Epichlorohydrin
Epoxy Resins (EP)
Structure Epoxy resins
Epoxy resins typically feature a molecular structure characterized by reactive epoxide groups, which are three-membered cyclic ethers with significant strain energy. In many commercial systems, these resins are produced by reacting bisphenol A with epichlorohydrin, yielding a diglycidyl ether that contains two epoxide groups attached to an aromatic backbone. This structure enables efficient crosslinking with various hardeners such as amines or anhydrides during the curing process. The resulting three-dimensional network of interlinked polymer chains is what imparts epoxy resins with their high mechanical strength, excellent chemical resistance, and durable performance in demanding applications.Properties Epoxy resins
Epoxy resins are valued for their robust mechanical strength and chemical resistance, combined with low shrinkage during the curing process. Their ability to firmly adhere to a variety of substrates, including metals, glass, and concrete, makes them particularly useful in structural and industrial applications. In addition, these thermosetting polymers exhibit excellent electrical insulation properties, ensuring their suitability for electronics and electrical encapsulation. Their high durability and resistance to environmental degradation further contribute to their performance in demanding conditions, and their properties can be tailored through the incorporation of additives or fillers to achieve specific performance criteria.Applications Epoxy resins
- Used as structural adhesives in aerospace, automotive, and construction industries
- Applied as protective coatings in industrial floors, marine environments, and chemical storage facilities
- Employed in composite materials reinforced with carbon or glass fibers for lightweight, high-strength applications
- Utilized for electronic encapsulation, potting, and PCB manufacturing due to its excellent electrical insulation properties
- Incorporated in construction materials such as grouts, sealants, and repair mortars
- Adopted in art and decorative projects, including resin art, jewelry, and tabletops
Advantages Epoxy resins
- Offers high mechanical strength and durability in demanding applications
- Provides excellent chemical and corrosion resistance, ensuring longevity
- Exhibits low shrinkage during curing, resulting in dimensional stability
- Delivers strong adhesion to a wide range of substrates, from metals to plastics
- Functions as an effective electrical insulator, ideal for electronic applications
- Allows for property customization through additives and fillers
Disadvantages Epoxy resins
- Can be brittle in some formulations, often requiring modification with toughening agents
- Presents potential toxicity during handling, necessitating proper safety precautions
- Generally higher in cost compared to alternative resins like polyester or vinyl ester systems
- Curing conditions can be sensitive to environmental factors, affecting final performance
- May exhibit limited UV resistance, often needing additional protective coatings for outdoor use
Esters Solvents
Ethanol (Ethyl Alcohol) 96% , 99%
Ether Solvents
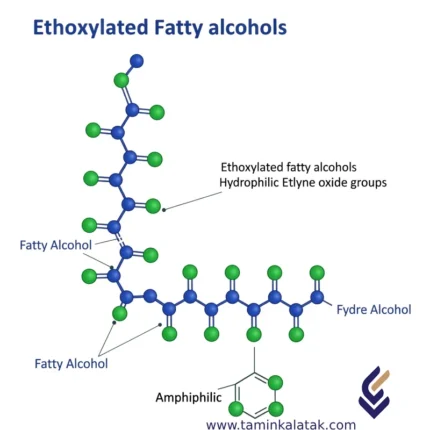
Ethoxylated fatty alcohols
Fatty Alcohol Ethoxylates (FAEs) are a group of nonionic surfactants produced through the ethoxylation reaction between natural or synthetic fatty alcohols (R–OH) and ethylene oxide (EO). These compounds contain both hydrophilic (ethoxylated chain) and hydrophobic (fatty chain) segments.
Due to their excellent surface tension–reducing properties, they are widely used in detergent, cosmetic, industrial, and agricultural formulations.
Chemical Structure of Fatty Alcohol Ethoxylates
-
General formula: R–(OCH₂CH₂)ₙ–OH
-
Fatty component (R): C₁₂–C₁₈ alkyl chain (natural or synthetic origin)
-
Number of EO units (n): typically between 1 and 20, determining functional performance
The molecular structure combines hydrophilic and lipophilic characteristics, making it an effective nonionic surfactant with versatile solubility and interfacial activity.
Physical and Chemical Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical state | Clear to pale yellow liquid (depending on alkyl chain and EO content) |
| Odor | Mild, soap-like |
| Boiling point | Typically above 250 °C or decomposes before boiling |
| Biodegradability | High for natural grades (C₁₂–C₁₄); low environmental persistence |
Applications of Fatty Alcohol Ethoxylates
1. Household and Industrial Detergents
-
Serve as primary nonionic surfactants in dishwashing liquids, laundry detergents, surface cleaners, descalers, and multi-purpose cleaners
-
Used in low-foam or foam-controlled formulations for industrial cleaning and machine-washing systems
-
Compatible with ionic and anionic surfactants, enhancing detergency and fat solubilization
2. Personal Care and Cosmetic Products
-
Act as emulsifiers, wetting agents, and mild cleansing agents in shampoos, creams, lotions, foams, and facial cleansers
-
Improve spreadability and penetration of active ingredients in skin and hair formulations
-
Show excellent skin and eye compatibility when used at controlled concentrations
3. Agricultural Formulations
-
Function as spreading agents and penetrants, improving the absorption of pesticides, herbicides, and foliar fertilizers
-
Reduce surface tension of spray droplets, enhancing uniform distribution on leaf surfaces
4. Textile and Leather Industries
-
Used as softeners, lubricants, wetting agents, and antistatic agents in washing, dyeing, and finishing processes
-
Improve dye penetration and reduce streaking or unevenness during dyeing operations
5. Coatings, Paints, and Inks
-
Act as emulsion stabilizers, wetting agents, and pigment dispersants
-
Lower surface tension and enhance film uniformity in coating applications
-
Suitable for water-based paints, printing inks, and industrial coating formulations
Industrial Application Sectors
-
Detergent industry
-
Cosmetics and personal care
-
Agriculture
-
Textile and leather
-
Paints, coatings, and inks
Advantages of Fatty Alcohol Ethoxylates
-
Nonionic nature: Compatible with anionic, cationic, and amphoteric surfactants
-
Controlled foaming: Ideal for low-foam applications
-
Biodegradable: Environmentally friendly (especially natural-based types)
-
Resistant to water hardness and pH variations
-
Adjustable properties by varying the number of EO units (n)
Disadvantages of Fatty Alcohol Ethoxylates
-
May cloud, thicken, or solidify at low temperatures (cloud point behavior)
-
Some grades produce low foam, requiring combination with high-foaming surfactants in certain formulations
-
Potential mild skin irritation at high concentrations or high EO content
-
Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents
-
Moderate aquatic toxicity at low EO numbers
Safety and Storage of Fatty Alcohol Ethoxylates
Fatty Alcohol Ethoxylates (FAEs) are among the most widely used nonionic surfactants in detergent, cosmetic, textile, agricultural, and pharmaceutical industries.
Proper storage and handling are essential to maintain product stability and prevent environmental or occupational hazards.
Safety Precautions
-
FAEs are low-hazard and relatively safe compounds; however, direct contact with skin or eyes may cause mild irritation.
-
Inhalation of vapors or mists, particularly during hot processes, can cause slight respiratory irritation.
-
Use chemical-resistant gloves, protective goggles, and ensure adequate ventilation during handling.
Storage Recommendations
-
Store in tightly closed, corrosion-resistant containers clearly labeled with product identification.
-
Keep in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight.
-
Avoid storage near strong acids, bases, or oxidizing agents.
-
Stable at ambient temperature, but protect from freezing and excessive heat, as these may affect viscosity and performance.
Ethoxylated Fatty Alcohols
Properties of Ethoxylated Fatty AlcoholsEmulsifying properties: These compounds act as emulsifiers and cause oily and aqueous substances to mix. Detergent properties: Ethoxylated fatty alcohols have good detergent properties and are used in the production of detergents. Softening properties: These compounds are used as softeners in the production of cosmetic and textile products. Solvent properties: Some types of ethoxylated fatty alcohols have good solvent properties and are used in the production of solvents.
Applications of ethoxylated fatty alcoholsCosmetics and health care industries: Used in the production of shampoos, soaps, lotions, creams and other cosmetic and health care products. Textile industry: Used as a softener, emulsifier and waterproofing agent in the textile industry. Oil and gas industry: Used in the production of additives for oil and gas. Agricultural industry: Used as an emulsifier in the production of agricultural pesticides.
Types of ethoxylated fatty alcoholsLinear ethoxylated fatty alcohols: These types of alcohols have a linear structure and are more biodegradable compared to branched types. Branched ethoxylated fatty alcohols: These types of alcohols have a branched structure and are more widely used in some applications due to their better properties. Advantages of using ethoxylated fatty alcohols Variety of properties: Ethoxylated fatty alcohols acquire diverse properties by changing the length of the alcohol chain and the number of ethylene oxide molecules. Environmental compatibility: Some types of ethoxylated fatty alcohols are biodegradable and do not harm the environment. Affordable price: These compounds are reasonably priced compared to other chemicals. Safety tips Skin and eye irritation: Direct contact with ethoxylated fatty alcohols may cause skin and eye irritation. Inhalation: Inhaling vapors of these compounds can irritate the respiratory tract. Storage: Store ethoxylated fatty alcohols in closed containers in a cool, dry place.
Ethoxylated fatty amines
Ethoxylated Fatty Amines are nonionic surfactants produced by the controlled reaction of long-chain fatty amines (C₁₂–C₂₂) with ethylene oxide (EO).
The resulting molecules contain a hydrophilic ethoxy chain and a hydrophobic alkyl chain, providing excellent wetting, emulsifying, and antistatic properties.
General Chemical Structure
R–NH–(CH₂CH₂O)ₙ–H
-
R: Saturated or unsaturated alkyl chain, typically derived from coconut oil, tallow, soybean, or rapeseed oil
-
n: Number of ethylene oxide units (commonly 2–20, and up to 50 in specialized grades)
Physical and Chemical Properties
| Property | Typical Value / Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Clear liquid to pale yellow wax (depending on alkyl chain length and EO content) |
| Viscosity (25°C) | Low to high (increases with higher EO content) |
| Density (20–25°C) | 0.95 – 1.00 g/cm³ |
| Solubility in Water | Varies with EO content — higher n = better solubility |
| pH (1% Solution) | 7.0 – 9.5 |
| Foaming Ability | Moderate |
| Surfactant Type | Nonionic |
Applications
Agriculture
-
Emulsifier in pesticide and liquid fertilizer formulations
-
Penetration enhancer (wetting agent) in foliar spray applications
Oil, Gas, and Drilling
-
Additive for drilling fluids and well-cleaning formulations
-
Foam stabilizer and contact angle modifier
Industrial Cleaning
-
Component of metal cleaners, automotive detergents, and hard surface cleaners
-
Antistatic additive in textile and fabric detergents
Textile, Leather, Paint, and Plastics
-
Antistatic, lubricant, and wetting agent
-
Dispersing agent for pigments and dyes
Advantages
-
Excellent wetting and emulsifying power
-
Stable over a wide pH range (3–11) and in hard water
-
Compatible with anionic, cationic, and amphoteric surfactants
-
Nonionic character → does not interfere with ionic or sensitive compounds
-
Biodegradable in suitable grades (OECD 301 compliant)
Limitations
-
Some grades may cause skin irritation with prolonged contact
-
Unstable in the presence of strong oxidizing agents
-
Hygroscopic at high EO content (absorbs moisture)
-
Higher cost compared to simple anionic surfactants
Safety and Handling
-
Skin/Eye Contact: May cause irritation — wear protective gloves and goggles
-
Inhalation: No significant hazard under proper ventilation
-
Flash Point: Above 150°C
-
Chemical Compatibility: Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents
-
Storage Conditions: Store in polymeric or HDPE containers, in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight
-
Environmental Stability: Biodegradable and low environmental risk at recommended concentrations
Summary
Ethoxylated Fatty Amines are versatile nonionic surfactants offering excellent wetting, emulsifying, and antistatic performance across a wide range of industrial and agricultural formulations.
Their broad compatibility, chemical stability, and biodegradability make them ideal for use in cleaning agents, emulsifiers, drilling fluids, textile aids, and crop protection formulations.
Ethoxylated isodecyl alcohol
Isodecyl Alcohol Ethoxylate (IAE) is a nonionic surfactant belonging to the class of ethoxylated branched fatty alcohols. It is produced by the ethoxylation reaction between isodecyl alcohol (C10, branched-chain) and ethylene oxide (EO). Due to its unique molecular structure, it serves as an effective wetting agent, emulsifier, solubilizer, and dispersant in a wide variety of formulations.
Chemical Structure of Isodecyl Alcohol Ethoxylate
General Formula: R–(OCH₂CH₂)ₙ–OH
-
R: Branched isodecyl (C10) alkyl chain
-
n: Number of ethylene oxide units (typically between 3 and 10, or more depending on the grade)
The molecule consists of a hydrophobic branched isodecyl segment and a hydrophilic ethoxylated chain, giving it dual functionality. This structural balance makes Isodecyl Alcohol Ethoxylate a highly efficient nonionic surfactant with controlled foaming, excellent compatibility, and strong wetting performance.
Physical and Chemical Properties
| Property | Description / Value |
|---|---|
| Odor | Mild, similar to fatty alcohol |
| Surfactant Type | Nonionic |
| pH (1% solution) | Approximately 6–8 |
| Foaming tendency | Low to medium — ideal for low-foam industrial cleaning systems |
| Hard water stability | Excellent; resistant to Ca²⁺ and Mg²⁺ ions |
| Cloud point | 40–70 °C (depending on EO content) |
| Viscosity | Moderate; increases at lower temperatures |
| Thermal & chemical stability | High; resistant to hydrolysis, acids, and alkalis |
| Biodegradability | High (especially in natural, non-petroleum-based grades) |
| Compatibility | Excellent with anionic, cationic, and amphoteric surfactants |
| Flash point | May be flammable in solvent-based grades |
Applications of Isodecyl Alcohol Ethoxylate
Industrial and Household Cleaning
-
Effective wetting agent for hard surfaces
-
Used in low-foam industrial detergents and cleaners
Agriculture
-
Acts as an emulsifier and dispersant in pesticide and foliar fertilizer formulations
-
Enhances absorption of active ingredients through leaf surfaces by reducing surface tension
Textile and Dyeing Industry
-
Functions as a primary wetting agent during fiber preparation and dyeing
-
Serves as a co-emulsifier to stabilize aqueous pigment dispersions
Paints and Resins
-
Efficient dispersing agent in water-based paints, promoting uniform pigment distribution
-
Improves surface wetting and reduces surface tension in waterborne coatings
Advantages of Isodecyl Alcohol Ethoxylate
-
Controlled foaming, ideal for industrial systems
-
Excellent stability across a wide pH range and in hard water
-
High biodegradability (especially in natural-origin grades)
-
Superb compatibility with other surfactants (anionic, cationic, amphoteric)
-
Outstanding resistance to heat, acids, bases, and oxidizing agents
-
Enhances leaf absorption of active ingredients in agricultural applications
Disadvantages and Limitations
-
Certain grades may need to be blended with foaming surfactants for specific applications
-
May become cloudy or viscous at low temperatures (due to the cloud point effect)
-
Can cause skin or eye irritation at high concentrations
-
Solvent-based grades may be flammable
Ethoxylated isooctyl alcohol
Alkoxylates are a class of non-ionic surfactants produced through the addition of alkylene oxides, such as ethylene oxide (EO), propylene oxide (PO), and butylene oxide (BO), to fatty alcohols, fatty acids, or fatty amines. This process, known as alkoxylation, results in molecules with both hydrophilic (water-loving) and hydrophobic (water-repelling) properties.
Applications of Alkoxylates
Alkoxylates find widespread use in various industries, including:
- Home Care
- Personal Care
- Industrial Cleaning
- Textile Industry
- Agrochemicals
Ethoxylated isotridecyl alcohol
Isotridecyl Alcohol Ethoxylate (ITDE) is a branched nonionic surfactant produced through the ethoxylation reaction of a branched-chain alcohol known as isotridecyl alcohol with ethylene oxide (EO). This compound functions as a surface-active agent, emulsifier, detergent, wetting agent, penetration enhancer, and dispersant in various industries. Owing to its excellent chemical stability and high performance in acidic, alkaline, and hard water environments, it is widely used in household and industrial cleaning formulations, as well as in textile and agricultural processes.
Chemical Structure of Isotridecyl Alcohol Ethoxylate
The molecule consists of a branched 13-carbon (C13) isotridecyl alcohol backbone, which is linked to multiple ethylene oxide (EO) units—typically between 3 and 12 moles, depending on the product grade.
It features two distinct segments:
-
Lipophilic (hydrophobic) part derived from the branched isotridecyl chain
-
Hydrophilic part derived from ethoxylate (EO) groups
This dual structure allows the compound to dissolve effectively in both aqueous and non-aqueous systems, exhibiting strong surface activity and excellent wetting and emulsifying properties.
Properties of Isotridecyl Alcohol Ethoxylate
-
Type: Nonionic surfactant
-
Solubility: Readily soluble in water, alcohols, and many organic solvents
-
Thermal and chemical stability: Excellent, especially within a pH range of 4–9
-
Foaming tendency: Moderate to low (depending on degree of ethoxylation)
-
Compatibility: Highly compatible with anionic, cationic, and amphoteric surfactants
-
Biodegradability: Good; meets OECD standards
-
Irritation potential: Low (in cosmetic-grade formulations suitable for personal care)
Applications of Isotridecyl Alcohol Ethoxylate
✔️ In detergent and cleaning formulations:
Used in dishwashing liquids, laundry detergents, shampoos, industrial hard-surface cleaners, and car wash products.
✔️ In textile processing:
Acts as a wetting, penetrating, and de-oiling agent during pretreatment and dyeing operations.
✔️ In leather, dyeing, and printing industries:
Serves as an emulsifier and emulsion stabilizer.
✔️ In agriculture:
Functions as a co-surfactant, wetting agent, and dispersant in pesticide and foliar fertilizer formulations, enhancing spreading and penetration on leaf surfaces.
✔️ In oil and gas industry:
Used in foam control systems, drilling fluids, degreasing, and phase separation processes.
✔️ In coatings, inks, and paints:
Improves pigment wetting, dispersion, and surface tension control in water-based systems.
Advantages of Isotridecyl Alcohol Ethoxylate
-
Excellent compatibility with both ionic and nonionic ingredients
-
Effective performance under both high and low temperature conditions
-
Safe for skin in personal care formulations
-
Enhances cleaning efficiency and reduces surface tension of solutions
-
Decreases phosphate demand in detergent systems
Disadvantages of Isotridecyl Alcohol Ethoxylate
❌ May exhibit low foaming in certain formulations and often requires blending with foaming surfactants (e.g., SLES)
❌ Higher cost compared to simple anionic surfactants
❌ Reduced stability under extreme pH conditions (below 3 or above 11)
❌ At high concentrations, may cause excessive degreasing (undesirable in skincare formulations)
Safety and Storage of Isotridecyl Alcohol Ethoxylate
Isotridecyl Alcohol Ethoxylate is one of the most commonly used nonionic surfactants in detergent, textile, and agricultural applications, and is classified as a low- to moderate-hazard substance in terms of safety. It is generally non-flammable, but direct contact with skin or eyes may cause mild irritation.
Safe Handling and Storage Recommendations:
-
Store in sealed, corrosion-resistant containers
-
Keep in a dry, cool, and well-ventilated area
-
Avoid freezing and exposure to high temperatures
-
Use protective gloves, safety goggles, and masks during handling
✅ Adhering to these safety guidelines helps maintain material stability and minimize potential hazards in the workplace.
Ethoxylated lauric acid
Applications
- Cleaning Agents: Fatty acid ethoxylates are widely used in household and industrial cleaning products due to their ability to reduce surface tension and improve the cleaning process.
- Emulsifying Agents: In cosmetics and personal care products, these surfactants help to stabilize emulsions, ensuring consistent and effective formulations.
- Textile Processing: Utilized in textile manufacturing for their ability to enhance the processing and finishing of fabrics.
- Agriculture: Employed in agricultural formulations as wetting agents, helping to improve the distribution and efficacy of pesticides and fertilizers.