Polymers are made up of very large molecules made up of many repeating units called monomers, which ultimately form this long polymer chain
Engineering polymers are high-performance plastics that exhibit superior mechanical, thermal, chemical, and electrical properties compared to standard commodity plastics.
Poly Tetra Fluoro Ethylene (PTFE / Teflon)
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known by the brand name Teflon, is a high-performance, white, waxy solid polymer that is well-known for its remarkable chemical resistance and low friction properties. PTFE belongs to the family of fluoropolymers and is made from the polymerization of tetrafluoroethylene (TFE) monomers.
Structure
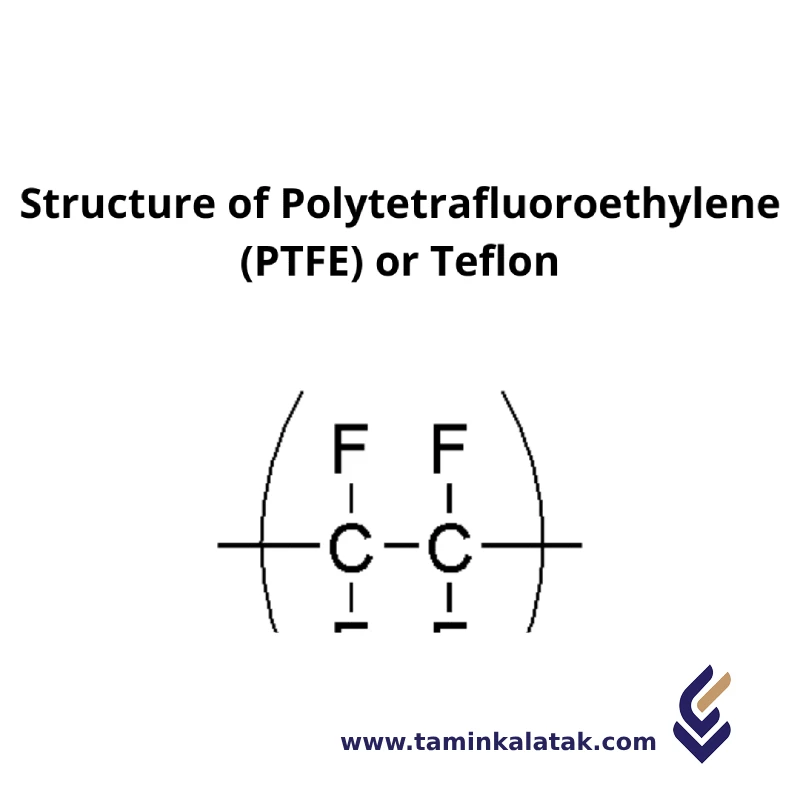
The structure of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, consists of a long chain of carbon atoms bonded to fluorine atoms. Each carbon atom in the polymer backbone is bonded to two fluorine atoms, creating a repeating unit of -C(F2)-C(F2)-. This configuration forms a linear polymer with a highly crystalline and tightly packed structure. The fluorine atoms surround the carbon backbone, creating a dense layer that shields the polymer from interacting with external substances. This structure is responsible for PTFE’s remarkable chemical resistance, non-stick properties, and low friction. The strong carbon-fluorine bonds in the polymer make PTFE highly resistant to heat, chemicals, and electrical conductivity, contributing to its widespread use in harsh environments and various industrial applications.
Properties
Poly tetra fluoro ethylene (PTFE), commonly known as Teflon, has a range of exceptional properties that make it highly suitable for demanding applications. It has outstanding chemical resistance, being virtually unaffected by most chemicals, acids, and solvents, which makes it ideal for use in aggressive environments. PTFE is also highly heat-resistant, with the ability to withstand temperatures ranging from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F) without degrading, maintaining its mechanical properties over a wide temperature range. Additionally, PTFE has a very low coefficient of friction, making it an excellent choice for applications requiring minimal friction, such as bearings, seals, and non-stick coatings. Its non-stick properties are widely known, particularly in cookware, where it prevents food from adhering to surfaces. PTFE is also a good electrical insulator, with excellent dielectric properties, making it ideal for use in electrical cables and insulation. Its low surface energy also provides resistance to staining, dirt, and moisture. However, PTFE can be brittle at low temperatures and requires special processing methods due to its high molecular weight. Despite these challenges, its unique combination of properties, including resistance to wear, high temperatures, and chemicals, makes it indispensable in various industries such as chemical processing, medical devices, and electronics.
Applications of PTFE (Teflon)
- Non-Stick Cookware: Commonly used as a coating for cookware due to its non-stick properties.
- Chemical Industry: Used in gaskets, seals, and lining for pipes and tanks because of its chemical resistance.
- Electrical Insulation: Employed in wires, cables, and electrical components due to its excellent dielectric properties and high-temperature resistance.
- Bearings and Bushings: Used in mechanical applications that require low friction and high durability.
- Medical Devices: Used for catheters, grafts, and other medical devices due to its biocompatibility and chemical inertness.
- Aerospace: Used in seals, lubricants, and fuel systems for high-performance applications in aerospace.
- Automotive: Used in components such as seals and bearings that need to withstand high temperatures and chemical exposure.
- Food Processing: Coatings for machinery and equipment that require non-stick surfaces or resistance to harsh cleaning agents.
Advantages of PTFE (Teflon)
- Chemical Resistance: Virtually inert to most chemicals, acids, and solvents, making it ideal for use in harsh chemical environments.
- High-Temperature Resistance: Can withstand a broad range of temperatures, from -200°C to 260°C, without degrading.
- Low Friction: PTFE has a very low coefficient of friction, reducing wear and improving performance in moving parts.
- Non-Stick Properties: Its non-stick nature makes it useful for cookware and other applications where minimal adhesion is required.
- Electrical Insulation: Excellent electrical insulating properties, ideal for use in cables and electrical components.
- Weather Resistance: Resistant to UV radiation and weathering, suitable for outdoor applications.
- Durability: Long-lasting material with high mechanical strength when reinforced.
Disadvantages of PTFE (Teflon)
- Brittleness at Low Temperatures: PTFE becomes brittle at very low temperatures, making it unsuitable for certain cold environment applications unless reinforced.
- Processing Difficulty: PTFE requires specific processing methods such as sintering and molding, which can be challenging and costly.
- Low Mechanical Strength: Pure PTFE has low mechanical strength and may need reinforcement (e.g., with glass fibers) for structural applications.
- Expensive: PTFE is relatively expensive compared to other polymers, making it less cost-effective for some applications.
- Limited Wear Resistance: While it has low friction, PTFE can wear over time under heavy load-bearing conditions unless enhanced with fillers.
Applications
| Applications | , , , , , |
|---|
Poly Tetra Fluoro Ethylene
| Products | Grade | MFI(g/10 min) | Density (g/Cm³) | Applications | Process method | Data Sheet | MSDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTFE Teflon | Teflon® PTFE 7B | 0.1-0.3 | 215,00 | seals and gaskets,cables and wires,bearings, bushings,pumps, valves | Compression Molding Extrusion Sintering Machining | ||
| PTFE Teflon | Teflon® PTFE 60 | 0.05 - 0.2 | 216,00 | pumps, valves, and reactors that handle aggressive chemicals, acids, and solvents Gaskets and Seals,bearings, bushings,seals, lubricants | Compression Molding Extrusion Sintering Machining |