Di Methyl Terephthalate (DMT)
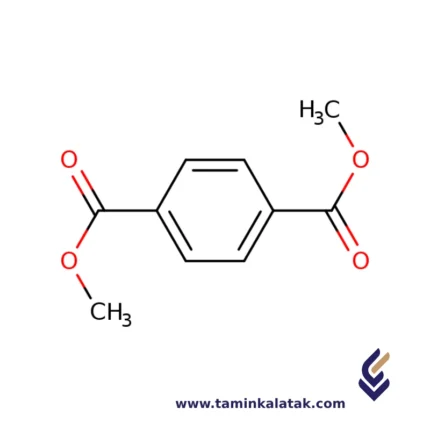
StructureThe structure of Dimethyl Terephthalate (DMT) consists of a benzene ring (C6H5) with two ester groups (-COOCH3) attached to the para positions of the ring. Each ester group is formed by the reaction of terephthalic acid and methanol, where the carboxyl group (-COOH) of the terephthalic acid is esterified with a methanol molecule to form the ester bond (-COOCH3). This gives DMT its molecular formula of C8H10O4. The structure includes a central benzene ring with two methoxy-carbonyl (-COOCH3) groups on opposite sides, making it a symmetrical compound. The ester groups contribute to the compound’s ability to polymerize, making it an important intermediate in the production of polyethylene terephthalate (PET).
PropertiesDimethyl Terephthalate (DMT) is a white crystalline solid with a slight aromatic odor. It has a melting point in the range of 140-143°C and a boiling point of approximately 284°C, making it relatively stable at high temperatures. DMT is slightly soluble in water but readily dissolves in organic solvents such as ethanol, acetone, and chloroform. Its density is around 1.305 g/cm³ at 25°C. As an ester, it has good reactivity, especially in esterification reactions, making it an essential intermediate in polyester production. DMT is stable under normal conditions but can decompose when exposed to very high temperatures or in the presence of strong acids or bases. It is also known for being flammable and should be handled with care in industrial processes. The compound has a low vapor pressure, meaning it doesn’t evaporate easily at room temperature.
Applications of Dimethyl Terephthalate (DMT)
- Polyester Production: Key precursor in the production of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), used in plastic bottles, films, and fibers.
- Textile Industry: Used in the manufacturing of polyester fibers for clothing, upholstery, and other fabric applications.
- Plastic Packaging: Important in producing plastic containers and packaging materials.
- Resins and Coatings: Used in the production of polyester resins for coatings, adhesives, and composites.
- Pharmaceutical and Agricultural Chemicals: Occasionally used in specialty chemical applications for pharmaceuticals and agricultural products.
Advantages of Dimethyl Terephthalate (DMT)
- Versatile Chemical: Acts as a key intermediate in the production of PET and other polyesters, making it highly valuable in various industries.
- Stable and Durable: Polyester products made from DMT are durable, resistant to abrasion, and possess good mechanical properties.
- Easy to Process: The esterification reaction with methanol is well-established, allowing for efficient production of DMT in large quantities.
- Recyclable: PET, produced from DMT, is widely recycled and used in new products, promoting sustainability.
Disadvantages of Dimethyl Terephthalate (DMT)
- Environmental Impact: The production of DMT can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other pollutants, requiring proper emission control measures.
- Flammability: DMT is flammable and poses a fire hazard if not handled properly during production and transportation.
- Cost: The cost of DMT can be relatively high compared to some other raw materials, especially when the demand for PET is fluctuating.
- Limited Chemical Resistance: While PET is generally durable, products made from DMT may not be as resistant to harsh chemicals and UV degradation compared to other polymers.
Di Methylene Amine 60%
N,N-Dimethylethanolamine (DMAE) — also known as Dimethylaminoethanol or DMEA — is a tertiary amine–primary alcohol compound, typically supplied as a 60% aqueous solution.
It is industrially produced by the reaction of dimethylamine with ethylene oxide.
DMAE is a versatile intermediate widely used as a reactive agent, emulsifier, catalyst, and pH modifier in various industries including resins, gas treatment, coatings, and personal care.
Chemical Structure
-
Molecular Formula: C₄H₁₁NO
-
Molecular Weight: 89.14 g/mol
-
Semi-Structural Formula: (CH₃)₂N–CH₂–CH₂–OH
-
IUPAC Name: 2-(Dimethylamino)ethanol
-
Chemical Family: Alkanolamines
Physical and Chemical Properties
| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Clear to pale-yellow liquid |
| Odor | Ammonia- or fish-like odor |
| Boiling Point (99% grade) | 134–136 °C |
| Solubility | Completely miscible with water (commonly supplied as 60% aqueous solution) |
| pH (10% solution) | ~3 |
| Flash Point (closed cup) | ~39 °C (flammable liquid) |
| Refractive Index (20 °C) | nD ≈ 1.438–1.439 |
Key Advantages
-
Dual functionality (amine + alcohol) — provides high reactivity for a wide range of chemical syntheses
-
Effective CO₂ absorber in gas sweetening and refining processes
-
Strong base for pH adjustment in formulations
-
Excellent water solubility — easy incorporation in aqueous and solvent-based systems
-
Useful synthetic intermediate for pharmaceuticals, surfactants, and polymers
Limitations & Precautions
-
Corrosive to skin, eyes, and respiratory tract
-
Flammable liquid with a low flash point (~39 °C)
-
May form carcinogenic nitrosamines in contact with nitrites
-
Strong odor at high concentrations
-
Requires careful storage and handling due to volatility and reactivity
Industrial Applications
-
Detergent & Personal Care Industry: buffering and emulsifying agent
-
Paints & Resins: catalyst and pH regulator in coatings, polyurethane, and resin systems
-
Gas Treatment: acid gas (CO₂, H₂S) absorption agent
-
Chemical Intermediate: precursor for pharmaceuticals, surfactants, and specialty polymers
-
Electronics & Specialty Chemicals: used in precision synthesis and fine chemical manufacturing
Safety and Handling
GHS Classification:
-
⚠️ Signal Word: DANGER
-
H226: Flammable liquid and vapor
-
H302: Harmful if swallowed
-
H312: Harmful in contact with skin
-
H314: Causes severe skin burns and eye damage
-
H332: Harmful if inhaled
-
Classification: Skin Corr. 1B, Eye Dam. 1, Acute Tox. 3 (inhalation)
Recommended PPE:
-
Nitrile or butyl rubber gloves
-
Chemical splash goggles or face shield
-
Protective clothing
-
Adequate ventilation or respirator in confined areas
Storage Conditions:
-
Store in tightly sealed containers below 30 °C
-
Keep away from heat, sparks, and open flame
-
Avoid contact with acids, oxidizing agents, and nitrites (risk of nitrosamine formation)
-
Ensure dry, well-ventilated storage area
Emergency Measures:
-
Skin Contact: Wash immediately with soap and plenty of water
-
Eye Contact: Rinse thoroughly with clean water for at least 15 minutes; seek medical attention
-
Inhalation: Move to fresh air; provide oxygen if needed
-
Spillage: Contain and absorb with inert material; dispose of safely per local regulations
Summary
DMAE 60% is a multi-functional tertiary amine and alcohol widely used as a catalyst, emulsifier, and reactive intermediate in coatings, gas treatment, and specialty chemical production.
Its strong alkalinity and high water solubility make it valuable in industrial formulations, provided that proper safety and storage measures are observed.
Di Octyl Phthalate (DOP)
Structure
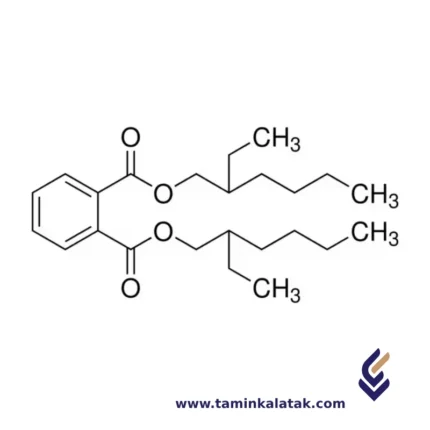
Di-Octyl Phthalate (DOP) is an organic ester compound derived from phthalic acid and is commonly used as a plasticizer in the production of flexible plastics. Its structure consists of a central benzene ring attached to two ester groups, each linked to a long alkyl chain. These alkyl chains are each composed of eight carbon atoms (hence the "octyl" name), and they are connected to the phthalate group through ester bonds. The molecule's overall structure is designed to provide flexibility to plastics, allowing the polymer chains to move more freely by increasing the distance between them, thus reducing intermolecular forces. This contributes to the plasticizing effect, making materials like polyvinyl chloride (PVC) more flexible and workable. The chemical formula of Di-Octyl Phthalate is C24H38O4.Properties
Di-Octyl Phthalate (DOP), also known as dioctyl phthalate, is a commonly used plasticizer in the production of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) plastics. It is a clear, colorless to pale yellow oily liquid with a slight aromatic odor. DOP has a boiling point of about 384°C and a melting point below -30°C, with a density of around 0.986 g/cm³ at 20°C. It is practically insoluble in water but dissolves in most organic solvents like alcohol, benzene, and ether. Known for its good thermal stability, DOP is used to impart flexibility and durability to plastics, though it can degrade at high temperatures over time, releasing potentially harmful compounds. While it has low acute toxicity, prolonged or high exposure can lead to adverse health effects, particularly regarding reproductive toxicity, and it is considered a potential endocrine disruptor. Due to these concerns, DOP is increasingly being regulated, especially in children's toys and food packaging. Its primary use is as a plasticizer in flexible PVC products such as flooring, cables, and synthetic leather, but it also finds application in rubber products. However, due to its low biodegradability and potential environmental impact, alternative plasticizers that are phthalate-free are being sought after.Applications of Di-Octyl Phthalate (DOP)
- Plasticizer for PVC: Primarily used in flexible PVC products like flooring, synthetic leather, and plastic films.
- Rubber Industry: Used to enhance the flexibility and durability of rubber products.
- Electrical Cables: Increases the flexibility and weather resistance of electrical wires and cables.
- Cosmetics and Personal Care Products: Occasionally used in products like nail polish and lotions (though less common today).
- Coatings and Paints: Used as a plasticizer in certain types of paints and coatings for improved flexibility.
Advantages of Di-Octyl Phthalate (DOP)
- Improves Flexibility: Significantly enhances the flexibility and workability of PVC and other polymers.
- Good Thermal Stability: DOP has a relatively high tolerance to heat, which helps in applications exposed to elevated temperatures.
- Low Volatility: It has a low evaporation rate, making it effective over a long period.
- Cost-Effective: It is relatively inexpensive compared to some alternative plasticizers.
Disadvantages of Di-Octyl Phthalate (DOP)
- Health Concerns: DOP is classified as a potential endocrine disruptor and has been linked to reproductive toxicity.
- Environmental Impact: It is not readily biodegradable and can accumulate in the environment, posing risks to wildlife.
- Regulatory Issues: Increasing regulation and bans on the use of phthalates in consumer products, especially those in contact with food or children’s products.
- Migration Issues: DOP can migrate out of plastics over time, leading to potential contamination of surrounding environments or materials.
- Toxicity: Prolonged or high exposure to DOP can result in harmful effects, particularly through skin absorption, inhalation, or ingestion.
Diacetone alcohol
- coatings
- cleaning
- metal working fluids
- polymer processing
- water treatment
- Paints
Diammonium Phosphate
Diammonium Phosphate PropertiesHigh solubility in water: It dissolves easily in water, and therefore plants can quickly use the elements in it. Rich source of nitrogen and phosphorus: Nitrogen is essential for vegetative growth of plants and phosphorus for root growth and flowering. Suitable pH: The pH of diammonium phosphate is in the neutral to slightly alkaline range, which is suitable for most soils. Miscibility: It mixes well with other fertilizers.
Diammonium Phosphate ApplicationsAgricultural fertilizer: The most important use of diammonium phosphate is as an agricultural fertilizer. This fertilizer is added directly to the soil or mixed with other fertilizers and used. Water treatment: It is used in water treatment as a coagulant and sedimentation agent. Food industry: It is used as a buffering agent and pH regulator in some food products. Other industries: It is also used in the textile, leather and paper industries.
Advantages of using diammonium phosphateSimultaneous supply of two essential elements: Nitrogen and phosphorus are two main elements required by plants, which are simultaneously provided by diammonium phosphate. Increased crop yield: The use of diammonium phosphate increases the yield and quality of agricultural products. Improved root growth: The phosphorus in diammonium phosphate strengthens the root system of plants. Increased plant resistance to diseases: Plants fed with diammonium phosphate have greater resistance to diseases and pests. Important points in using diammonium phosphate Amount of use: The amount of diammonium phosphate used depends on the type of soil, type of plant and weather conditions. Time of use: The best time to use diammonium phosphate is at planting or during the growing season. Mixing with other fertilizers: Diammonium phosphate can be mixed with other fertilizers, but before mixing, it is better to consult agricultural experts.
Dibasic Sodium Phosphate
Properties of Dibasic Sodium PhosphateHigh solubility in water: This property makes it easy to use in various applications. Alkaline pH: It forms alkaline solutions when dissolved in water. Buffering agent: It can help maintain a stable pH in solutions. Food additive: It is used as a food additive to control pH and as a buffer.
Applications of Dibasic Sodium PhosphateFood Industry: Food additive: It is used as a food additive to control pH, as a buffer, and as an emulsifier. Meat tenderizer: It is used to tenderize meat by breaking down proteins. Dairy products: It is used in the production of cheese and other dairy products. Pharmaceutical Industry: Buffering agent: It is used to adjust the pH of pharmaceutical formulations. Excipient: It is used as an excipient in various pharmaceutical products. Water Treatment: Water softening: It is used to soften hard water by removing calcium and magnesium ions. Cleaning Products: Detergents: It is used as a cleaning agent in detergents.
Safety ConsiderationsWhile dibasic sodium phosphate is generally safe for use in food and other applications, it can cause skin and eye irritation. It is important to handle it with care and avoid contact with skin and eyes.
Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Dihydrate
Properties of dibasic sodium phosphate dihydrateHigh solubility in water: It dissolves easily in water and creates alkaline solutions. Buffering property: It can reduce pH changes in solutions. Phosphorus source: It contains a large amount of phosphorus, which is essential for many biological processes. Hygroscopic: It absorbs moisture from the air.
Applications of dibasic sodium phosphate dihydrateFood industry: PH adjuster: It is used to adjust the pH in food products such as cheese, soft drinks, and processed meats. Emulsifying agent: It acts as an emulsifier in the production of dairy products and ice cream. Anti-caking agent: Used in washing powders and other powdered products. Pharmaceutical industry: Drug carrier: Used as a drug carrier in some formulations. pH regulator: Used to adjust pH in pharmaceutical products. Water and wastewater industry: Water softener: Used to soften hard water. Water treatment: Used as a coagulant in water treatment. Other industries: Textile industry: Used as a softening and anti-wrinkle agent in the textile industry. Paper industry: Used as a quality improvement agent in paper production.
Advantages of using dibasic sodium phosphate dihydrateHigh solubility: Easily dissolves in formulations. Buffering property: Helps maintain pH stability. Phosphorus source: Essential for many biological processes. Wide applications: Used in various industries. Important notes on using dibasic sodium phosphate dihydrate Skin and eye contact: Contact with skin and eyes may cause irritation. Inhalation: Inhalation of dust from this material can cause respiratory problems. Storage: Store in closed containers in a cool, dry place.
Dicyandiamide
Properties of dicyandiamideHigh thermal stability: Dicyandiamide is stable to heat and does not decompose up to high temperatures. Solubility: It dissolves slightly in cold water and more soluble in hot water. It also dissolves in some organic solvents such as dimethylformamide. Reactivity: Dicyandiamide has high reactivity due to the presence of amide functional groups and can be combined with many other chemicals.
Applications of dicyandiamidePlastics industry: Production of melamine resins: Dicyandiamide is used as a raw material in the production of melamine resins. Melamine resins are used in the production of disposable tableware, wood coatings, and electrical insulation. Adhesive production: Used in the production of industrial adhesives and heat-resistant adhesives. Agricultural industry: Chemical fertilizer: Used as a raw material in the production of some chemical fertilizers. Herbicides: Used as an active ingredient in the production of some herbicides. Pharmaceutical industry: Drug production: Used as a raw material in the production of some drugs. Textile industry: Dye fixation: Used in the textile industry to fix dye on fibers.
Diethylene Glycol
Properties of Diethylene GlycolHygroscopicity: It readily absorbs moisture from the air. Solubility: Miscible with water, alcohols, and many other organic solvents. Viscosity: Higher viscosity compared to ethylene glycol. Boiling Point: Relatively high boiling point.
Applications of Diethylene GlycolDiethylene glycol is a versatile compound with numerous applications in various industries: Industrial Applications: Solvent: Used as a solvent for paints, varnishes, and inks. Plasticizer: Employed in the production of plastics and resins. Intermediate: Used as an intermediate in the synthesis of other chemicals. Humectant: Used to retain moisture in products like tobacco and paper. Heat Transfer Fluid: Used in heating and cooling systems. Personal Care Products: Used as a humectant in cosmetics and skincare products. Food Industry: Used as a solvent and carrier for food additives. Safety Considerations While diethylene glycol has many useful applications, it is important to handle it with care. It can be toxic if ingested or absorbed through the skin. It is also flammable and can irritate the skin and eyes.
DiethyleneTriaMine Penta (DTMP)
DTMP PropertiesStrong chelating: Due to its complex molecular structure, this substance has the ability to form complexes with various metal ions such as calcium, magnesium, iron and copper. This property makes it act as a very strong chelating agent and prevents the formation of sediment in aquatic systems. Thermal stability: In general, this substance is very stable against heat and maintains its chelating properties even at high temperatures. Compatibility with other chemicals: It is compatible with many other chemicals and can be used in various formulations. Environmental friendliness: It is generally harmless to the environment and is easily decomposed.
DiethyleneTriaMine Penta (DTMP) ApplicationsWater and Wastewater Industry: Water Softener: Reduces water hardness by forming a complex with water hardness ions. Anti-scale: Prevents scale formation in boilers, pipes and other water equipment. Corrosion Control: Prevents corrosion by forming a protective layer on metal surfaces. Oil and Gas Industry: Scaling Control: Used in water injection systems to prevent scale formation. Corrosion Inhibitor: Used to protect metal equipment from corrosion. Paper Industry: Scaling Control: Used in paper production systems to prevent scale formation. Textile Industry: Softener: Used as a softener in the textile industry. Pharmaceutical Industry: Chelating Agent: Used as a chelating agent in some drugs.
Advantages of using DiethyleneTriaMine Penta (DTMP)Very high efficiency: It is very effective as a scale inhibitor and chelating agent. High stability at high temperatures: It maintains its chelating properties even at high temperatures. Environmental compatibility: It is generally harmless to the environment.
DiethyleneTriamine PentaMethylenePhosphonic acid (DTPMP)
DTPMP Applications
- Detergents and Cleaners
- water treatment
- Anti-fouling
- Anti-corrosion
- Chelating agent
- Flocculation
- Sediment inhibitor
- Scaling inhibitor
- Agriculture industry
Benefits of Using DTPMPHigh Efficiency: DTPMP is very effective as a scale inhibitor and chelating agent. High Stability at High Temperatures: DTPMP maintains its chelating properties even at high temperatures. Environmental Compatibility: It is generally harmless to the environment.
Diisobutyl Ketone
Key Properties:
- Appearance: Colorless liquid
- Odor: Mild, sweetish
- Density: 0.81 g/cm³ at 20°C
- Boiling Point: 163-173°C
- Solubility: Low water solubility
- Non-HAP: Non-hazardous air pollutant (non-HAP)
- Non-SARA: Non-SARA reportable quantity
- REACH Compliant: Complies with REACH regulations
- Biodegradability: Readily biodegradable
Applications Diisobutyl Ketone
- Industrial Coatings: Used as a retarder solvent to improve flow and minimize humidity blushing.
- Printing Inks: Enhances the performance of commercial printing inks.
- Synthetic Resins: Solvent for various synthetic resins, improving their application and performance.
- Environmental Monitoring: Employed in methods for detecting pollutants in environmental waters.
Safety Measures:
- Hazards: Can be an irritant at higher concentrations.
- Precautions: Keep away from heat, sparks, and open flames. Use explosion-proof equipment and non-sparking tools
- Storage: Store below 30°C and keep container tightly closed