Isopropyl Alcohol
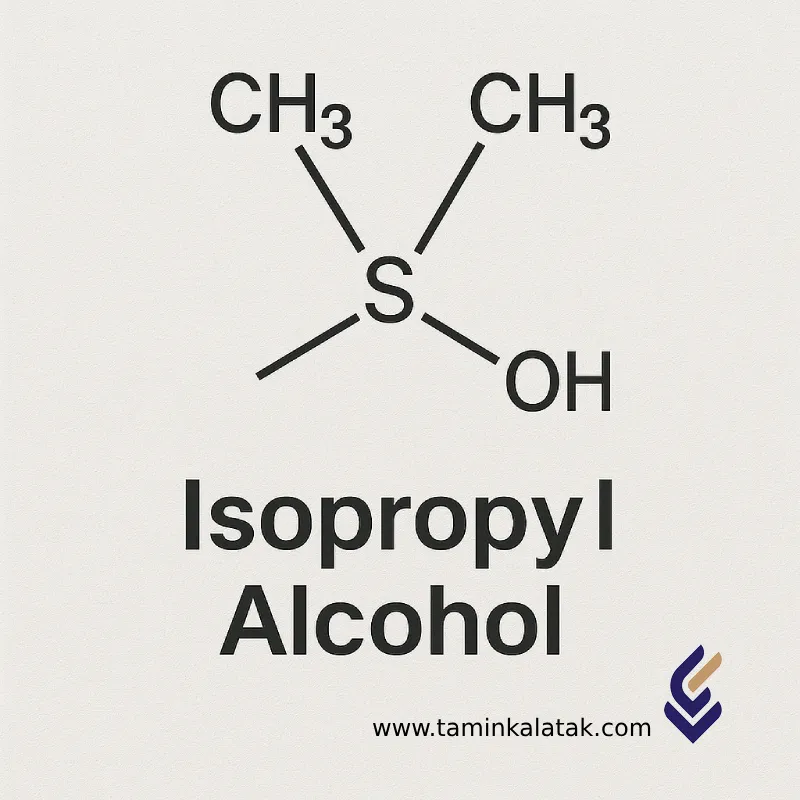
Isopropyl Alcohol (Isopropanol or 2-Propanol) is an organic compound from the alcohol family with the chemical formula C₃H₈O or CH₃CHOHCH₃. It is classified as a secondary alcohol and appears as a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a strong, characteristic odor.
Due to its antiseptic properties, high solvency, rapid evaporation, and compatibility with various substances, isopropyl alcohol is widely used across medical, hygienic, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, chemical, electronic, and printing industries.
Chemical Structure of Isopropyl Alcohol
-
Molecular formula: C₃H₈O
-
IUPAC name: Propan-2-ol
-
Structural formula: CH₃–CHOH–CH₃
-
Type of alcohol: Secondary alcohol
-
Molecular weight: 60.10 g/mol
The hydroxyl group (–OH) in this compound is attached to the second carbon atom, distinguishing it from other simple alcohols such as ethanol or 1-propanol (n-propanol).
Physical and Chemical Properties
Isopropyl alcohol possesses a set of physical and chemical properties that make it particularly suitable for industrial and medical use:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Odor | Sharp, alcoholic, characteristic |
| Boiling point | 82.6 °C |
| Flash point | 12 °C – highly flammable |
| Refractive index (20 °C) | 1.377 |
| Common grades | 70% (medical), 99% (industrial, laboratory) |
| pH (aqueous solution) | Neutral to slightly acidic (~6) |
Applications of Isopropyl Alcohol
1. Medical and Disinfection Uses
-
Used as a disinfectant for skin, hands, medical instruments, and hard surfaces before injections or surgeries
-
Formulated in alcohol swabs, sanitizing sprays, hand gels, and skin prep solutions
-
Effective against a broad spectrum of bacteria, viruses, and fungi at concentrations of 60–80%
2. Cosmetics and Personal Care
-
Serves as a solvent base in toners, makeup removers, aftershaves, body sprays, and perfumes
-
Provides fast-drying properties without oily residue
-
Helps regulate viscosity and enhance microbial stability in formulations
3. Electronics and Optics
-
Functions as a residue-free cleaner for electronic boards, chips, connectors, and precision instruments
-
Cleans optical lenses, sensors, and glass surfaces
-
Removes grease, oil, and dust without water
4. Laboratory and Chemical Synthesis
-
Acts as a universal solvent in organic reactions, solution preparation, and laboratory glassware cleaning
-
Used as an intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and fragrances
-
Serves as a drying agent in sample preparation for microscopy
5. Printing and Ink Industry
-
Functions as a co-solvent in printing inks and solvent-based formulations
-
Enhances ink evaporation rate for quick drying and reduced smudging
-
Adjusts viscosity and improves adhesion to print surfaces
Industries Utilizing Isopropyl Alcohol
-
Electronics Industry
-
Cosmetics and Personal Care
-
Medical and Healthcare Sector
-
Chemical Manufacturing
-
Printing and Packaging
-
Pharmaceutical Industry
Advantages of Isopropyl Alcohol
-
Rapid evaporation without leaving grease or residue
-
Excellent solvent power for a wide range of organic and inorganic compounds
-
Antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal activity at appropriate concentrations
-
Effective as both diluted (70%) and pure (99%) solutions
-
Compatible with materials such as glass, metals, ceramics, and many plastics
-
Non-corrosive under most conditions
-
Chemically stable under normal storage conditions
Disadvantages of Isopropyl Alcohol
-
Highly flammable – must be stored in sealed containers, away from heat sources and with proper ventilation
-
Inhalation of vapors may cause headache, dizziness, respiratory irritation, or nausea
-
Repeated skin contact may result in dryness, itching, or mild irritation
-
Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents (e.g., permanganates, peroxides)
-
Not suitable for ingestion or injection – improper use can be toxic and dangerous
Safety and Storage of Isopropyl Alcohol
Isopropyl alcohol (C₃H₈O) is one of the most commonly used solvents in pharmaceutical, cosmetic, hygienic, and chemical industries. However, despite its extensive use, strict safety and storage measures are required to ensure safe handling.
Safety Guidelines:
-
Highly flammable; its vapors can form explosive mixtures with air
-
Avoid working near open flames, sparks, or heat sources
-
May cause mild to moderate irritation upon skin or eye contact; prolonged exposure can dry out the skin
-
Inhalation in poorly ventilated spaces may lead to headache, dizziness, or nausea
Storage Conditions:
-
Store in tightly sealed metal or chemical-resistant plastic containers with proper labeling
-
Keep in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight
-
Avoid exposure to oxidizing agents, heat, and open flames
-
Maintain in shaded environments to ensure product stability and safety
Isopropyl Alcohol
| Products | Chemical formula | CAS number | Grade | Solubility in water | Vapor pressure | Melting point | Density (at 20°C) | Physical appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isopropyl Alcohol or 2-Propanol | C₃H₈O یا CH₃–CHOH–CH₃ | 67-63-0 | Industrial (99%), Medical (70%), Laboratory (≥99.5%) | Completely soluble (completely miscible with water in all proportions) | 33 mmHg (approximately 4.4 kPa) | -89°C | 0.785 g/cm³ | Clear, colorless liquid with a characteristic, penetrating odor. |