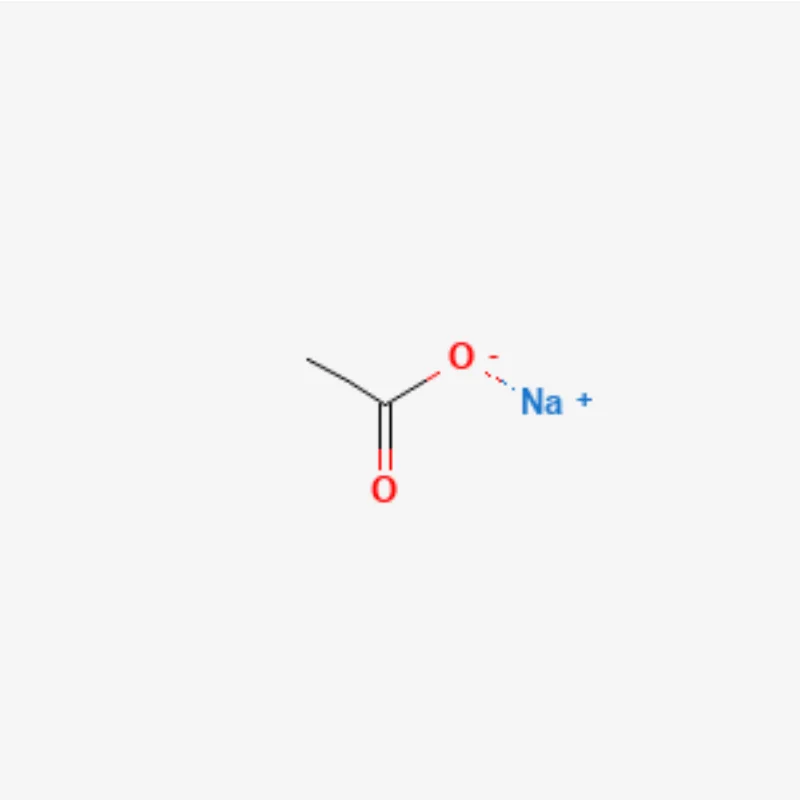
Sodium acetate
Sodium Acetate, with the chemical formula CH₃COONa, is the sodium salt of acetic acid. It appears as a white crystalline powder, odorless or with a mild vinegar-like smell (especially when heated). Sodium acetate is moderately hygroscopic, particularly in its anhydrous form. It is available in two forms: anhydrous and hydrated (commonly the trihydrate form, CH₃COONa·3H₂O).
Structure of Sodium Acetate
Sodium acetate is an ionic compound composed of a sodium cation (Na⁺) and an acetate anion (CH₃COO⁻). The acetate ion consists of a methyl group (CH₃) bonded to a carboxylate group (COO⁻). In the carboxylate group, the double bond between carbon and oxygen exhibits resonance, meaning the negative charge is delocalized over the two oxygen atoms.
Chemical Formula: CH₃COONa
Resonance Structure: O=C–O⁻ ⇄ ⁻O–C=O
Properties of Sodium Acetate
-
Appearance: White crystalline powder
-
Odor: Odorless; may release a vinegar-like smell when heated
-
Solubility: Highly soluble in water; moderately soluble in ethanol (~1.4 g/100 mL)
-
Hygroscopicity: Anhydrous form absorbs moisture from the air
-
Basic Nature: As the salt of a weak acid and strong base (NaOH), its aqueous solution is slightly alkaline (pH ~8–9 for a 0.1 M solution)
-
Melting Point: Anhydrous form decomposes around 324°C; trihydrate melts at ~58°C, releasing water of crystallization
-
Buffering Properties: In combination with acetic acid, it forms a buffer solution effective within a pH range of 4 to 6.5
-
Chemical Behavior: Can release gases such as acetic acid or CO₂ when in contact with strong acids or oxidizing agents
Applications of Sodium Acetate
Food Industry
-
Used as a food additive (E262) for pH regulation, providing a salty/sour taste, and as a preservative
-
Acts as an antibacterial and antifungal agent in some food formulations
Pharmaceutical and Medical
-
Serves as a sodium source in IV injections or dialysis solutions
-
Functions as a buffer component in drug formulations and biological reactions
Textile Industry
-
Used in dye baths to control pH and aid in dye uptake
-
Neutralizes residual acids like H₂SO₄
-
Helps prevent static electricity buildup
Construction Industry
-
Acts as an additive to control pH and improve freeze resistance in concrete (e.g., in sealants)
Laboratory Use
-
Employed in buffer preparation (especially in biochemistry and DNA extraction)
-
Used as a carbon source in bacterial culture media
-
Forms part of extraction buffers in molecular biology
Hand Warmers and Heating Pads
-
Utilizes supersaturated sodium acetate trihydrate solution that releases latent heat (~264–289 kJ/kg) upon sudden crystallization
Other Uses
-
Delays curing in chloroprene rubber production
-
Used in leather tanning and dye manufacturing
Advantages of Sodium Acetate
-
Generally safe for food use as approved by the FDA in regulated amounts
-
Effective buffering capacity
-
Highly compatible with industrial processes
-
Low cost
-
Preservative effect (antimicrobial)
-
Useful in phase-change thermal storage systems
Disadvantages of Sodium Acetate
-
Moderately hygroscopic (especially in anhydrous form) → requires airtight storage
-
Irritant to eyes and skin upon contact
-
Dust inhalation may cause respiratory irritation
-
Ingestion in high amounts may lead to digestive upset or hypernatremia
-
Thermal decomposition at high temperatures may release irritating vapors
-
Caution in patients with kidney or heart issues due to electrolyte imbalances
-
Pharmaceutical forms may contain aluminum or other excipients; special care is needed in premature infants or patients with renal insufficiency
Applications
| Applications | , , , , |
|---|
Sodium acetate
| Chemical name | Chemical formula | CAS number | Grade | Vapor pressure | Physical appearance | Density (at 20°C) | Melting point | Solubility in water |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium acetate | CH₃COONa | 0127-09-03 | Industrial, Laboratory, Pharmaceutical (USP) | Negligible (≈ 0 mmHg at room temperature) | White crystalline powder | 1.528 g/cm³ (anhydrous) | 324°C (anhydrous form, with decomposition) | Complete solution (72 g/100 mL at 20°C for anhydrous form) |
| Sodium acetate | CH₃COONa·3H₂O | 6131-90-4 | (Food grade)، | Negligible (≈ 0 mmHg at room temperature) | White crystalline powder | 1.45 g/cm³ (trihydrate) | 58°C (trihydrate form) | Complete solution (72 g/100 mL at 20°C for anhydrous form) |