Polymers are made up of very large molecules made up of many repeating units called monomers, which ultimately form this long polymer chain
A compound is a polymer blend mixed with additives, fillers, and reinforcements to achieve specific properties for end-use applications. A masterbatch is a concentrated mixture of additives or pigments in a carrier resin, used to enhance plastics without altering their base properties.
Maleic Anhydride Grafted PP
Maleic Anhydride Grafted Polypropylene (MAH-g-PP) is a modified polypropylene (PP) in which maleic anhydride (MAH) is grafted onto the PP backbone through a reactive extrusion or chemical grafting process. This modification enhances the compatibility of PP with polar materials, making it widely used as a compatibilizer, coupling agent, and adhesion promoter in various applications.
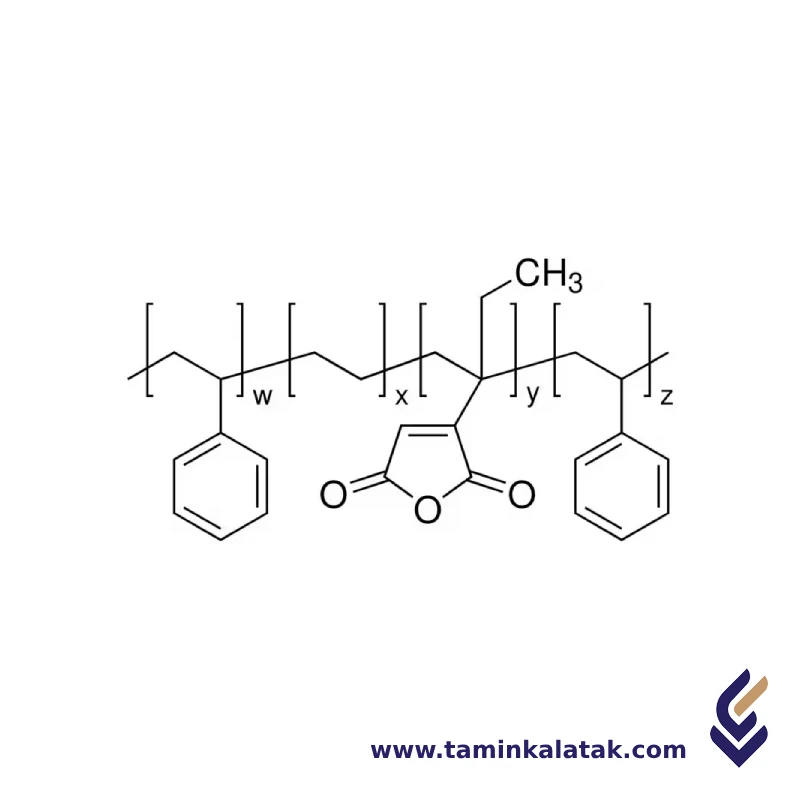
Structure Maleic Anhydride Grafted PP
Maleic anhydride grafted polypropylene (MAH-g-PP) consists of a polypropylene backbone with randomly grafted maleic anhydride functional groups. The polypropylene provides the non-polar, hydrophobic character typical of polyolefins, while the maleic anhydride groups introduce polar functionality, allowing interaction with other polar materials. The grafting process occurs through a reactive extrusion method, where maleic anhydride and a free radical initiator, such as peroxide, create active sites on the polypropylene chains, leading to covalent bonding of the maleic anhydride units. The resulting structure retains the mechanical and thermal properties of polypropylene while enhancing its compatibility with fillers, glass fibers, polar polymers, and other materials. The grafted maleic anhydride groups, typically in a low concentration, are distributed along the polymer chain and can form hydrogen bonds or covalent interactions with hydroxyl, amine, or carboxyl functional groups in other materials, making it highly effective as a coupling agent and adhesion promoter.
Properties Maleic Anhydride Grafted PP
Maleic anhydride grafted polypropylene exhibits a combination of properties from both polypropylene and maleic anhydride functionality. It retains the inherent characteristics of polypropylene, such as lightweight nature, good mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, while gaining enhanced compatibility with polar materials due to the presence of grafted maleic anhydride groups. This modification improves interfacial adhesion in composites, leading to better dispersion of fillers, reinforcement with glass fibers, and stronger bonding in polymer blends. It also increases surface polarity, making the material more suitable for adhesion, coatings, and compatibilization with engineering plastics like nylon and PET. The grafted maleic anhydride groups can interact with hydroxyl, amine, or carboxyl functional groups, improving overall processability and performance in applications where polypropylene alone would have poor adhesion. Additionally, it maintains good impact resistance, weatherability, and processability, making it a versatile material for various industrial applications, including automotive, packaging, and fiber-reinforced composites.
Applications Maleic Anhydride Grafted PP
- Compatibilizer in polymer blends such as polypropylene with nylon (PA), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)
- Coupling agent in glass fiber-reinforced polypropylene composites for enhanced mechanical strength
- Adhesion promoter in coatings, paints, and hot melt adhesives
- Surface modifier in multilayer films and packaging to improve barrier properties and adhesion
- Filler and reinforcement enhancer for mineral-filled polypropylene composites
- Automotive components such as bumpers, dashboards, and under-the-hood parts for improved durability and impact resistance
- Pipe coatings and wire insulation for better adhesion and performance
Advantages Maleic Anhydride Grafted PP
- Enhances compatibility between non-polar polypropylene and polar materials
- Improves adhesion to fillers, fibers, and other polymers
- Increases mechanical properties such as tensile strength and impact resistance in composites
- Retains the lightweight and processable nature of polypropylene
- Improves the dispersion of fillers, leading to better structural performance
- Provides better thermal and chemical resistance compared to unmodified polypropylene
Disadvantages Maleic Anhydride Grafted PP
- Slight reduction in thermal stability due to grafting modifications
- Can introduce brittleness in some formulations if the grafting level is too high
- Processing conditions need to be carefully controlled to prevent degradation
- Higher cost compared to regular polypropylene due to the additional modification process
Applications
| Applications | , , , |
|---|
Maleic anhydride grafted PP
| Products | MFI(g/10 min) | Density (g/Cm3) | Process method | Applications | Data Sheet | MSDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| grafted PP | 1-10 | 0.89-0.91 | Reactive Extrusion Solution Grafting Solid-State Grafting | Compatibilizer for Polymer Blends Glass Fiber-Reinforced Composites Automotive Parts Adhesives and Coatings |