Cycle Tire Mould
Cyclohexanone
Physical and chemical propertiesPhysical state: Colorless oily liquid Odor: Similar to benzaldehyde (bitter almond) Solubility: Soluble in water and also soluble in many organic solvents such as alcohols, ethers, and aromatic hydrocarbons. Density: Less than water Boiling point: 155.7 °C Melting point: -31 °C Flammability: Cyclohexanone vapors are flammable. Production method Cyclohexanone is produced industrially by the oxidation of cyclohexane in the presence of cobalt catalysts. In this process, cyclohexanol is also produced as a by-product. The mixture resulting from this reaction is known as KA oil (Ketone-Alcohol oil) and is used as a raw material for the production of adipic acid.
Applications of cyclohexanoneChemical industry: Used as a raw material in the production of nylon, resins, paints, adhesives and solvents. Solvent: Used as a solvent for paints, varnishes, resins and other organic materials. Pharmaceutical production: Used in the synthesis of some pharmaceuticals. Textile industry: Used as a solvent in dyeing and printing processes.
DAP
DEIPA 85%
Diethanolamine (DEA) is a secondary amine with the chemical formula C₄H₁₁NO₂, typically supplied at 85% concentration.
It is a colorless to pale-yellow viscous liquid with a mild ammonia-like odor.
DEA is widely used in resin manufacturing, gas treatment, detergents, paints, pharmaceuticals, and various industrial formulations.
In industrial processes, it acts as a pH adjuster, catalyst, neutralizing agent, and emulsifier.
Chemical Structure
-
Molecular Formula: C₄H₁₁NO₂
-
Molecular Weight: 105.14 g/mol
-
Structure: Contains two hydroxyl (-OH) groups and one secondary amine (-NH) group.
Solidifies into deliquescent crystals that form a viscous liquid upon melting.
Physical and Chemical Properties
| Property | Typical Value |
|---|---|
| Physical State | Viscous liquid or meltable crystals |
| Color | Colorless to pale yellow (≤15 APHA) |
| Odor | Ammoniacal / fishy |
| Density (20 °C) | 1.09 g/mL |
| Melting Point | ≈ 28 °C |
| Boiling Point | ≈ 268 °C (at 1 atm) |
| Viscosity (30 °C) | ≈ 352 cP |
| Vapor Pressure (20 °C) | < 0.01 mmHg (~0.00037 hPa) |
| Solubility in Water | Completely miscible |
| Refractive Index (nᴅ) | ≈ 1.477 |
| pKa (25 °C) | ≈ 8.9 |
| Explosion Range (air) | 1.6–9.8% (v/v) |
| Ecotoxicity | Harmful to aquatic life with long-term effects |
Key Advantages
-
Bifunctional molecule — contains both amine and hydroxyl groups, enabling diverse chemical reactivity.
-
Effective pH regulator and catalyst in resin production, polyurethane foams, detergents, agrochemicals, and cosmetics.
-
High solubility in water and polar solvents; easily blends with various formulations.
-
Capable of absorbing acidic gases (CO₂, H₂S) in gas treatment systems.
Limitations and Hazards
-
Corrosive to skin and eyes — may cause severe burns or tissue damage.
-
Toxic upon chronic exposure — prolonged inhalation or contact may harm the liver, kidneys, or blood system.
-
Oral LD₅₀ (rat): ≈ 1.6 g/kg
-
-
Harmful to aquatic organisms — must be neutralized or diluted before disposal.
-
Incompatible with strong acids, oxidizers, and acid chlorides (may cause exothermic reactions).
Industrial Applications
-
Gas Sweetening:
Absorption of CO₂ and H₂S from natural gas and process streams. -
Paints, Resins & Adhesives:
Used as a catalyst, stabilizer, and neutralizing agent in epoxy and alkyd systems. -
Detergents & Personal Care:
pH adjustment, foam stabilizer, and emulsifier in soaps and cosmetic formulations. -
Pharmaceutical & Cosmetic Industry:
Intermediate in the production of emollients, conditioners, and surface-active agents. -
Agrochemicals:
Solvent and intermediate for fertilizers and pesticide formulations. -
Other Uses:
Emulsion additive in photographic chemicals and cement admixtures to enhance performance.
Safety and Handling
Main Hazards:
-
Strong irritant to skin and eyes
-
May be absorbed through the skin and cause systemic toxicity
-
Harmful to aquatic environments
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
-
Chemical-resistant gloves and protective clothing
-
Safety goggles or face shield
-
Adequate ventilation or respiratory protection (P2/P3 filter) in confined spaces
Storage Conditions:
-
Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area
-
Keep away from acids, oxidizing agents, and heat sources
-
Maintain temperature below the melting point (≈ 28 °C) to prevent solidification
-
Use tightly sealed containers with clear labeling
Emergency Measures:
-
Skin contact: Wash immediately with plenty of water and soap
-
Eye contact: Rinse continuously with water for at least 15 minutes and seek medical attention
-
Inhalation: Move victim to fresh air; administer oxygen if necessary
-
Spill cleanup: Absorb with inert materials and dispose according to environmental regulations
Summary:
Diethanolamine (DEA 85%) is a versatile industrial chemical with strong pH-regulating, emulsifying, and gas-absorbing properties.
It plays a critical role in gas purification, resin synthesis, detergents, and personal care formulations.
Proper handling, protective measures, and controlled use are essential due to its corrosive and toxic nature.
Dense Soda
Dense Soda, also known as Heavy Sodium Carbonate or Na₂CO₃, is an alkaline inorganic salt that appears as a white, odorless, coarse-grained crystalline solid.
Unlike Light Soda Ash, the dense grade has higher bulk density and larger particle size, making it suitable for processes that require greater physical strength or slower dissolution rates.
Chemical Structure of Dense Soda
-
Chemical Name: Dense Sodium Carbonate
-
Chemical Formula: Na₂CO₃
-
Structure: Ionic crystalline lattice composed of Na⁺ and CO₃²⁻ ions
-
CAS Number: 497-19-8
-
EC Number: 207-838-8
-
Molecular Weight: 105.99 g/mol
Physical and Chemical Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical State | White crystalline solid, coarse granules |
| Apparent Density (20°C) | Approx. 1.04 g/cm³ (depending on compaction) |
| Bulk Density | 1.0 – 1.2 g/cm³ (typically 1.1 g/cm³) |
| True Density | 2.53 g/cm³ |
| Boiling Point / Decomposition | Decomposes at high temperature to Na₂O and CO₂ |
| pH (1% aqueous solution) | Approximately 11.4 – 11.6 |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Corrosiveness | Non-corrosive under normal conditions; alkaline and irritating to skin and eyes |
| Chemical Stability | Stable under normal conditions; tends to cake when exposed to moisture |
Applications of Dense Soda
Glass Industry
-
One of the three primary raw materials in glass manufacturing (along with silica and lime)
-
Reduces the melting point of silica and improves molten glass properties
Water Treatment
-
Used to adjust pH and reduce temporary hardness
-
Neutralizes acids and enhances precipitation efficiency
Detergent Manufacturing
-
Used in industrial laundry powders to increase alkalinity and remove hardness ions
-
Enhances the cleaning efficiency of surfactants
Pulp, Paper, and Textile Industries
-
Used for recovery of cellulose fibers and pulp cleaning
-
Controls acidity in bleaching and dyeing processes
Metallurgical and Petrochemical Industries
-
pH regulator in metal extraction processes
-
Alkaline cleaning agent or pH stabilizer in chemical plants
Advantages of Dense Soda
-
Higher bulk density → lower consumption compared to light soda ash
-
Reduced dusting → safer and cleaner handling and storage
-
High thermal and chemical stability
-
Cost-effective and readily available on an industrial scale
-
Compatible with a wide range of industrial systems
Disadvantages of Dense Soda
-
Strongly alkaline → requires care to avoid skin and eye contact
-
Reacts with acids → generates heat and releases CO₂ gas
-
Hygroscopic → absorbs moisture, leading to caking if improperly stored
-
Must be stored in dry conditions, away from acids and moisture sources
Safety and Handling Information
-
GHS Classification: Irritant – H319 (Causes serious eye irritation), H315 (Causes skin irritation)
-
Skin Contact: Use rubber or nitrile gloves
-
Eye Contact: Use safety goggles or face shield
-
Dust Inhalation: Wear filtered respirator masks in confined or dusty areas
-
Packaging: Multi-layer moisture-resistant bags, typically 25 kg or 50 kg
-
Storage Conditions: Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area, away from acids and humidity
-
Transportation: Non-hazardous solid; standard dry cargo classification
Desulfurization Plasticator
Devulcanizer
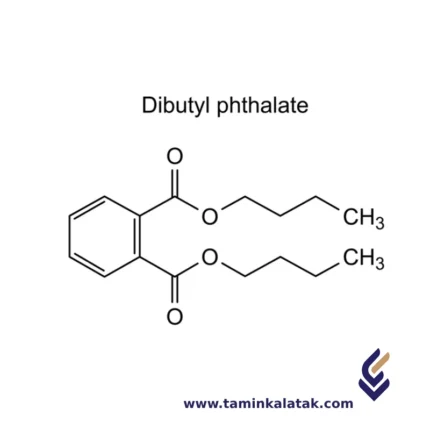
Di Butyl Phthalate (DBP)
- C12H18O4 (Di-n-butyl phthalate)
StructureDi Butyl Phthalate (DBP) is an ester compound composed of a phthalate group and two butyl groups. Its molecular structure consists of a benzene ring (C6H5) attached to a carbonyl group (C=O), which is further connected to two butyl ester groups. Each butyl group consists of a four-carbon chain (C4H9) with a terminal -CH2 group attached to the ester linkage. The two butyl groups are attached to the carbonyl group through ester bonds, making DBP a typical phthalate ester. This structure imparts the chemical its characteristic properties, including its use as a plasticizer in various industrial applications.
PropertiesDi Butyl Phthalate (DBP) is a colorless, oily liquid with a faint, characteristic odor. It has a relatively high boiling point of around 340°C and a low freezing point, making it stable across a wide range of temperatures. DBP is soluble in many organic solvents but is only slightly soluble in water. It is known for its ability to act as a plasticizer, meaning it can increase the flexibility, workability, and durability of plastics, especially polyvinyl chloride (PVC). DBP is also resistant to oxidation and has a relatively low volatility, contributing to its effectiveness in various industrial applications. However, it is considered to have potential health risks, with concerns about its toxicity and environmental impact, leading to increasing regulatory scrutiny.
Applications of Di Butyl Phthalate (DBP)
- Used as a plasticizer in the production of flexible polyvinyl chloride (PVC) products such as flooring, coatings, and electrical cables.
- Commonly found in adhesives, sealants, and paints to enhance flexibility and durability.
- Employed in the manufacturing of personal care products like nail polishes, perfumes, and cosmetics.
- Used in the production of synthetic rubbers and plastics to improve workability and softness.
- Applied in the formulation of some lubricants and coatings for various industrial uses.
Advantages of Di Butyl Phthalate (DBP)
- Improves the flexibility and elongation properties of plastics and other materials.
- Enhances the durability and longevity of products by preventing them from becoming brittle.
- Acts as a stabilizer and dispersant in certain chemical formulations.
- Helps in producing smoother textures in personal care products.
- Cost-effective compared to other plasticizers for certain industrial applications.
Disadvantages of Di Butyl Phthalate (DBP)
- Potential health risks, including endocrine disruption and reproductive toxicity.
- Environmental concerns due to its persistence and potential for bioaccumulation.
- Increasing regulatory restrictions and bans in certain regions due to safety concerns.
- Can migrate out of materials over time, leading to potential exposure in consumer products.
Di Ethanol Amine
Diethanolamine (DEA) is an organic compound containing two hydroxyl (-OH) groups and one secondary amine (-NH-) group.
It belongs to the class of secondary amines and di-alcohols (dialkanolamines), exhibiting both amine and alcohol reactivity.
Due to this dual functionality, DEA acts as a weak base, emulsifier, pH stabilizer, and metal ion complexing agent in numerous industrial formulations.
Molecular Structure:
HO–CH₂–CH₂–NH–CH₂–CH₂–OH
Chemical and Physical Properties
| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Colorless to pale-yellow viscous liquid |
| Odor | Mild ammonia-like odor |
| Molecular Weight | 105.14 g/mol |
| Boiling Point | ~269 °C (at atmospheric pressure) |
| Density (20–25 °C) | 1.097 g/cm³ |
| Solubility | Completely miscible with water, ethanol, and glycerol; insoluble in hydrocarbons |
| pH (1% aqueous solution) | 10.0–11.5 |
| Chemical Nature | Weak base, hygroscopic, non-volatile |
Applications of Diethanolamine (DEA)
1. Detergent, Cosmetic, and Personal Care Industries
-
Active base for the formulation of shampoos, liquid soaps, creams, and lotions
-
pH regulator and stable emulsifier in surfactant systems
2. Oil and Gas Industry
-
Used for acid gas removal (CO₂ and H₂S) in gas sweetening units
-
Acts as a corrosion inhibitor in pipeline and refinery systems
3. Agriculture and Fertilizer
-
Serves as a chelating agent in liquid fertilizers
-
Functions as a pH stabilizer in pesticide and fungicide formulations
4. Paints, Inks, and Resins
-
Co-emulsifier in water-based coatings
-
Improves viscosity, stability, and durability of paints and inks
5. Cement and Construction
-
Used as a Grinding Aid in cement production
-
Enhances workability and compressive strength of concrete under varying temperatures
Advantages
-
Multi-functional and cost-effective across various industries
-
Excellent chemical stability in alkaline media
-
High solubility in aqueous systems
-
Compatible with surfactants, oils, and alcohols
Limitations
-
Irritant to skin and eyes upon direct contact
-
Potential formation of carcinogenic nitrosamines in the presence of nitrites
-
Sensitization risk in long-term exposure, especially in leave-on cosmetic products
-
Requires dose control in food and pharmaceutical-related applications
Safety and Regulatory Information (GHS / SDS)
-
H302: Harmful if swallowed
-
H315: Causes skin irritation
-
H319: Causes serious eye irritation
-
H351: Suspected of causing cancer (IARC Group 2B – limited evidence in humans)
Storage and Handling
-
Store in tightly sealed containers made of polyethylene or stainless steel
-
Keep in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area (10–30 °C)
-
Protect from direct sunlight, heat sources, and oxidizing agents
-
Use chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and adequate ventilation during handling
Summary
Diethanolamine (DEA) is a versatile alkanolamine used extensively in detergents, gas treatment, agricultural chemicals, and resin production.
Its dual functionality as both an amine and an alcohol makes it a valuable intermediate, though it requires strict handling and dosage control due to toxicity and sensitization potential.
Di Ethylene Tri Amine
Diethylenetriamine (DETA) is a trifunctional aliphatic amine (triamine) appearing as a colorless to pale-yellow liquid with a strong ammonia-like odor.
It serves as an epoxy curing agent, chelating agent, and acid gas absorber, making it a key raw material in resin, gas treatment, and specialty chemical industries.
Chemical Structure
-
Molecular Formula: C₄H₁₃N₃
-
Molecular Weight: 103.17 g/mol
-
Structural Formula: (NH₂–CH₂–CH₂)₂–NH
-
IUPAC Name: N′-(2-aminoethyl)ethane-1,2-diamine
-
Chemical Family: Polyamines
Typical Physical and Chemical Properties
| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Clear to light-yellow liquid |
| Odor | Strong, ammonia-like |
| Boiling Point | 207–208 °C |
| Flash Point (closed cup) | 94–98 °C |
| Density (20 °C) | ~0.955 g/cm³ |
| Viscosity (25 °C) | ~2 mPa·s |
| Refractive Index (nD 20 °C) | 1.474–1.476 |
| pH (1% solution) | 11.5–12.0 |
| Water Solubility | Completely miscible |
| Hygroscopicity | Absorbs moisture from air |
Advantages
-
High reactivity with epoxy resins, enabling rapid and efficient curing
-
Functions as a tridentate ligand in metal coordination chemistry
-
Excellent CO₂ and H₂S absorption capacity for gas sweetening applications
-
Highly water-soluble and compatible with polar solvents
-
Economical and widely available in industrial grades
Limitations
-
Strongly corrosive to skin, eyes, and respiratory tissues
-
Hygroscopic – requires moisture-proof packaging and handling
-
May oxidize and discolor on exposure to air and light
-
Heavier-than-air vapors may accumulate in low areas, posing inhalation risks
-
Pungent odor can limit use in enclosed environments
Main Applications
-
Epoxy resin and adhesive systems: curing agent for coatings, composites, and adhesives
-
Coordination chemistry: ligand for forming complexes (e.g., [Co(dien)(NO₂)₃])
-
Oil & gas industry: absorption of CO₂ and H₂S in gas treatment units
-
Additive manufacturing: corrosion inhibitor and lubricant additive
-
Polymer chemistry: precursor for polyamides, polyimides, and specialty resins
Safety and Handling
UN Number: 2079 Hazard Class: 8 (Corrosive) Packing Group: II
GHS Classification:
⚠️ Signal Word: DANGER
Hazard Statements:
-
H302: Harmful if swallowed
-
H312: Harmful in contact with skin
-
H314: Causes severe skin burns and eye damage
-
H317: May cause allergic skin reaction
-
H334: May cause respiratory sensitization
Recommended PPE:
-
Nitrile or butyl rubber gloves
-
Chemical-resistant goggles or face shield
-
Protective clothing
-
Respirator or air filtration system in enclosed spaces
Storage Conditions:
-
Store in tightly closed, corrosion-resistant containers
-
Keep in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area (preferably below 15 °C)
-
Avoid contact with strong acids, oxidizing agents, and moisture
-
Protect from heat and direct sunlight
Summary
Diethylenetriamine (DETA) is a highly reactive, multifunctional amine widely used in epoxy resin curing, gas absorption, and chelation chemistry.
It offers excellent reactivity, solubility, and cost-effectiveness — provided it is handled under controlled, corrosion-safe, and well-ventilated conditions.
Di Iso Nonyl Phthalate (DINP)
StructureDi-Iso-Nonyl Phthalate (DINP) is an organic compound belonging to the phthalate ester family. Its chemical structure consists of a phthalic acid core, where two ester functional groups are attached to iso-nonyl alcohol chains. The phthalic acid backbone is composed of a benzene ring with two carboxylate (-COO) groups positioned at the ortho positions. These carboxylate groups are esterified with branched iso-nonyl groups, which typically contain nine carbon atoms in a varied structural arrangement. The branching in the iso-nonyl chains contributes to DINP's higher molecular weight and lower volatility compared to lower molecular weight phthalates. This structural feature enhances its stability and flexibility when used as a plasticizer in polymers such as PVC. Due to its chemical nature, dinp is hydrophobic, poorly soluble in water, but readily dissolves in organic solvents and plastic materials, allowing it to impart flexibility and durability to a wide range of products.
PropertiesDi-Iso-Nonyl Phthalate (DINP) is a clear, colorless to slightly yellow, oily liquid with a high molecular weight and low volatility. It has a molecular formula of C₂₆H₄₂O₄ and a molecular weight of approximately 418.6 g/mol. DINP is insoluble in water but highly soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, benzene, and other non-polar compounds. It has a boiling point of around 244°C at low pressure and a density of approximately 0.97 g/cm³ at 20°C. DINP is chemically stable, resistant to heat and oxidation, and does not easily evaporate, making it a preferred plasticizer for long-lasting applications. Due to its branched iso-nonyl groups, it provides enhanced flexibility, low migration, and good compatibility with polymers like polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Its low volatility and high permanence make it suitable for applications requiring durability and resistance to leaching.
Applications of Di-Iso-Nonyl Phthalate (DINP)
- Plastics Industry: Used as a plasticizer in polyvinyl chloride (PVC) products such as flooring, cables, and roofing materials.
- Consumer Products: Found in flexible vinyl toys, synthetic leather, footwear, and sporting goods.
- Automotive Industry: Used in car interiors, underbody coatings, sealants, and hoses to improve flexibility and durability.
- Construction Materials: Applied in gaskets, insulation materials, and adhesives.
- Electrical Applications: Enhances flexibility in electrical cables and wire insulation.
- Coatings and Sealants: Used in paints, varnishes, and coatings to improve plasticity and longevity.
Advantages of Di-Iso-Nonyl Phthalate (DINP)
- High flexibility and durability when used in plastics.
- Low volatility and migration, making it ideal for long-term applications.
- Good resistance to heat and oxidation, ensuring stability in high-temperature environments.
- Better environmental performance compared to lower molecular weight phthalates, as it has lower bioavailability and leaching potential.
- Cost-effective and widely available, making it a preferred plasticizer for many industrial applications.
Disadvantages of Di-Iso-Nonyl Phthalate (DINP)
- Potential health concerns as it has been associated with endocrine-disrupting effects and possible reproductive toxicity at high exposure levels.
- Environmental persistence due to its chemical stability, which can lead to accumulation in ecosystems.
- Regulatory restrictions in regions such as the EU and the US, limiting its use in children's toys and childcare products.
- Limited biodegradability, contributing to plastic pollution concerns.
- Possible material compatibility issues with certain polymers or applications requiring ultra-low migration plasticizers.
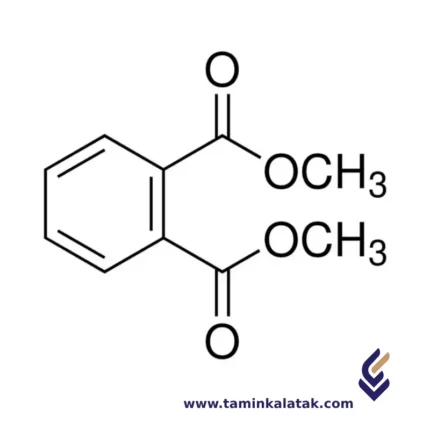
Di Methyl Phthalate (DMP)
StructureThe structure of Dimethyl Phthalate consists of a benzene ring, which is a six-membered carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds. Attached to the benzene ring are two ester groups (-COOCH3), where each ester group consists of a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to a methoxy group (-OCH3). The methoxy groups are positioned at the 2- and 6-positions on the benzene ring, which places the ester groups in the ortho positions relative to each other. The two methoxy groups are connected to the ester groups, giving the molecule its characteristic structure as a phthalate ester. This structure makes Dimethyl Phthalate a relatively simple, but functional compound used primarily as a plasticizer and solvent in various applications.
PropertiesDimethyl Phthalate is a colorless, oily liquid with a faint odor. It has a molecular weight of 194.17 g/mol and a boiling point of 282°C, indicating it is relatively stable at high temperatures. Its melting point is quite low at around -24°C, which makes it a liquid at room temperature. Dimethyl Phthalate is only slightly soluble in water, but it is easily soluble in many organic solvents like alcohol, acetone, and benzene. Its low water solubility and high solvency power make it a useful plasticizer and solvent in various industrial applications. The compound is known for its ability to impart flexibility to plastics and is commonly used in the production of coatings, adhesives, and other materials. Additionally, it is an effective fixative and solvent in fragrances and certain types of pesticides. Despite its utility, Dimethyl Phthalate is considered to be an environmental pollutant and may pose health risks due to its potential as an endocrine disruptor.
Applications of Dimethyl Phthalate
- Plasticizer: Used to increase the flexibility and durability of plastics, particularly in the production of films, coatings, and synthetic materials.
- Fragrance Fixative: Commonly used in perfumes, deodorants, and other personal care products to help the fragrance last longer.
- Solvent: Employed as a solvent in various industrial processes, including in paints, coatings, adhesives, and varnishes.
- Pesticides: Used in some formulations of pesticides and insecticides.
- Pharmaceuticals: Occasionally used in the formulation of certain drug delivery systems.
Advantages of Dimethyl Phthalate
- Improved Flexibility: It enhances the flexibility and workability of plastics, making it essential in manufacturing flexible vinyl and other polymer-based products.
- Effective Fragrance Fixative: In personal care products, it helps extend the longevity of fragrances.
- Solvent Properties: It is a versatile solvent in several industrial applications, improving the solubility of other substances in formulations.
- Low Cost: Dimethyl Phthalate is relatively inexpensive and widely available, making it cost-effective for industrial use.
Disadvantages of Dimethyl Phthalate
- Health Risks: It is considered an endocrine disruptor, potentially affecting hormonal balance and reproductive health when exposure occurs over extended periods.
- Environmental Impact: Dimethyl Phthalate is not easily biodegradable and can accumulate in the environment, potentially harming aquatic life and ecosystems.
- Regulatory Concerns: Due to its potential health and environmental effects, its use is restricted or banned in certain products, particularly those in contact with food and children.
- Toxicity: Prolonged exposure can lead to toxicity, including liver damage and reproductive system disruption, posing risks to both humans and animals.