Polymers are made up of very large molecules made up of many repeating units called monomers, which ultimately form this long polymer chain
HDPE stands for High-Density Polyethylene, which is one of the most widely used materials in the world and is used in various industries due to its unique properties.
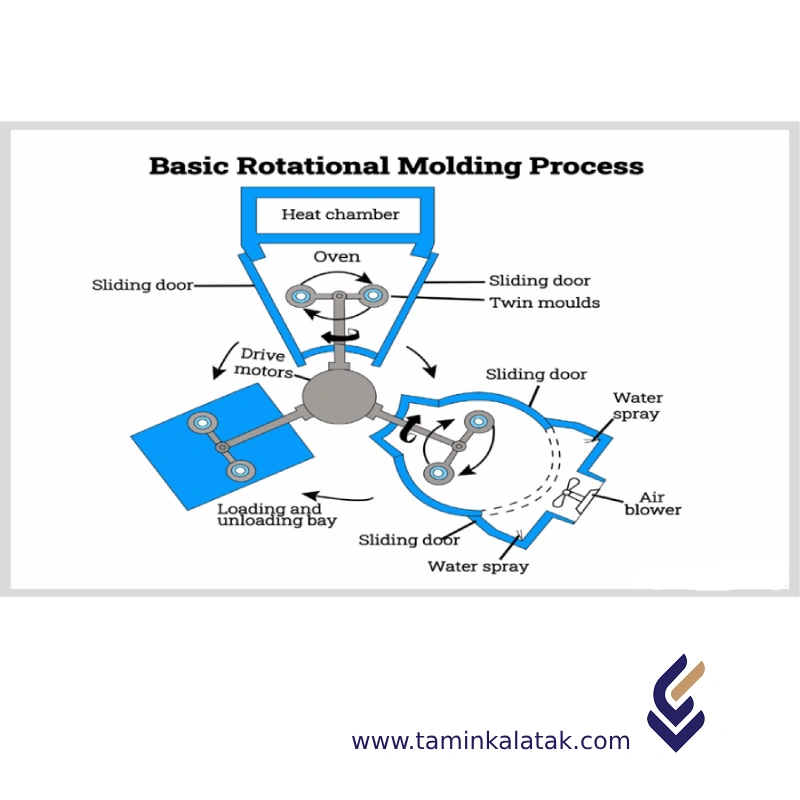
Rotational Molding
The rotational molding process is a straightforward yet effective method. In this technique, a plastic material, typically in powdered form, is placed inside a hollow mold. This mold is usually made of cast aluminum or fabricated from sheet steel. Once sealed, the mold rotates slowly around two axes. Simultaneously, it is heated inside an oven while continuously rotating. As the temperature rises, the plastic powder melts and evenly coats the inner surface of the mold. When the plastic has completely liquefied, the mold is transferred to a cooling station, where it is cooled using air or occasionally a fine mist of water. During this phase, the plastic gradually solidifies and takes its final shape. Once the material has cooled sufficiently and detaches from the mold’s surface, the process is halted, and the finished product is removed from the mold.
Types of rotational molding
Clamshell Rotational Molding
- Uses a single-arm machine with an oven and cooling chamber combined.
- Best for smaller production runs or prototyping.
- Less efficient than multi-arm machines but requires less space.
Rock and Roll Rotational Molding
- Designed for long and narrow products like kayaks and boats.
- The mold rotates on one axis while rocking back and forth on another axis.
- Ideal for making large, elongated parts with uniform wall thickness.
Shuttle Rotational Molding
- Features two arms that shuttle between heating and cooling stations.
- Allows simultaneous molding and cooling, increasing production efficiency.
- Suitable for medium to large-scale manufacturing.
Vertical Rotational Molding
- Uses a vertical rotation system rather than the traditional horizontal axis.
- Provides more control over material distribution.
- Less common but useful for specific applications requiring precise thickness control.
Carousel Rotational Molding
- The most common and efficient type, often with three to four arms.
- Molds move continuously between loading, heating, cooling, and unloading stations.
- Ideal for high-volume production and large-scale manufacturing.
Advantages of rotational molding
- Cost-Effective Tooling – Molds are cheaper compared to injection or blow molding.
- Uniform Wall Thickness – Ensures even material distribution with no weak spots.
- Seamless and Hollow Structures – Produces one-piece parts without welds or joints.
- Design Flexibility – Allows for complex shapes, undercuts, and integrated features.
- Strong and Durable Products – High impact resistance with reinforced corners.
- Wide Range of Materials – Can use polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and nylon.
- Minimal Material Waste – Excess plastic can be recycled and reused.
- Large Part Capability – Ideal for tanks, containers, and oversized plastic products.
- Consistent and Repeatable Process – Ensures uniformity in mass production.
- Eco-Friendly Process – Lower energy consumption and recyclable materials.
Disadvantages of rotational molding
- Longer Cycle Times – Slower process compared to injection or blow molding.
- Higher Material Costs – Limited to specific thermoplastics, which can be more expensive.
- Limited to Hollow Parts – Not suitable for solid or highly detailed small components.
- Lower Precision and Tolerance – Less accuracy in dimensional control compared to injection molding.
- Limited Automation – More labor-intensive, leading to higher production costs for large runs.
- Surface Finish Limitations – May require post-processing for a smooth or polished surface.
- Lower Production Efficiency – Not ideal for high-volume production due to longer cycles.
- Thicker Walls Required for Strength – Thinner-walled parts may lack the necessary strength.
- Cooling Time Can Be Long – Extended cooling periods increase overall production time.
Applications of rotational molding
- Storage Tanks – Water tanks, fuel tanks, and chemical storage containers.
- Automotive Parts – Fuel tanks, air ducts, mudguards, and fenders.
- Industrial Containers – Bins, hoppers, and transport containers.
- Playground Equipment – Slides, climbing structures, and outdoor playsets.
- Furniture – Modern plastic chairs, tables, and decorative items.
- Marine & Boating – Kayaks, canoes, buoys, and dock floats.
- Medical Equipment – Enclosures, casings, and patient support devices.
- Agricultural Products – Feed storage bins, water troughs, and irrigation tanks.
- Recreational & Sports Gear – Helmets, cones, and protective padding.
- Road & Traffic Safety – Barriers, traffic cones, and road markers.
- Consumer Goods – Coolers, toolboxes, and custom cases.
Applications
Rotomolding
| Prodact | Grade | MFI(190oC/ 21.6 kg) | Density (g/cm3) | Process metod | Description / Application | Data Sheet | MSDS | Brochure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDPE ROTOMOLDING | MD38504UV | 3.5-5 g/10 min | 0.938-0.940 | rotational molding | Water Storage Tanks,Fuel Tanks ,Marine Buoys & Floats ,Agricultural Containers ,Chemical Storage Drums ,Playground Equipment ,Road Safety Barriers | MD-38504 is a UV stabilized linear medium density polyethylenee grade with a narrow molecular weight distribution. It is suitable for rotational molding and some injection molding application such as technical parts and closures. Characteristics include: good impact Strength, excellent external and internal surface finish, and is UV stabilized. |