Polymers are made up of very large molecules made up of many repeating units called monomers, which ultimately form this long polymer chain
Engineering polymers are high-performance plastics that exhibit superior mechanical, thermal, chemical, and electrical properties compared to standard commodity plastics.
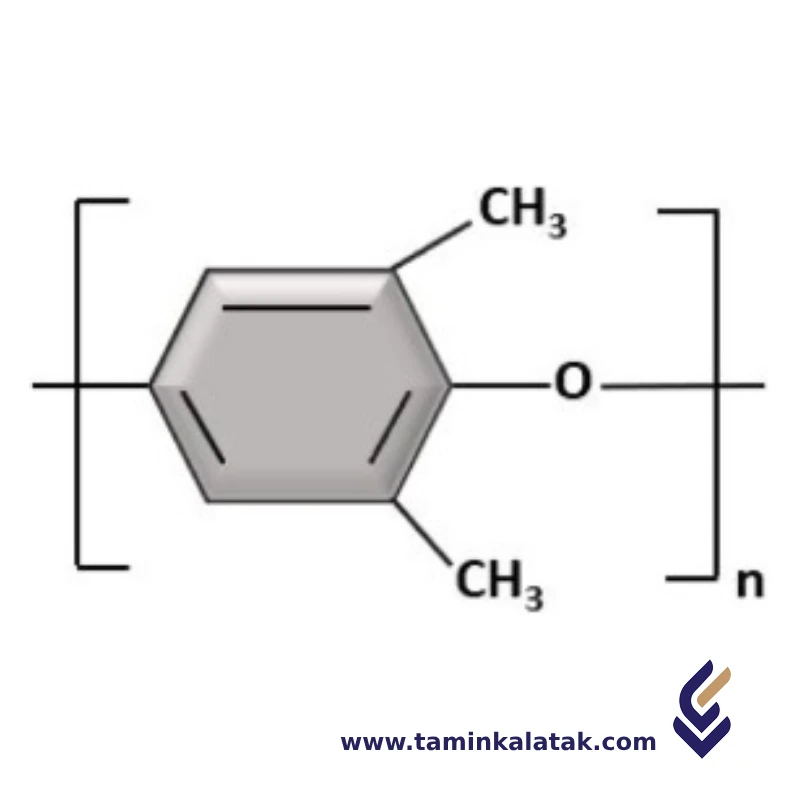
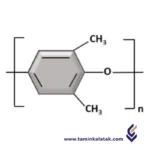
Poly Phenylene Oxide (PPO)
Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO), also known as Polyphenylene Ether (PPE), is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties. It is often blended with other polymers, such as polystyrene (PS), to improve processability and lower costs.
Structure
Poly Phenylene Oxide (PPO) is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic with a repeating unit structure based on the phenylene oxide group. Its molecular structure consists of a backbone of alternating phenylene rings and oxygen atoms, connected via ether linkages. The presence of these ether bonds contributes to its high thermal stability, low moisture absorption, and excellent electrical insulating properties. The polymer is typically synthesized through an oxidative coupling reaction of 2,6-dimethylphenol, using catalysts such as copper-amine complexes. PPO is often blended with polystyrene to improve its processability while retaining its desirable mechanical and thermal properties, making it suitable for applications in electrical components, automotive parts, and household appliances.
Properties
Poly Phenylene Oxide (PPO) exhibits a combination of excellent thermal, mechanical, and electrical properties, making it a widely used engineering thermoplastic. It has high heat resistance, with a glass transition temperature around 210°C, and maintains dimensional stability over a wide temperature range. PPO has low moisture absorption, contributing to its resistance to hydrolysis and making it suitable for applications in humid environments. It is inherently flame-retardant and has excellent electrical insulating properties, which are essential for electronic and electrical applications. The polymer also offers good chemical resistance to acids, bases, and certain solvents. However, in its pure form, PPO is difficult to process due to its high glass transition temperature, so it is often blended with polystyrene to improve its moldability while maintaining its desirable properties. These characteristics make PPO ideal for use in automotive parts, electrical housings, medical equipment, and fluid-handling components.
Applications of Polyphenylene Oxide
- Electrical and electronic components such as connectors, circuit boards, and insulators due to its excellent electrical insulating properties.
- Automotive parts including dashboards, grilles, and under-the-hood components due to its heat resistance and dimensional stability.
- Household appliances such as microwave components, coffee makers, and dishwasher parts because of its thermal stability and moisture resistance.
- Medical equipment including sterilizable trays and devices due to its chemical resistance and ability to withstand repeated sterilization.
- Fluid-handling components like pump housings and valve parts due to its low moisture absorption and chemical resistance.
Advantages
- High heat resistance and dimensional stability.
- Excellent electrical insulating properties, making it ideal for electrical applications.
- Low moisture absorption, enhancing its durability in humid environments.
- Good chemical resistance against acids, bases, and solvents.
- Inherent flame resistance, providing safety benefits in various applications.
- Can be blended with other polymers, such as polystyrene, to improve processability and cost-effectiveness.
Disadvantages
- Pure PPO is difficult to process due to its high glass transition temperature.
- Prone to oxidation and degradation when exposed to UV light without stabilizers.
- Can be expensive compared to other engineering plastics.
- Limited resistance to certain solvents, especially aromatic and chlorinated hydrocarbons.
- Mechanical properties may decrease when blended with polystyrene, depending on the ratio used.
Applications
| Applications | , , , , , |
|---|
Poly Phenylene Oxide (PPO)
| Products | Grade | MFI(g/10 min) | Density (g/Cm3) | APPlications | Process method | Data Sheet | MSDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poly Phenylene Oxide | Noryl™ | 3-40 | 1.06-1.10 | microwave components,dishwasher parts sterilizable trays, diagnostic equipment, instrument housings pump housings, valve components, water filtration | Injection Molding Extrusion Blow Molding Thermoforming | ||
| Poly Phenylene Oxide | Sumikaexcel® | 5-50 | 1.06-1.10 | nstrument panels, battery enclosures, under-the-hood components sterilizable trays, surgical instruments, diagnostic equipment pump housings, valve components, n microwave components, coffee makers,dishwasher parts | Injection Molding Extrusion Blow Molding Thermoforming |