Polymers are made up of very large molecules made up of many repeating units called monomers, which ultimately form this long polymer chain
Engineering polymers are high-performance plastics that exhibit superior mechanical, thermal, chemical, and electrical properties compared to standard commodity plastics.
PolyPhenylene Sulfide (PPS)
PPS is a high-performance, semi-crystalline engineering thermoplastic known for its excellent thermal and chemical resistance, dimensional stability, and inherent flame retardancy. It is commonly used in demanding applications across automotive, aerospace, electronics, and industrial sectors.
Structure
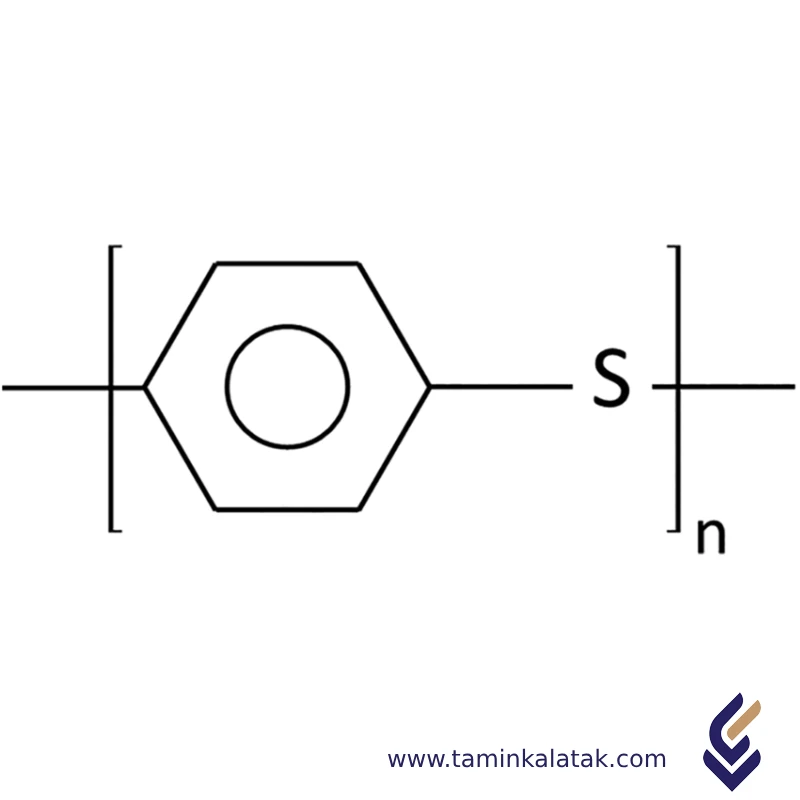
Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) is a semi-crystalline polymer with a repeating backbone structure consisting of alternating benzene rings and sulfur atoms. This structure gives PPS its exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength. The rigid benzene rings contribute to its high stiffness and dimensional stability, while the sulfur atoms provide resistance to heat and oxidation. PPS is inherently flame-retardant due to the presence of sulfur, which limits flammability and smoke generation. Depending on the polymerization method, PPS can be either linear or cross-linked, with linear PPS offering better processability and toughness. The polymer’s highly ordered crystalline regions enhance its strength and resistance to solvents, making it suitable for high-performance applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
Properties
Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) exhibits a unique combination of properties that make it suitable for high-performance applications. It has excellent thermal stability, withstanding continuous use temperatures of up to 260°C, and maintains its mechanical strength even at elevated temperatures. Its inherent chemical resistance allows it to resist strong acids, bases, and solvents without degradation. PPS also has exceptional dimensional stability due to its low moisture absorption, which prevents swelling or warping. The polymer is naturally flame-retardant, with a UL 94 V-0 rating, meaning it self-extinguishes when exposed to flame. Additionally, PPS has high stiffness and rigidity, along with good wear and fatigue resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring long-term durability. Its excellent electrical insulation properties make it a preferred material in electronic and electrical components. Depending on the grade, PPS can be reinforced with glass fibers or other fillers to further enhance its mechanical properties, ensuring it meets the demanding requirements of industries such as automotive, aerospace, and industrial manufacturing.
Applications of Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS)
- Automotive: Fuel system components, coolant system parts, electrical connectors, under-the-hood applications.
- Aerospace: Lightweight structural components, flame-retardant electronic parts.
- Electronics & Electrical: Connectors, sockets, switches, bobbins, high-performance circuit boards.
- Industrial: Chemical processing equipment, pump components, filtration systems, gears, bearings.
- Medical: Sterilization-resistant instruments and surgical tools.
- Household Appliances & Power Tools: High-heat-resistant components, durable mechanical parts.
Advantages of PPS
- High Thermal Stability: Can withstand continuous temperatures up to 260°C.
- Excellent Chemical Resistance: Resistant to acids, bases, solvents, and fuels.
- Dimensional Stability: Low moisture absorption prevents warping or swelling.
- Flame Retardant: UL 94 V-0 rating, meaning it self-extinguishes when exposed to flames.
- High Mechanical Strength: Stiff and rigid, with good wear and fatigue resistance.
- Excellent Electrical Insulation: Suitable for high-performance electronic components.
- Low Friction & Wear Resistance: Ideal for sliding and moving parts.
Disadvantages of PPS
- Brittleness: Pure PPS is brittle and requires reinforcement for improved toughness.
- High Cost: More expensive than some other engineering plastics.
- Processing Complexity: Requires high-temperature molding, increasing production costs.
- Sensitivity to Strong Oxidizers: While chemically resistant, it can degrade in strong oxidizing environments.
Applications
| Applications | , , , , |
|---|
PolyPhenylene Sulfide
| Products | Grade | Density(g/cm³) | Applications | Process method | Data Sheet | MSDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PolyPhenylene Sulfide | Fortron® | 1.65 | electrical housings, chassisblower, pump parts, housings, impellers, flowmeters, sensors | Injection Molding Extrusion Blow Molding | ||
| PolyPhenylene Sulfide | Ryton® | depends on the grade and filler content | electronic connectors, connectors, sockets, relays, switches, bobbins, coils, electronic packaging, encapsulated devices | Injection Molding Extrusion |