Polymers are made up of very large molecules made up of many repeating units called monomers, which ultimately form this long polymer chain
Engineering polymers are high-performance plastics that exhibit superior mechanical, thermal, chemical, and electrical properties compared to standard commodity plastics.
PolyCarbonates (PC)
Polycarbonate (PC) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its transparency, impact resistance, heat resistance, and dimensional stability. It is widely used in applications requiring toughness and optical clarity.
Structure
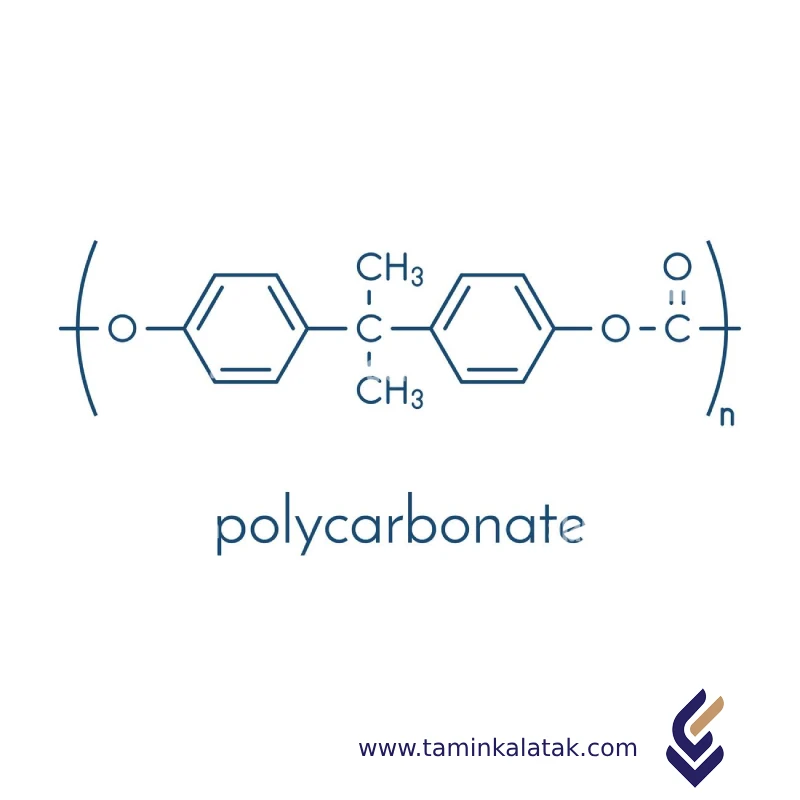
Polycarbonate (PC) is a thermoplastic polymer with a molecular structure characterized by carbonate (-O-(C=O)-O-) groups in its backbone. It is typically synthesized through the reaction of bisphenol A (BPA) and phosgene (COCl₂) or via melt polymerization using diphenyl carbonate. The resulting polymer chain consists of repeating aromatic rings linked by carbonate groups, which contribute to its high impact resistance, optical clarity, and thermal stability. The rigid aromatic rings provide mechanical strength, while the carbonate linkages allow for some flexibility, making polycarbonate both strong and tough. This unique structure gives it excellent transparency, high heat resistance, and good electrical insulation properties, making it suitable for a wide range of applications in industries such as automotive, electronics, and construction.
Properties
Polycarbonate (PC) is known for its exceptional impact resistance, high optical clarity, and excellent thermal stability. It has a high glass transition temperature of around 150°C, allowing it to maintain its shape and mechanical properties under elevated temperatures. PC exhibits good dimensional stability and is resistant to deformation under stress, making it suitable for precision applications. It also possesses inherent flame resistance, with some grades meeting UL 94 V-0 standards. Due to its excellent electrical insulation properties, polycarbonate is widely used in electronic and electrical components. It has moderate chemical resistance but is sensitive to certain solvents and alkaline substances, which can cause stress cracking. Additionally, PC is highly transparent, with light transmission comparable to glass, making it useful in optical applications such as lenses and protective screens. While it offers good weather resistance, prolonged exposure to UV radiation can lead to yellowing and degradation unless stabilized with additives. These properties make polycarbonate a versatile material used in various industries, including automotive, construction, medical, and consumer electronics.
Applications of Polycarbonate (PC)
- Automotive: Headlamp covers, sunroofs, interior panels, dashboards.
- Electronics & Electrical: Laptop housings, smartphone cases, electrical enclosures, connectors.
- Construction: Roofing panels, safety glazing, greenhouses, sound barriers.
- Medical: Surgical instruments, syringe components, medical device housings.
- Consumer Goods: Eyewear lenses, CDs/DVDs, reusable water bottles, protective shields.
- Industrial: Machine guards, safety helmets, bulletproof glass laminates.
Advantages of Polycarbonate (PC)
- High Impact Resistance: Nearly unbreakable, making it ideal for safety applications.
- Optical Clarity: Transparent with light transmission similar to glass.
- Heat Resistance: Withstands high temperatures without deforming.
- Good Electrical Insulation: Suitable for electronic and electrical applications.
- Flame Resistance: Some grades meet UL 94 V-0 standards.
- Lightweight: Much lighter than glass while maintaining high strength.
- Easy to Process: Can be molded into complex shapes.
Disadvantages of Polycarbonate (PC)
- Prone to Scratching: Requires special coatings for improved surface hardness.
- Chemical Sensitivity: Susceptible to stress cracking from certain solvents and chemicals.
- UV Sensitivity: Can yellow and degrade under prolonged UV exposure unless treated.
- Higher Cost: More expensive than other plastics like acrylic or ABS.
- Not Very Flexible: Can be brittle under extreme conditions despite its toughness.
Applications
| Applications | , , , , |
|---|
PolyCarbonates (PC)
| Products | MFI(g/10 min) | Density (g/Cm3) | Applications | Processing Method | Data Sheet | MSDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PolyCarbonates (PC) | 3 – 20 | 1.18 – 1.22 | Headlamp covers, dashboards, sunroofs, Laptop casings, mobile phone housings | Injection Molding Extrusion Blow Molding Thermoforming 3D Printing (FDM & SLS) |