Poly(butylene succinate-co-adipate) (PBSA) is a biodegradable polyester synthesized from the combination of butylene succinate and butylene adipate. This polymer is designed to reduce environmental impacts and can be produced from either renewable resources or fossil fuels. Due to its favorable mechanical properties and excellent processability, PBSA is widely used as an alternative to conventional plastics in various applications.
Structure
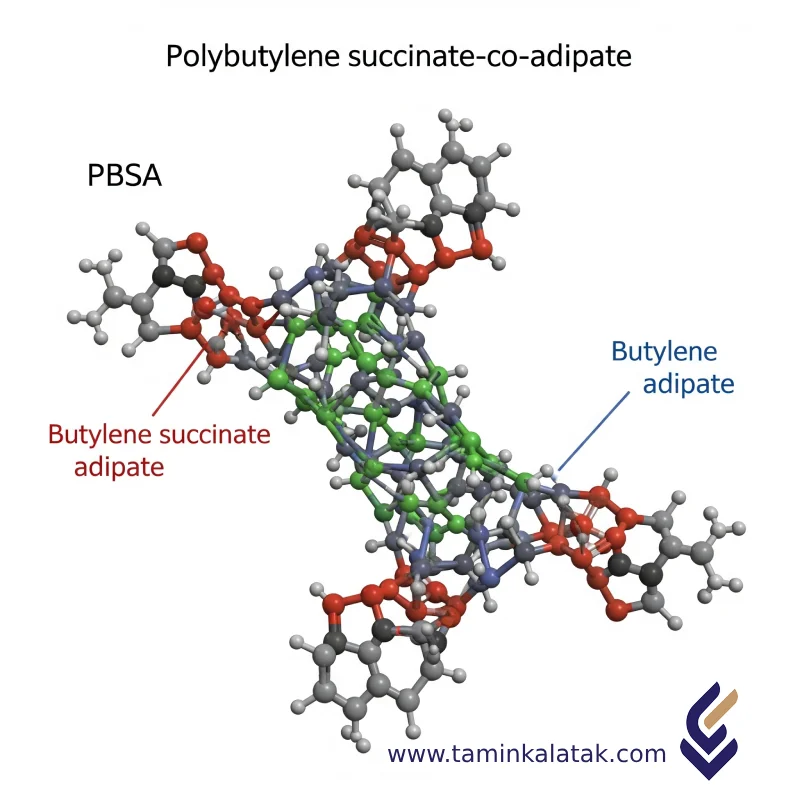
PBSA has a copolymeric structure consisting of butylene succinate and butylene adipate units. This structure enhances flexibility and lowers the glass transition temperature (Tg) of the polymer. The presence of ester linkages in the main polymer chain enables biodegradability.
Properties
-
Biodegradable under industrial composting conditions
-
Higher flexibility compared to poly(butylene succinate) (PBS)
-
Good resistance to stress cracking
-
Excellent processability using extrusion, injection molding, and blow molding methods
-
Compatible with other biodegradable polymers such as PLA and TPS
Applications
Due to its unique combination of properties, PBSA is used in a variety of industries, including:
-
Production of compostable bags
-
Food and agricultural packaging
-
Agricultural films and biodegradable mulches
-
Biodegradable medical products
-
Environmentally friendly disposable containers
Disadvantages
-
Higher cost compared to conventional petroleum-based polymers
-
Reduced mechanical properties in humid environments
-
Requires specific conditions for complete degradation (industrial composting)
Advantages
-
Reduces negative environmental impacts
-
Compatible with conventional plastic manufacturing processes
-
Approved for food contact by international standards (FDA, EU)