N- Hexane
n-Hexane is a saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon belonging to the alkane family, consisting of a straight carbon chain. In its pure form, it is a colorless liquid with a mild odor, high volatility, and extreme flammability. It is mainly obtained from the distillation of light naphtha fractions and crude oil derivatives.
n-Hexane is one of the most widely used non-polar organic solvents in various industries, particularly in chemical, food, pharmaceutical, and laboratory processes.
Chemical Formula and Structure of n-Hexane
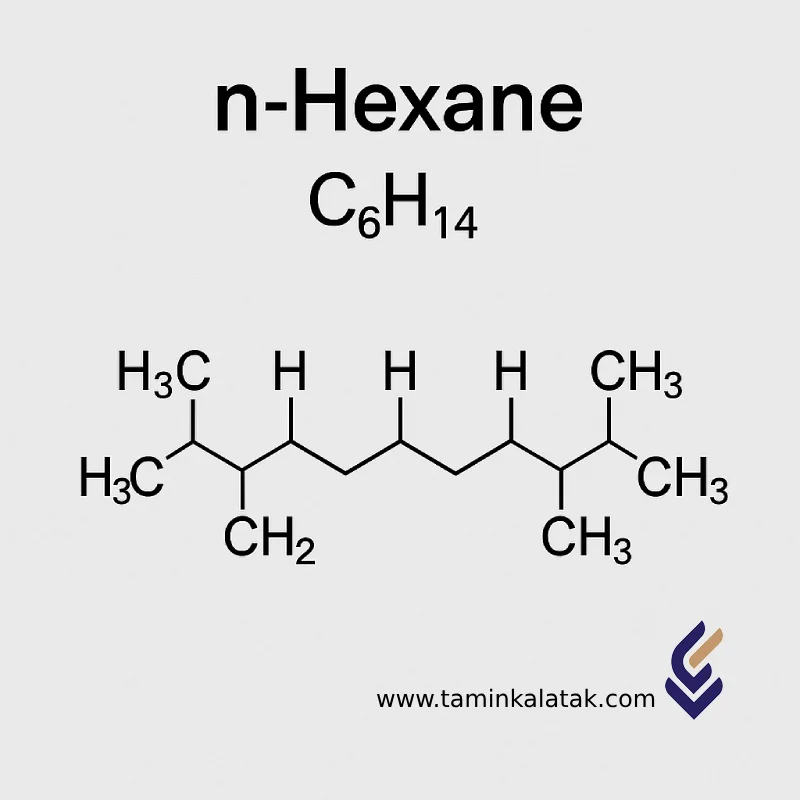
The molecular formula of n-Hexane is C₆H₁₄, and its molar mass is 86.18 g/mol.
Its structure consists of a linear chain of six carbon atoms connected by single bonds, each carbon atom being saturated with hydrogen atoms.
The structural formula is represented as CH₃–(CH₂)₄–CH₃.
The IUPAC name of the compound is Hexane. For the linear isomer, the prefix “n-” (normal) is added, making it n-Hexane.
It is one of several hexane isomers, along with 2-methylpentane and 3-methylpentane, which are also found in industrial hexane mixtures.
Physical and Chemical Properties of n-Hexane
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Colorless liquid with a mild, gasoline-like odor |
| Boiling point | 68.7 °C |
| Kinematic viscosity | 0.31 cP at 25 °C |
| Water solubility | Very low; approximately 9.5 mg/L at room temperature |
| Flash point | –22 °C (highly flammable) |
| Log P (octanol/water partition coefficient) | 3.9–4.1, indicating high lipophilicity and strong affinity for organic phases |
Industrial Applications of n-Hexane
n-Hexane is one of the most common non-polar organic solvents used in various industries:
Food Industry
-
Used for extraction of vegetable oils from seeds such as soybean, canola, cottonseed, and sunflower.
-
Applied in fat separation during food processing (industrial scale only — residual solvent must be completely removed).
Pharmaceutical and Chemical Industries
-
Used as a solvent in the synthesis of pharmaceutical compounds.
-
Extraction of bioactive compounds from plants.
-
Washing and crystallization of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
Rubber and Adhesive Industries
-
Acts as a diluent for industrial adhesives.
-
Solvent for rubber, elastomeric polymers, and certain resins.
Electronics and Laboratory Applications
-
Used as a surface cleaner for sensitive electronic components.
-
Employed for glassware cleaning under controlled, well-ventilated conditions.
Advantages of n-Hexane
-
Excellent solvent power for non-polar organic compounds such as oils, fats, and resins.
-
Rapid evaporation and high volatility, enabling quick drying of surfaces.
-
Wide availability and relatively low cost on an industrial scale.
-
Colorless and low-odor at low concentrations.
-
Leaves minimal residue upon complete evaporation.
Disadvantages of n-Hexane
Despite its advantages, n-Hexane has significant drawbacks that must be carefully managed in industrial and laboratory use:
-
Highly flammable — vapors can easily ignite at room temperature with even small sparks.
-
Neurotoxic (neurotoxicant) under chronic exposure, especially in occupational settings — may cause peripheral polyneuritis, muscle weakness, and numbness in hands and feet.
-
High environmental hazard in case of spillage or improper disposal; can contaminate soil and surface water.
-
Very low miscibility with water, making removal from aqueous environments difficult.
-
Potential for bioaccumulation with prolonged environmental exposure.
Safety and Storage of n-Hexane
GHS Hazard Classification:
-
H225: Highly flammable liquid and vapor
-
H336: May cause drowsiness or dizziness
-
H304: May be fatal if swallowed and enters airways
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
-
Nitrile gloves, safety goggles, half-face respirator with organic vapor filter (A-type), and solvent-resistant lab coat.
Ventilation:
-
Mandatory — must be used in a chemical fume hood or well-ventilated area.
Safe Storage:
-
Store in metal or HDPE solvent-resistant containers, tightly sealed.
-
Keep in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area, away from heat sources, flames, sparks, and direct sunlight.
Emergency Measures:
-
In case of spillage, cover the area with absorbent material (e.g., sand, vermiculite), and ensure immediate ventilation.
-
Skin and eye contact: Rinse immediately with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes.
-
Ingestion: Do not induce vomiting; seek immediate medical attention.
Applications
| Applications | , , , |
|---|
N- Hexane
| Products | Grade | Vapor pressure | Physical appearance | Solubility in water | Melting point | Density (at 20°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n-Hexane | ACS grade / HPLC grade / Industrial grade | ~160 mmHg | Clear, colorless liquid with a mild gasoline-like odor. | Very low, about 9.5 mg/L at 25°C | -95 °C | 0.660 – 0.673 g/cm³ |