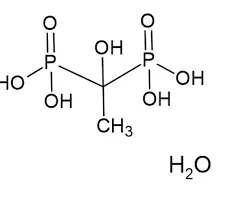
Etidronic acid
Calcium Diacetate is a chemical compound with the formula Ca(CH₃COO)₂. It is found as a white crystalline powder and is usually odorless or has a faint vinegar-like smell. Other names include calcium acetate and calcium ethanoate. The anhydrous form is very hygroscopic, so it is commonly supplied as the monohydrate (Ca(CH₃COO)₂·H₂O).
Structure of Calcium Diacetate
A molecule of calcium diacetate consists of one Ca²⁺ cation and two acetate anions (CH₃COO⁻). The calcium ion serves as the central cation, ionically bonded to two negatively charged acetate groups. Its crystalline structure varies depending on hydration.
Key Properties of Calcium Diacetate
-
Appearance: White crystalline powder
-
Odor: Generally odorless, or faint vinegar smell
-
Solubility: Freely soluble in water; slightly soluble in methanol; insoluble in acetone, ethanol, and benzene
-
Molar Mass: Approximately 158.17 g/mol (anhydrous)
-
Melting/Decomposition Point: Decomposes around 160 °C
-
Density: About 1.509 g/cm³
-
pH of Aqueous Solution: Neutral to slightly alkaline (pH ~6.3–9.6 for 10% solutions)
-
Hygroscopicity: The anhydrous form strongly absorbs moisture
Advantages of Calcium Diacetate
-
Source of Calcium: Used in dietary and pharmaceutical supplements
-
Food Preservative: Added under E263, inhibits mold growth and extends shelf life of baked goods
-
pH Regulator: Acts as a buffering agent in food processing
-
Stabilizer: Used in textile dyeing for color fixation and in food like canned vegetables and tofu to improve texture
-
Generally Recognized as Safe: Considered non-toxic at permitted levels
-
Good Water Solubility: Facilitates incorporation in various formulations
Disadvantages of Calcium Diacetate
-
Digestive Side Effects: Overconsumption or sensitivity may cause mild GI symptoms like bloating, constipation, or gas
-
Hygroscopic Nature: Needs dry storage to prevent moisture absorption
-
Drug Interactions: May interfere with absorption of certain medications—consultation advised when taken concurrently
-
Risk of Hypercalcemia: Excessive intake can raise blood calcium levels, leading to related health risks
Applications of Calcium Diacetate
Food Industry:
-
Preservative (anti-mold) in breads, pastries, and other baked goods
-
pH regulator and buffer
-
Stabilizer/firming agent in foods such as tofu (as a preferred alternative to calcium sulfate) and canned vegetables
-
Ingredient in candies, desserts, puddings
-
Additive in animal feed
Pharmaceutical Sector:
-
Buffering agent in medicinal formulations
-
Calcium supplement for deficiency
-
Phosphate binder for dialysis patients with high blood phosphate
Textile Industry:
-
Used as a color fixer
Chemical Industry:
-
Catalyst in select chemical reactions
-
Previously used in acetone production
Wastewater Treatment:
-
Employed to remove phosphate from wastewater
Soap Production:
-
Utilized as an alkali in certain soap manufacturing
Fire Gel Production:
-
When dissolved in alcohol at saturation, it forms a semi-solid, combustible gel suitable for flame use
Etidronic acid
| Products | Density | Melting point | pH (1% w/w solution in water) | Applications | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1-Hydroxyethylidene)bisphosphonic acid | For powder form about 1.45 g/cm3 (at 20∘C); for solutions it varies depending on concentration. | About 198−200∘C (with decomposition) | Usually less than 2 (very acidic) | Industrial water treatment (cooling towers, boilers, RO), detergent and cleaner formulations, cosmetics and health industries, textile and tanning industries, oil and gas industries. | White crystalline powder or colorless to pale yellow liquid (depending on grade and concentration) |