Polymers are made up of very large molecules made up of many repeating units called monomers, which ultimately form this long polymer chain
A thermoplastic is a type of plastic polymer that becomes moldable or flexible at a certain temperature and solidifies upon cooling. This property allows it to be repeatedly softened by heating and hardened by cooling without significant chemical change.
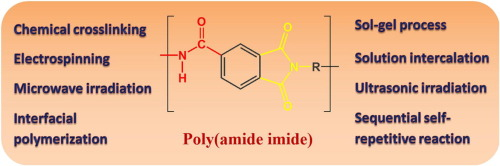
PolyAmide-Imide (PAI)
Polyamide-imide (PAI) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional mechanical, thermal, and chemical resistance properties. It is commonly used in demanding applications requiring strength, wear resistance, and high-temperature stability.
Structure
Polyamide-imide (PAI) is a high-performance thermoplastic polymer characterized by the presence of both amide (-CONH-) and imide (-CO-N-CO-) functional groups in its molecular backbone. The structure consists of aromatic rings connected by these amide and imide linkages, which contribute to its exceptional thermal and mechanical properties. The aromatic nature of PAI enhances rigidity and stability, while the amide groups provide flexibility and processability. The imide groups, known for their high thermal resistance, contribute to PAI’s ability to withstand extreme temperatures without significant degradation. This unique combination of structural elements results in a polymer that exhibits excellent strength, wear resistance, and chemical stability, making it ideal for demanding industrial applications.
Properties
Polyamide-imide (PAI) exhibits a unique combination of high mechanical strength, excellent thermal stability, and outstanding wear resistance, making it one of the most durable engineering thermoplastics. It maintains its mechanical integrity at elevated temperatures, with a continuous service temperature of up to 260°C and short-term exposure tolerances even higher. PAI has exceptional resistance to wear, friction, and creep, allowing it to perform reliably in high-load and high-speed applications. Its chemical resistance is superior, withstanding exposure to most solvents, fuels, and acids. Additionally, PAI demonstrates excellent electrical insulating properties, ensuring stability in electrical and electronic applications. With low thermal expansion and high dimensional stability, it retains its shape and structural performance under extreme conditions. These properties make PAI an ideal choice for aerospace, automotive, industrial, and electronic applications where strength, heat resistance, and durability are critical.
Applications of Polyamide-Imide (PAI):
- Aerospace & Automotive: High-performance bearings, bushings, seals, thrust washers, and gears.
- Industrial Equipment: Pump components, compressor vanes, and wear-resistant parts.
- Oil & Gas Industry: Components for high-pressure and high-temperature environments.
- Electronics & Electrical: High-temperature insulators, connectors, and semiconductor components.
- Medical Devices: Sterilization-resistant parts used in surgical instruments.
- Textile & Printing Industry: Rollers, guides, and wear-resistant coatings.
Advantages of Polyamide-Imide (PAI):
- High Temperature Resistance: Can operate continuously at temperatures up to 260°C (500°F).
- Exceptional Wear & Friction Resistance: Ideal for applications requiring durability and longevity.
- High Mechanical Strength & Stiffness: Retains its structural integrity under heavy loads.
- Good Chemical Resistance: Withstands exposure to fuels, solvents, and acids.
- Excellent Electrical Insulation Properties: Performs well in high-temperature electrical applications.
- Dimensional Stability: Low thermal expansion and minimal deformation under stress.
Disadvantages of Polyamide-Imide (PAI):
- High Cost: More expensive than conventional engineering plastics.
- Difficult to Process: Requires specialized molding or machining techniques due to its high melting point.
- Hygroscopic Nature: Absorbs moisture, which can affect dimensional stability in humid environments.
- Brittle Compared to Some Polymers: While strong, it can be prone to cracking under high impact.
Applications
| Applications | , , , , |
|---|
PolyAmide-Imide (PAI)
| Products | MFI (g/10 min) | Density (g/Cm3) | Process Method | Applications | Data Sheet | MSDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PolyAmide-Imide (PAI) | Very Low MFI | 1.41–1.46 | njection Molding Compression Molding Extrusion Powder Sintering Solution Casting | Engine components, bushings,Bearings, gears, seals |