Polymers are made up of very large molecules made up of many repeating units called monomers, which ultimately form this long polymer chain
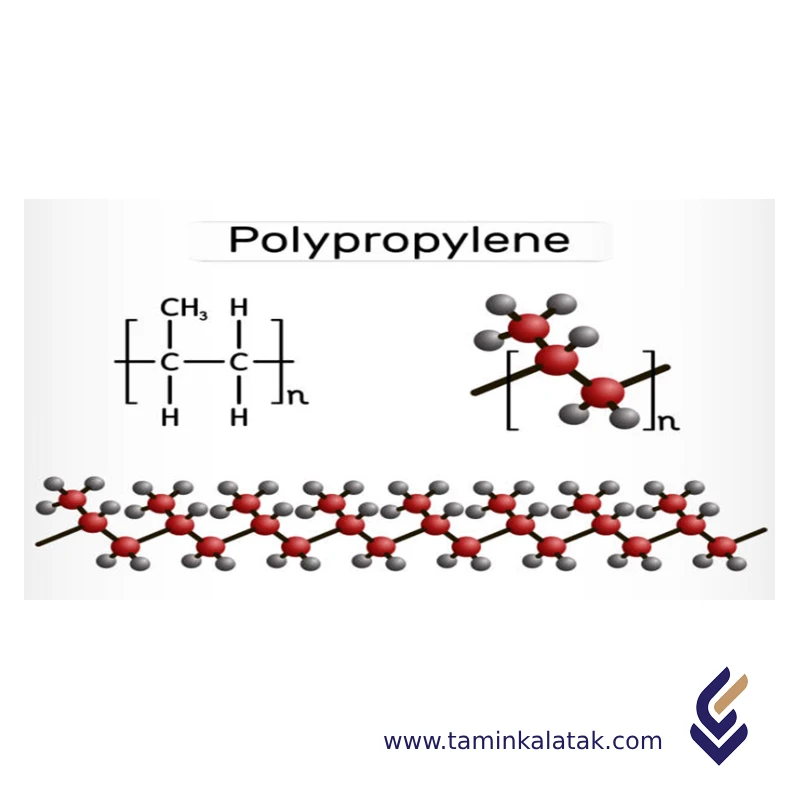
Polypropylene or PP is one of the most widely used thermoplastic plastics in the world. This polymer is made from the monomer propylene and is widely used in various industries due to its unique properties such as high chemical resistance, low density, and heat resistance.
PolyPropylene (PP Chemical)
Polypropylene (PP) is one of the most widely used thermoplastic polymers, known for its high strength, chemical resistance, and versatility. It is used in industries ranging from packaging and textiles to automotive and medical applications.
Structure of Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic polymer derived from propene (C₃H₆) monomers through the polymerization process.
- Molecular Structure:
- Composed of repeating propylene units (C₃H₆) linked together in a chain-like structure.
- Exists in three main forms:
- Isotactic PP – Most commonly used, with all methyl groups (CH₃) aligned on one side of the polymer chain, resulting in high crystallinity and strength.
- Syndiotactic PP – Alternating arrangement of methyl groups, making it more flexible but less crystalline.
- Atactic PP – Random arrangement of methyl groups, leading to an amorphous structure with low strength.
- Polymerization Process:
- Polypropylene is synthesized using Ziegler-Natta catalysts or metallocene catalysts in industrial polymerization reactions.
- It is classified as a thermoplastic, meaning it can be melted and reshaped multiple times without significant degradation.
Properties of Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene possesses a combination of mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties, making it ideal for diverse applications.
1. Mechanical Properties:
✔ High Tensile Strength – Strong yet lightweight, making it ideal for packaging and textiles.
✔ Impact Resistance – Can withstand moderate shocks and impacts.
✔ Good Elasticity & Flexibility – Suitable for films, fibers, and flexible containers.
2. Thermal Properties:
✔ High Melting Point (~160°C – 170°C) – More heat-resistant than polyethylene (PE).
✔ Low Thermal Conductivity – Acts as an insulating material.
✔ Resistant to Temperature Fluctuations – Can handle both hot and cold environments.
3. Chemical Properties:
✔ Resistant to Acids, Alkalis, and Solvents – Does not degrade easily when exposed to chemicals.
✔ Low Water Absorption – Maintains mechanical properties in humid environments.
✔ Good Fatigue Resistance – Ideal for repeated bending applications like hinges.
4. Electrical Properties:
✔ Excellent Electrical Insulation – Used in wires, cables, and electrical components.
5. Environmental Properties:
✔ Recyclable (#5 plastic code) – Can be reused in eco-friendly applications.
✔ UV Sensitivity – Can degrade when exposed to prolonged UV radiation unless treated with stabilizers.
Applications of Polypropylene (PP)
- Packaging Industry
- Textile Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Medical & Healthcare Applications
- Household & Consumer Products
- Industrial Applications
Advantages of Polypropylene (PP)
✔ Lightweight & Strong – Provides durability without adding extra weight.
✔ Excellent Chemical Resistance – Withstands exposure to acids, bases, and solvents.
✔ High Heat Resistance – Can be used in microwaves and hot water applications.
✔ Waterproof & Moisture-Resistant – Ideal for food packaging and textiles.
✔ Recyclable & Eco-Friendly – Can be reused, reducing plastic waste.
✔ Affordable & Cost-Effective – Inexpensive compared to other polymers.
✔ Non-Toxic & Safe – Used in medical and food-grade applications.
Disadvantages of Polypropylene (PP)
✘ UV Degradation – Can become brittle when exposed to sunlight for long periods unless UV stabilizers are added.
✘ Low Impact Resistance at Low Temperatures – Can crack in extremely cold conditions.
✘ Flammability – Easily combustible and requires flame retardants for certain applications.
✘ Difficult to Paint or Glue – Requires special surface treatments for adhesion.
✘ Limited Transparency – Unlike PET, PP is not completely clear.
✘ Environmental Concerns – Though recyclable, it is not biodegradable, leading to plastic waste issues.
Applications
| Applications | , , , |
|---|
Chemical (pp)
| Prodact | Grade | MFI (g/10 min) | Density (g/Cm3) | Process metod | Application / Description | Data Sheet | MSDS | Brochure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene | HP 525 J | 3,00 | 0.9 | Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene (BOPP) Film Production,Thermoforming | BOPP packaging films Solid Phase Thermoforming sheets | |||
| Polypropylene | HP 550 J | 3,00 | 0.9 | Extrusion,Thermoforming | Film yarn, raffia, tapes, and strapping. Baler twines, packaging twines, and ropes. Brush and broom fillings | |||
| Polypropylene | HP 510 L | 6,00 | 0.9 | Extrusion | Baler twines, packaging twines, and ropes Brush and broom fillings,Straws | |||
| Polypropylene | HP 552 R | 25,00 | 0.9 | Extrusion | wipes, tissues , straps | |||
| Polypropylene | HP 564 S | 42,00 | 0.9 | Extrusion | Medical textiles Hygiene products Agricultural covers Geotextiles |