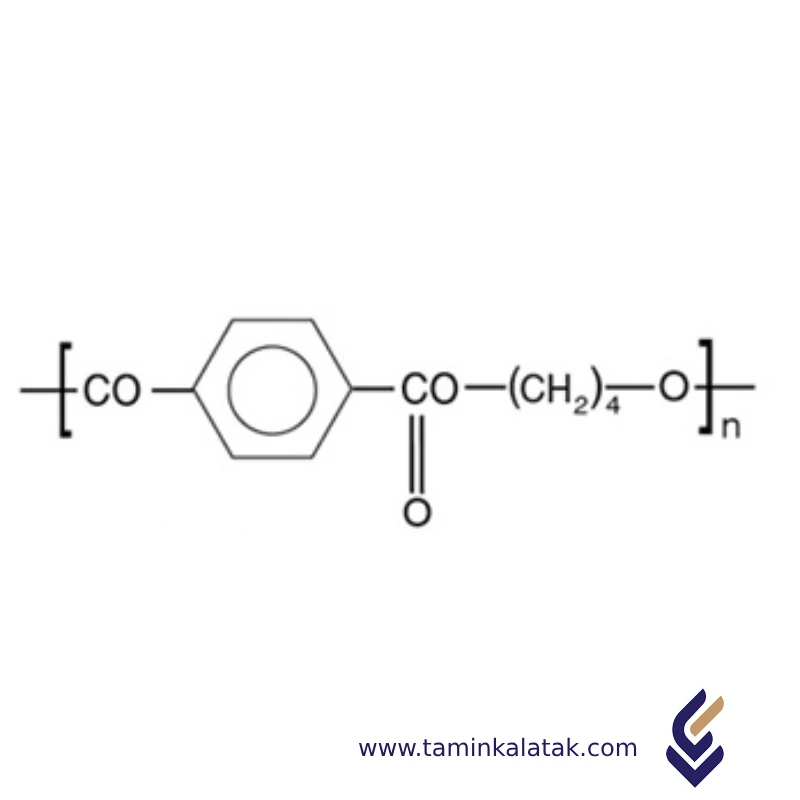
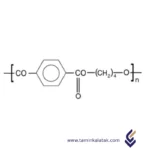
Polymers are made up of very large molecules made up of many repeating units called monomers, which ultimately form this long polymer chain
Engineering polymers are high-performance plastics that exhibit superior mechanical, thermal, chemical, and electrical properties compared to standard commodity plastics.
PolyButylene Terephthalate (PBT)
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) is a high-performance thermoplastic polyester known for its excellent mechanical, electrical, and thermal properties. It is widely used in electrical and automotive industries due to its strength, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability.
Structure
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic polyester composed of repeating ester functional groups in its molecular structure. It is synthesized through the polycondensation of terephthalic acid or dimethyl terephthalate with 1,4-butanediol. The resulting polymer consists of long-chain macromolecules with alternating aromatic terephthalate units and flexible butylene segments. This combination provides a balance of rigidity from the aromatic rings and flexibility from the aliphatic segments. The ester bonds contribute to its thermal stability and chemical resistance, while the linear structure allows for good crystallinity, which enhances its mechanical strength and dimensional stability. The semi-crystalline nature of PBT also contributes to its excellent electrical insulating properties and resistance to moisture absorption, making it widely used in engineering applications.
Properties
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic polyester known for its excellent mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties. It has high tensile strength, stiffness, and impact resistance, making it suitable for demanding engineering applications. PBT exhibits good thermal stability and can withstand high temperatures without significant deformation. Its low moisture absorption ensures dimensional stability, even in humid environments. The polymer is highly resistant to chemicals, including oils, solvents, and fuels, which enhances its durability in harsh conditions. Additionally, PBT possesses excellent electrical insulating properties, making it ideal for electronic and electrical applications. Some grades of PBT are also flame retardant, providing added safety in applications where fire resistance is required. The material is easy to process through injection molding and extrusion, offering versatility in manufacturing various components.
Applications of Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
- Electrical and Electronics: Connectors, switches, circuit breakers, coil bobbins, and insulators.
- Automotive Industry: Headlamp housings, ignition system components, fuel system parts, and sensors.
- Consumer Goods: Appliance housings, power tool casings, keyboard keycaps, and toothbrush bristles.
- Industrial Components: Gears, bearings, pump housings, and mechanical parts requiring high wear resistance.
- Medical Equipment: Certain grades are used in medical devices due to their chemical resistance and stability.
Advantages of Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
- High strength, stiffness, and toughness, providing durability.
- Excellent thermal stability, allowing it to withstand high temperatures.
- Low moisture absorption, ensuring dimensional stability.
- Strong resistance to chemicals, oils, and solvents.
- Good electrical insulation properties, making it ideal for electrical applications.
- Easy to process through injection molding and extrusion.
- Certain grades offer flame retardancy for enhanced safety.
Disadvantages of Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
- Lower impact resistance compared to some other engineering plastics.
- Can degrade under prolonged UV exposure unless stabilized with additives.
- Brittle at very low temperatures, limiting its use in extreme cold environments.
- Slightly lower strength and stiffness compared to Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET).
- Can be prone to hydrolysis under prolonged exposure to hot water or steam.
Applications
| Applications | , , , , |
|---|
PolyButylene Terephthalate (PBT)
| Products | Grade | Mfi (g/10 min) | Density (g/mm3) | Process Metod | Applications | Brochure | MSDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PolyButylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Ultradur B4300G6 | 11 Cm³/min | 1.53 | Windscreen wipers Printed circuit boards Cases Consoles Contact carriers Cover | Injection molding | ||
| PolyButylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Valox 310 | 33 g/min | 1.35 | Electrical components, keyboards, switches | Injection molding | ||
| PolyButylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Arnit TVCh 261 | 18 Cm³/min | 1.51 | Automotive components, electrical connectors and housings | Injection molding |