serve as flame-retardant plasticizers. By modifying polymer structures, plasticizers enhance flexibility, durability, and processability, making them essential in applications like PVC, rubber, and coatings.
PropertiesA plasticizer modifier possesses several key properties that enhance the flexibility, processability, and durability of polymers. It typically has low volatility, preventing it from evaporating easily and ensuring long-term effectiveness. High compatibility with the polymer matrix is essential to avoid phase separation or migration. Thermal stability is another crucial property, allowing the plasticizer to withstand high processing and operating temperatures without degrading. By lowering the glass transition temperature (Tg) of a polymer, plasticizers make materials softer and more pliable at lower temperatures. They also exhibit good solvency power, helping to disperse polymer chains and reduce rigidity. Resistance to extraction ensures that the plasticizer remains within the polymer even when exposed to water, oils, or chemicals. In some cases, plasticizers provide flame retardancy, such as phosphate esters, which enhance fire resistance. Additionally, they improve mechanical flexibility by increasing elongation and impact resistance while reducing brittleness. Certain plasticizers also offer UV and oxidation resistance, preventing polymer degradation due to light or air exposure. These properties make plasticizer modifiers essential in applications such as PVC, rubber, adhesives, coatings, and elastomers, where flexibility and durability are critical.
Applications of Plasticizer Modifiers
- PVC Products – Used in flexible PVC for cables, flooring, tubing, and synthetic leather.
- Rubber Industry – Enhances elasticity and softness in rubber-based products.
- Adhesives and Sealants – Improves flexibility and adhesion properties.
- Coatings and Paints – Enhances spreadability and durability.
- Medical Devices – Used in flexible materials like IV bags and tubing.
- Automotive Industry – Found in interior components, dashboards, and flexible seals.
- Textiles and Films – Used in synthetic fabrics and plastic films for improved softness.
Advantages of Plasticizer Modifiers
- Increases flexibility and softness of polymers.
- Improves processability during manufacturing.
- Reduces brittleness, enhancing impact resistance.
- Lowers the glass transition temperature (Tg) for better performance in cold conditions.
- Some provide flame retardancy for added safety.
- Enhances elongation and durability of materials.
Disadvantages of Plasticizer Modifiers
- Some plasticizers, like phthalates, raise health and environmental concerns.
- Migration issues can occur, leading to loss of properties over time.
- Certain plasticizers may cause chemical incompatibility with specific polymers.
- Volatility in some types may lead to material degradation or unpleasant odors.
- Some plasticizers reduce mechanical strength in high concentrations.
- Environmental impact can be a concern, especially for non-biodegradable plasticizers.
Mono Ammonium Phosphate
Properties of Monoammonium PhosphateHigh solubility in water: This property makes it easily accessible to plants. Source of nitrogen and phosphorus: It provides two essential nutrients for plant growth. Acidic nature: It has a slightly acidic pH, which can help balance soil pH. Non-hygroscopic: It does not absorb moisture from the air, ensuring its stability.
Applications of Monoammonium PhosphateAgriculture Fertilizer: Monoammonium Phosphate is a popular fertilizer as it provides both nitrogen and phosphorus, which are crucial nutrients for plant growth. It promotes healthy root development, enhances flowering, and improves overall plant health. Fire Safety Fire Extinguishers: Monoammonium Phosphate is a key component in dry chemical fire extinguishers. When heated, it releases ammonia gas, which smothers fires by displacing oxygen. Other Applications Food Industry: It can be used as a food additive to regulate pH and as a yeast nutrient. Textile Industry: It can be used as a fire retardant for textiles. Industrial Processes: It has various industrial applications, including in the production of fertilizers, pesticides, and other chemicals.
Benefits of Using Monoammonium PhosphateEnhanced Plant Growth: Provides essential nutrients for healthy plant development. Improved Soil Health: Helps maintain optimal soil pH levels. Effective Fire Suppression: Suppresses fires by displacing oxygen. Versatile Applications: Can be used in various industries, from agriculture to fire safety. Safety Considerations While Monoammonium Phosphate is generally safe to handle, it's important to follow safety guidelines: Avoid Inhalation: Avoid inhaling the powder. Eye and Skin Contact: Avoid contact with eyes and skin. Storage: Store in a cool, dry place away from moisture and incompatible substances.
Mono Ethanol Amin
Monoethanolamine (MEA), with the chemical formula C₂H₇NO and CAS No. 141-43-5, is a primary amine containing two reactive functional groups — an amino group (–NH₂) and a hydroxyl group (–OH).
It appears as a colorless, viscous liquid with a strong ammonia-like odor.
Due to its unique chemical reactivity, MEA is widely used in gas treatment, detergents, oil and gas, cement additives, catalyst production, and personal care formulations.
Chemical Structure
-
IUPAC Name: 2-Aminoethan-1-ol
-
Molecular Structure: Bifunctional molecule containing –NH₂ and –OH groups
-
Chemical Family: Simplest member of the ethanolamines
Physical and Chemical Properties
| Property | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Colorless, viscous liquid with ammonia-like odor |
| Density (20°C) | 1.0117 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 10.3°C |
| Boiling Point | 170°C |
| Vapor Pressure (20°C) | ≈ 64 Pa |
| pKa (25°C) | 9.50 |
| Water Solubility | Fully miscible with water and alcohols |
| Viscosity (20°C) | 23.2 mPa·s |
| Refractive Index (nD) | 1.4539 |
Key Advantages
-
Efficient absorber of acid gases (CO₂ and H₂S) in gas sweetening units
-
Adjustable neutralizing and emulsifying agent for detergents and personal care products
-
Versatile chemical intermediate in the synthesis of polymers, pharmaceuticals, dyes, and resins
-
Catalyst in polyurethane foam production and other industrial reactions
Limitations and Precautions
-
Highly corrosive and irritating – causes severe burns to skin and eyes on contact
-
Vapor irritation – may affect respiratory system with prolonged exposure
-
Oral toxicity: LD₅₀ (rat) ≈ 3320 mg/kg → moderate toxicity
-
Environmental hazard: harmful to aquatic life; neutralization or dilution required prior to disposal
Applications
1. Gas Treatment (Gas Sweetening)
Used for removing CO₂ and H₂S from natural gas, process gases, and flue gases in power plants.
2. Detergents and Cleaners
Functions as an emulsifier and pH regulator in industrial, cosmetic, and household formulations.
3. Cement and Construction
Acts as an additive to improve cement fluidity and reduce permeability.
4. Chemical Intermediate
Used in the synthesis of EDTA, pharmaceuticals, dyes, resins, and surfactants.
Safety and Handling
GHS Classification:
-
H314: Causes severe skin burns and eye damage
-
H335: May cause respiratory irritation
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
-
Chemical-resistant clothing
-
Nitrile gloves
-
Safety goggles or face shield
-
Respiratory protection in confined areas
Storage Conditions:
-
Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area
-
Keep away from heat sources, sparks, and oxidizing agents
-
Use tightly sealed containers with clear labeling
Emergency Measures:
-
Skin contact: Rinse immediately with plenty of water
-
Eye contact: Flush for at least 15 minutes and seek medical attention
-
Inhalation: Move to fresh air immediately
-
Spillage: Absorb with dry inert material and prevent vapor release
Monoethanolamine (MEA) is a key industrial chemical valued for its reactivity, versatility, and neutralizing properties.
It plays a critical role in gas purification systems, detergents, and chemical synthesis, provided that proper safety and handling measures are observed.
Monobasic Sodium Phosphate Anhydrous
Properties of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate AnhydrousHigh solubility in water: It dissolves easily in water and creates acidic solutions. Buffering property: It can reduce pH changes in solutions. Phosphorus source: It contains a large amount of phosphorus, which is essential for many biological processes. Non-hygroscopic: It does not absorb moisture from the air.
Applications of Monobasic Sodium Phosphate AnhydrousFood industry: PH adjuster: It is used to adjust the pH in food products such as cheese, soft drinks, and processed meats. Emulsifying agent: It acts as an emulsifier in the production of dairy products and ice cream. Pharmaceutical Industry: Drug Carrier: Used as a drug carrier in some formulations. pH Regulator: Used to adjust the pH in pharmaceutical products. Water Industry Water Purification: Used as a coagulant in water purification. Other Industries: Textile Industry: Used as a softening and anti-wrinkle agent in the textile industry. Paper Industry: Used as a quality improvement agent in paper production.
Advantages of using anhydrous monosodium phosphateHigh solubility: Easily dissolves in formulations. Buffering property: Helps maintain pH stability. Source of phosphorus: Essential for many biological processes. Widespread applications: Used in various industries. Important points in using anhydrous monosodium phosphate Skin and eye contact: Causes irritation if it comes into contact with the skin and eyes. Inhalation: Inhalation of dust from this substance can cause respiratory problems. Storage: Store in closed containers in a cool, dry place.
Monoethylene Glycol
Applications of monoethylene glycolAntifreeze: The main use of monoethylene glycol is as an antifreeze in automotive and industrial cooling systems. Solvent: It is used as a solvent in the production of paints, resins, inks, and some other chemicals. Plasticizer: Used as a plasticizer in the production of synthetic fibers and plastics. Raw material: Used as a raw material in the production of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which is used in the manufacture of plastic bottles. Desiccant: Used as a desiccant in some industries due to its moisture absorption properties.
Advantages of using monoethylene glycolLow freezing point: Very effective as an antifreeze. High solubility: Miscible in many solvents. Suitable viscosity: Acts as a lubricant. Safety tips
MonoPropylene Glycol
Applications of MonoPropylene GlycolMonoPropylene Glycol has a wide range of applications across various industries: Food Industry: Food Additive: Used as a humectant to retain moisture in food products. Flavor Carrier: Used to disperse flavoring agents in food and beverages. Solvent: Used as a solvent in food extracts and flavorings. Pharmaceutical Industry: Solvent: Used as a solvent in various pharmaceutical formulations. Carrier: Used as a carrier for drugs and other active ingredients. Humectant: Used to prevent drying out of pharmaceutical products. Cosmetics and Personal Care: Humectant: Used to retain moisture in skin and hair care products. Solvent: Used as a solvent for various cosmetic ingredients. Carrier: Used to deliver active ingredients to the skin. Industrial Applications: Antifreeze: Used as an antifreeze in various industrial applications. Heat Transfer Fluid: Used in heat transfer systems. Solvent: Used as a solvent in paints, coatings, and inks.
Monosodium Phosphate
Properties of Monosodium PhosphateHigh solubility in water: It dissolves easily in water and creates acidic solutions. Buffering property: It can reduce pH changes in solutions. Phosphorus source: It contains a large amount of phosphorus, which is essential for many biological processes. Non-hygroscopic: It does not absorb moisture from the air.
Applications of Monosodium PhosphateFood industry: PH regulator: It is used to adjust the pH in food products such as cheese, soft drinks, and processed meats. Emulsifying agent: It acts as an emulsifier in the production of dairy products and ice cream. Anti-caking agent: It is used in washing powders and other powdered products. Pharmaceutical Industry: Drug Carrier: Used as a drug carrier in some formulations. PH Regulator: Used to adjust the pH in pharmaceutical products. Water and Wastewater Industry: Water Softener: Used to soften hard water. Water Treatment: Used as a coagulant in water treatment. Other Industries: Textile Industry: Used as a softening and anti-wrinkle agent in the textile industry. Paper Industry: Used as a quality improvement agent in paper production.
Advantages of Using Monosodium PhosphateHigh Solubility: Easily dissolves in formulations. Buffering Property: Helps maintain pH stability. Source of Phosphorus: Essential for many biological processes. Wide Applications: Used in various industries. Important Points in Using Monosodium Phosphate Skin and Eye Contact: Causes irritation if contacted with skin and eyes. Inhalation: Inhalation of dust from this material can cause respiratory problems. Storage: Store in closed containers in a cool, dry place.
Motorcycle Tire Building Machine
Motorcycle Tires
Mould for Non-tire Rubber Products
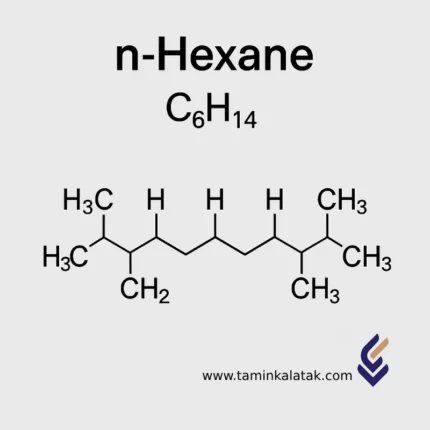
N- Hexane
n-Hexane is a saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon belonging to the alkane family, consisting of a straight carbon chain. In its pure form, it is a colorless liquid with a mild odor, high volatility, and extreme flammability. It is mainly obtained from the distillation of light naphtha fractions and crude oil derivatives.
n-Hexane is one of the most widely used non-polar organic solvents in various industries, particularly in chemical, food, pharmaceutical, and laboratory processes.
Chemical Formula and Structure of n-Hexane
The molecular formula of n-Hexane is C₆H₁₄, and its molar mass is 86.18 g/mol.
Its structure consists of a linear chain of six carbon atoms connected by single bonds, each carbon atom being saturated with hydrogen atoms.
The structural formula is represented as CH₃–(CH₂)₄–CH₃.
The IUPAC name of the compound is Hexane. For the linear isomer, the prefix “n-” (normal) is added, making it n-Hexane.
It is one of several hexane isomers, along with 2-methylpentane and 3-methylpentane, which are also found in industrial hexane mixtures.
Physical and Chemical Properties of n-Hexane
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Colorless liquid with a mild, gasoline-like odor |
| Boiling point | 68.7 °C |
| Kinematic viscosity | 0.31 cP at 25 °C |
| Water solubility | Very low; approximately 9.5 mg/L at room temperature |
| Flash point | –22 °C (highly flammable) |
| Log P (octanol/water partition coefficient) | 3.9–4.1, indicating high lipophilicity and strong affinity for organic phases |
Industrial Applications of n-Hexane
n-Hexane is one of the most common non-polar organic solvents used in various industries:
Food Industry
-
Used for extraction of vegetable oils from seeds such as soybean, canola, cottonseed, and sunflower.
-
Applied in fat separation during food processing (industrial scale only — residual solvent must be completely removed).
Pharmaceutical and Chemical Industries
-
Used as a solvent in the synthesis of pharmaceutical compounds.
-
Extraction of bioactive compounds from plants.
-
Washing and crystallization of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
Rubber and Adhesive Industries
-
Acts as a diluent for industrial adhesives.
-
Solvent for rubber, elastomeric polymers, and certain resins.
Electronics and Laboratory Applications
-
Used as a surface cleaner for sensitive electronic components.
-
Employed for glassware cleaning under controlled, well-ventilated conditions.
Advantages of n-Hexane
-
Excellent solvent power for non-polar organic compounds such as oils, fats, and resins.
-
Rapid evaporation and high volatility, enabling quick drying of surfaces.
-
Wide availability and relatively low cost on an industrial scale.
-
Colorless and low-odor at low concentrations.
-
Leaves minimal residue upon complete evaporation.
Disadvantages of n-Hexane
Despite its advantages, n-Hexane has significant drawbacks that must be carefully managed in industrial and laboratory use:
-
Highly flammable — vapors can easily ignite at room temperature with even small sparks.
-
Neurotoxic (neurotoxicant) under chronic exposure, especially in occupational settings — may cause peripheral polyneuritis, muscle weakness, and numbness in hands and feet.
-
High environmental hazard in case of spillage or improper disposal; can contaminate soil and surface water.
-
Very low miscibility with water, making removal from aqueous environments difficult.
-
Potential for bioaccumulation with prolonged environmental exposure.
Safety and Storage of n-Hexane
GHS Hazard Classification:
-
H225: Highly flammable liquid and vapor
-
H336: May cause drowsiness or dizziness
-
H304: May be fatal if swallowed and enters airways
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
-
Nitrile gloves, safety goggles, half-face respirator with organic vapor filter (A-type), and solvent-resistant lab coat.
Ventilation:
-
Mandatory — must be used in a chemical fume hood or well-ventilated area.
Safe Storage:
-
Store in metal or HDPE solvent-resistant containers, tightly sealed.
-
Keep in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area, away from heat sources, flames, sparks, and direct sunlight.
Emergency Measures:
-
In case of spillage, cover the area with absorbent material (e.g., sand, vermiculite), and ensure immediate ventilation.
-
Skin and eye contact: Rinse immediately with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes.
-
Ingestion: Do not induce vomiting; seek immediate medical attention.