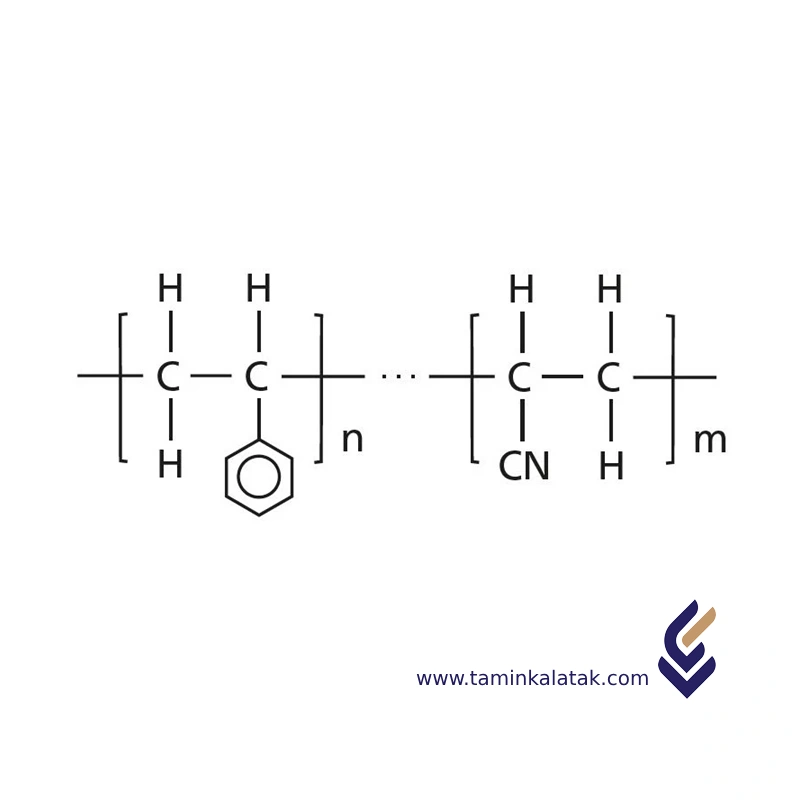
Polymers are made up of very large molecules made up of many repeating units called monomers, which ultimately form this long polymer chain
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or fomed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. As a thermoplastic polymer, polystyrene is in a solid (glassy) state at room temperature but flows if heated above about 100 °C, its glass transition temperature.and also It has wide applications in various industries including packaging, construction, and automotive.
Styrene AcryloNitrile resin (SAN)
SAN polymer, with the chemical name styrene-acrylonitrile copolymer, is a versatile plastic that is characterised above all by its excellent transparency and chemical resistance. In addition, it has high stiffness and good dimensional stability which allow it to be used in demanding environments.
styrene acrylonitrile structure
Styrene acrylonitrile resin (SAN) is a copolymer plastic consisting of styrene and acrylonitrile. The typical composition of SAN polymers is:
- Styrene: ~70–80%
- Acrylonitrile: ~20–30%
The ratio affects the polymer’s properties, such as rigidity, toughness, and chemical resistance. SAN is largely amorphous due to the bulky benzene rings of styrene, which hinder regular packing of polymer chains.
styrene acrylonitrile resin properties
SAN is similar in use to polystyrene. Like polystyrene itself, it is transparent and brittle. The copolymer has a glass transition temperature greater than 100 °C owing to the acrylonitrile units in the chain, thus making the material resistant to boiling water. SAN is known for its excellent tensile and flexural strength, which makes it suitable for structural applications. It resists oils, fats, dilute acids, and alkalis, making it suitable for use in chemical containers and food storage.
styrene acrylonitrile applications
Household Products:
Plastic tumblers, food trays, storage containers
Automotive:
Interior components, knobs, handles, instrument panels
Medical:
Test tubes, Petri dishes, laboratory equipment
Electronics:
Housings, enclosures, transparent electronic parts
Advantages
- High Mechanical Strength
- Ease of Processing
- Lightweight
- Cost-Effective
- Transparency
- Good Electrical Insulation
Disadvantages
- Limited Impact Strength
- Environmental Stress Cracking
- Flammability
- Limited Weatherability
Applications
SAN
| Products | Grade | MFI(g/10 min) | Density (g/mm3) | process method | Applications | MSDS | brochur |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAN | HF80 | At 230°C with a 3.8 kg load: 10 g/10 min | 1.07 | injection molding | Used in parts of refrigerators, electrical components and parts. | ||
| SAN | 310CTR | At 230°C with a 3.8 kg load: 10.0 g/10 min | 1.07 | injection molding | cosmetic containers, mixers, and transparent containers |