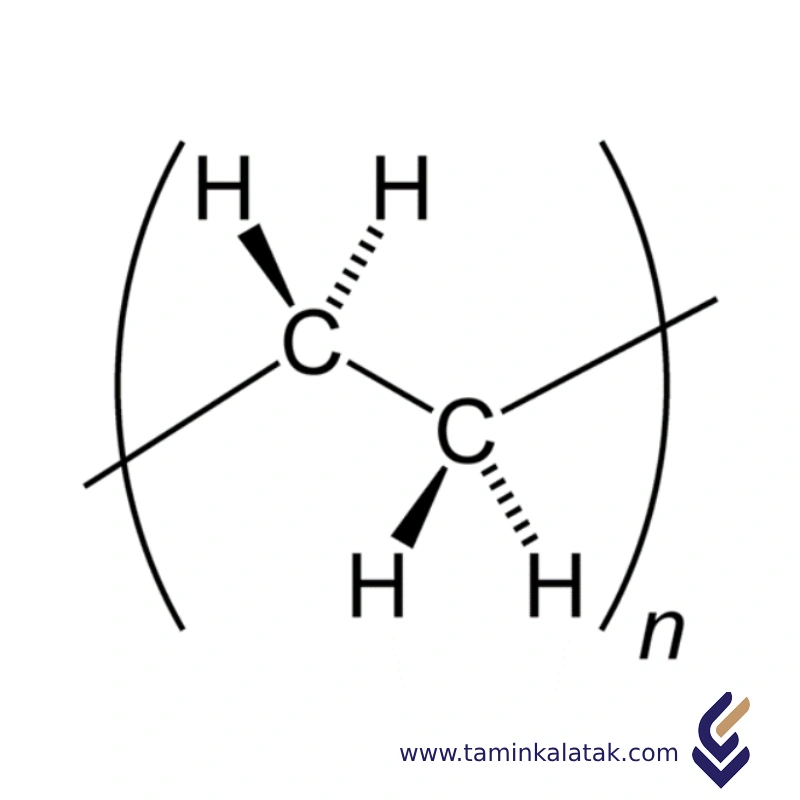
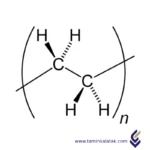
Polymers are made up of very large molecules made up of many repeating units called monomers, which ultimately form this long polymer chain
HDPE stands for High-Density Polyethylene, which is one of the most widely used materials in the world and is used in various industries due to its unique properties.
High Density PolyEthylene Film (HDPE)
High Density Polyethylene (HDPE for short) is a thermoplastic polymer derived from petroleum with a generalized chemical formula (C2H4)n. The HDPE formula represents the repeating monomer unit of ethylene and forms a poly-ethylene molecular chain. HDPE is distinct from other forms of polyethylene in that its side chain branching frequency is lower than other polyethylene types, where hdpe film is commonly referred to as a “linear” chain. This linear structure allows high density polyethylene film to pack together more tightly and is the reason for its impressive material characteristics.
Structure
The structure of High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is characterized by long, linear chains of repeating ethylene units (–CH₂–CH₂–) with minimal or negligible branching. This linear configuration allows the polymer chains to pack closely together, resulting in a high degree of crystallinity (up to 80-90%) and a dense molecular arrangement. The compact structure enhances intermolecular van der Waals forces, giving HDPE its high tensile strength, rigidity, and chemical resistance. The lack of branching, achieved through polymerization methods like Ziegler-Natta or metallocene catalysis, is a defining feature that differentiates HDPE from other polyethylene types, such as Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE). This tightly packed and highly organized structure makes HDPE a robust and durable material, widely used in industrial and consumer applications.
Properties
- High Strength-to-Density Ratio: While lightweight, HDPE exhibits excellent tensile strength, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Chemical Resistance: It is resistant to a wide range of chemicals, acids, and bases, ensuring durability in corrosive environments.
- Low Moisture Absorption: HDPE’s low water absorption ensures its effectiveness in moisture-prone applications.
- Flexibility and Impact Resistance: It withstands impact and environmental stress, even under extreme conditions.
- Thermal Resistance: HDPE maintains integrity in a broad temperature range, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial uses.
Applications
HDPE plastic is used in a laundry list of applications, as it is currently one of the most versatile plastic materials worldwide. Its strength, impact and corrosion resistance, chemical profile, and other valuable characteristics make it an ideal product material for various industries. Below is a brief list of some of the many uses of HDPE plastic:
- Corrosion-resistant piping, HDPE sheet, and stock material
- Fuel tanks
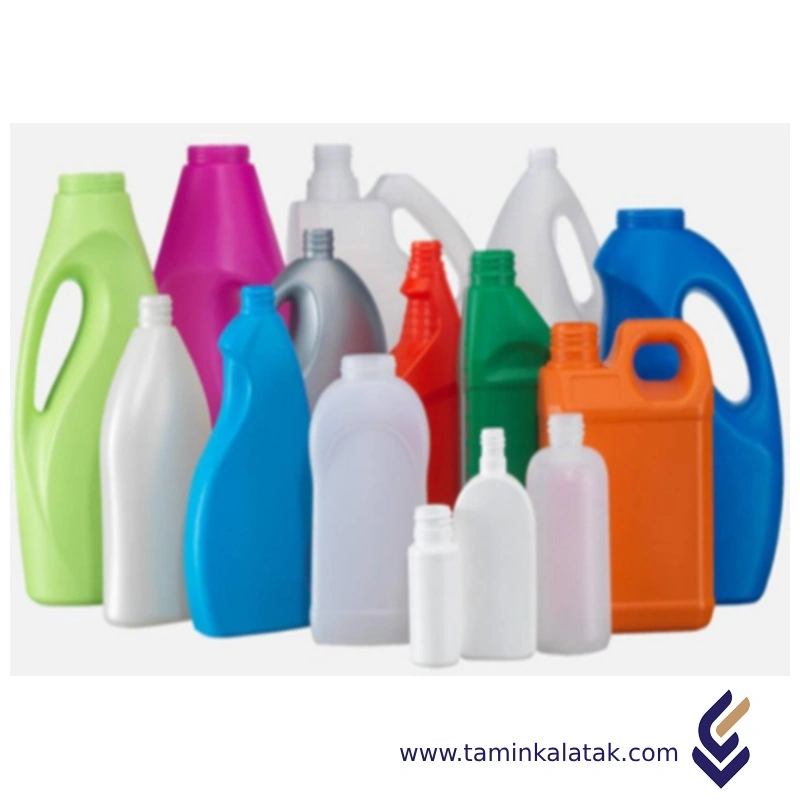
- Food and beverage containers, plastic bottles, milk jugs, cups, etc.
- Shampoo/conditioner bottles, ointment tubes, personal care product containers, etc.
- Trash cans, recycle bins, plastic containers, etc.
- Bread bags, cereal box liners, food storage containers, etc.
- Laundry detergent bottles
- Recycled plastic lumber and composites
- Medical equipment
- 3D printing filament
- Boating components
- Coax cable insulators
- Sewage mains
- Pyrotechnic components
and many, many more applications.
Advantages
- High strength-to-weight ratio
- Low friction coefficient and low moisture absorption
- High impact strength, resistant to dents and scratches
- Mold, mildew, rotting, mineral acids/bases, soil, and weather-resistant
- Resistant to chemicals, water, solvents, acids, detergents, and cleaning fluids
- Very malleable when heated and experiences medium to low shrinkage
- Easily recycled
- Can be sterilized via boiling, does not harbor bacteria well, and is dishwasher safe
- Replaces heavier materials in some applications
- Cost-effective
Disadvantages
- In certain forms, it can be flammable as it is a petroleum-based product
- Exhibits high thermal expansion
- Weak to oxidizers and chlorinated hydrocarbons
- Difficult to bond
- Sensitive to stress-cracking in suboptimal environments
HDPE FILM
| Prodact | Grade | MFI (g/10 min) | Density (g/cm3) | Process Metod | Application / Description | Description | Data Sheet | MSDS | Brochure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDPE Film | HD 7000F | 4,00 | 952,00 | film blowing | tissue-like films, garment bags, grocery bags, merchandise bags, disposal waste bags, counter bags, grocery sacks, and trash bags. | ||||
| HDPE Film | EX5 | 8,00 | 949,00 | blown film extrusion | counter bags, carrier bags, and wrapping films | ||||
| HDPE Film | HF5110 | 10,00 | 951,00 | blown film extrusion | high-strength grocery sacks, shopping bags, and high-quality thin films for uni/multi-wall packaging | ||||
| HDPE Film | HM9450F (EX5) | 28,00 | 949,00 | blown film extrusion | For paper-quality blown films, suitable for counter bags, carrier bags and packaging films Excellent processing | HM-9450F (EX5) رزین درجه فیلم دمیده است که با پلیمریزاسیون سوسپانسیون مونومر اتیلن تولید می شود. HM-9450F (EX5) یک پلی اتیلن با چگالی بالا دو حالته با 1-بوتن به عنوان کومونومر است. | |||
| HDPE Film | HFI 5110 | 10,00 | 951,00 | blown film extrusion | Grocery Sacks,Shopping Bags,Thin Packaging Films, Multi-Wall Bag Liners | HFI 5110 is a high molecular weight, high-density polyethylene with broad molecular weight distribution and 1-hexene as a co-monomer, specially developed for producing thin films with excellent strength and rigidity. This product is suitable for manufacturing of high strength grocery sacks, shopping bags and high quality thin films for uni/multi-wall packaging. Films produced with this grade can be readily treated and printed to give high quality graphics. HFI 5110 has been manufactured under Basell license | |||
| HDPE Film | MFI 3713 | 13,00 | 937,00 | blown film extrusion | High-strength carrier bags. Thin films for uni/multi-wall packaging. | ||||
| HDPE Film | EX5 | 8,00 | 949,00 | blown film extrusion | Counter bags,Carrier bags,Wrapping films and sheets,Blending partner in various film applications | ||||
| FILM | MFI3313 | 13,00 | 933,00 | blown film extrusion | High-strength carrier bags,High-quality thin films for uni/multi-wall packaging | MFI 3313 is a medium density polyethylene, which has a broad molecular weight distribution and high melt strength. This product which is produced by 1-hexene as a comonomer, specially designed for producing thin films with high tear resistance, good sealability, high strength and high draw down. This product is suitable for manufacturing of high strength carrier bags and high quality thin films for uni/multi-wall packaging. MFI 3313 has been manufactured under Basell license. | |||
| FILM | MFI3820 | 20,00 | 938,00 | blown film extrusion | Packaging films,Geomembranes,High-strength carrier bags Uni/multi-wall packaging | MFI 3820 is a medium density polyethylene, which has a broad molecular weight distribution and high melt strength. This product which is produced by 1-hexene as a comonomer, specially designed for producing thin films with high tear resistance, good sealability, high strength and high draw down. MFI 3820 has been manufactured under Basell license. | |||
| FILM | MFI3713 | 13,00 | 937,00 | blown film extrusion | High-strength carrier bags,Thin films for uni/multi-wall packaging. | MFI 3713 is a medium density polyethylene, which has a broad molecular weight distribution and high melt strength. This product which is produced by 1-hexene as a comonomer, specially designed for producing thin films with high tear resistance, good sealability, high strength and high draw down. This product is suitable for manufacturing of high strength carrier bags and high quality thin films for uni/multi-wall packaging. MFI 3713 has been manufactured under Basell license. | |||
| FILM | MFI3820 | 20,00 | 938,00 | blown film extrusion | Packaging films.,Geomembranes.,High-strength carrier bags, Uni/multi-wall packaging | MFI 3820 is a medium density polyethylene, which has a broad molecular weight distribution and high melt strength. This product which is produced by 1-hexene as a comonomer, specially designed for producing thin films with high tear resistance, good sealability, high strength and high draw down. MFI 3820 has been manufactured under Basell license. |