Polymers are made up of very large molecules made up of many repeating units called monomers, which ultimately form this long polymer chain
A compound is a polymer blend mixed with additives, fillers, and reinforcements to achieve specific properties for end-use applications. A masterbatch is a concentrated mixture of additives or pigments in a carrier resin, used to enhance plastics without altering their base properties.
Melamine/ Formaldehyde resins (MF)
Melamine-formaldehyde (MF) resins are thermosetting polymers created by the polymerization of melamine and formaldehyde. They are widely used due to their excellent heat resistance, hardness, chemical resistance, and durability.
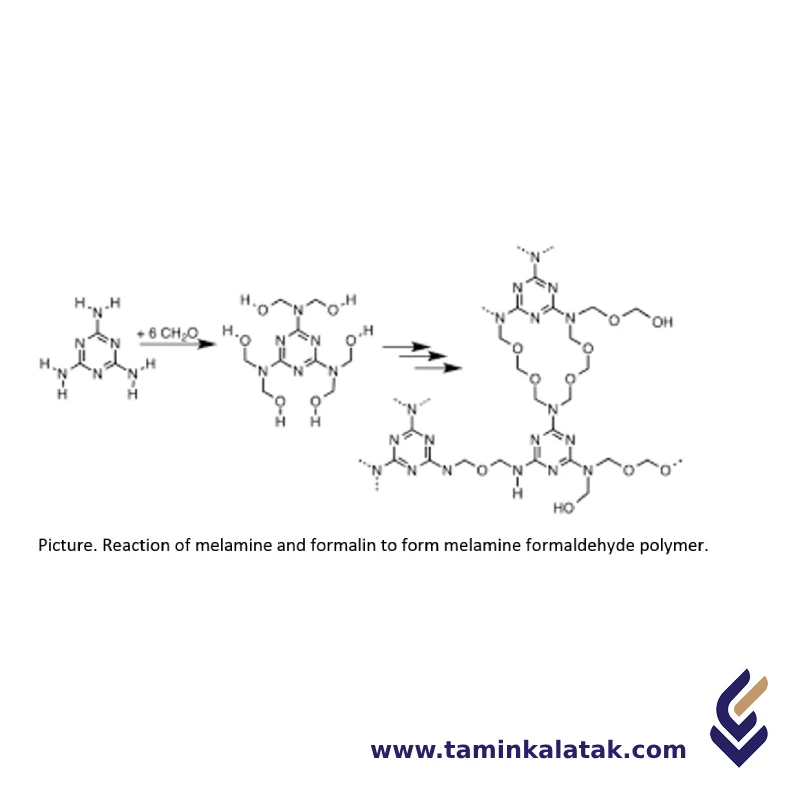
Structure Melamine/ Formaldehyde resins
Melamine-formaldehyde (MF) resins have a highly cross-linked polymeric structure formed through the polycondensation reaction of melamine and formaldehyde. Initially, melamine, a triazine-based compound with three amino groups, reacts with formaldehyde to form methylol derivatives. These methylol groups then undergo further condensation, leading to the formation of methylene and ether linkages, resulting in a rigid, three-dimensional network. This cross-linked structure is responsible for the resin’s excellent thermal stability, hardness, and chemical resistance. The final polymer is a thermoset material, meaning it does not soften upon heating and maintains its structural integrity even under high temperatures and harsh environmental conditions.
Properties Melamine/ Formaldehyde resins
Melamine-formaldehyde resins possess a unique combination of properties that make them highly valuable in various applications. They exhibit excellent hardness and scratch resistance, ensuring durability in high-wear environments. These resins are known for their exceptional heat resistance, withstanding elevated temperatures without losing their structural integrity. They also have good chemical and moisture resistance, making them suitable for applications exposed to water and harsh chemicals. Additionally, MF resins provide excellent electrical insulation, which is crucial for electrical and electronic components. Their ability to form a highly cross-linked network results in a rigid and dimensionally stable material, making them ideal for laminates, coatings, and molded products. Despite their many advantages, they tend to be brittle and cannot be remelted or reshaped due to their thermosetting nature.
Applications of Melamine/Formaldehyde Resins (MF)
- Laminates – Used in high-pressure laminates (HPL) for furniture, countertops, and flooring.
- Molded Products – Common in dinnerware, kitchenware, electrical components, and buttons.
- Wood Adhesives – Used in plywood, particleboard, and other composite wood products.
- Surface Coatings – Provides protective and decorative finishes for paper, textiles, and metals.
- Automotive & Aerospace – Used for heat-resistant components due to its durability.
- Electrical Insulation – Applied in circuit boards and insulating materials for electrical appliances.
Advantages of Melamine/Formaldehyde Resins (MF)
- High heat resistance and retains shape under high temperatures.
- Excellent hardness, scratch resistance, and durability.
- Resistant to water, chemicals, and stains, making it suitable for harsh environments.
- Provides good electrical insulation, used in electrical components.
- Can be molded into complex shapes with a smooth finish.
Disadvantages of Melamine/Formaldehyde Resins (MF)
- Brittle nature, prone to cracking under heavy impact.
- Non-recyclable due to its thermosetting structure.
- May release small amounts of formaldehyde, which can be a health concern.
- Higher cost compared to urea-formaldehyde resins.
- Difficult to repair or modify once fully cured.
Applications
| Applications | , , , , , |
|---|
Melamine/ Formaldehyde resins (MF)
| Products | Viscosity(mPa.s) | Density (g/Cm³) | Applications | Data Sheet | MSDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Melamine formaldehyde resins | 100-500 | 1.5-1.8 | Laminates Molded Products Wood Adhesives Surface Coatings Automotive and Aerospace Components Electrical Insulation Textile and Paper Treatment |