Polymers are made up of very large molecules made up of many repeating units called monomers, which ultimately form this long polymer chain
Plasticizers are chemical additives added to polymers to increase their flexibility, ductility, and processability.
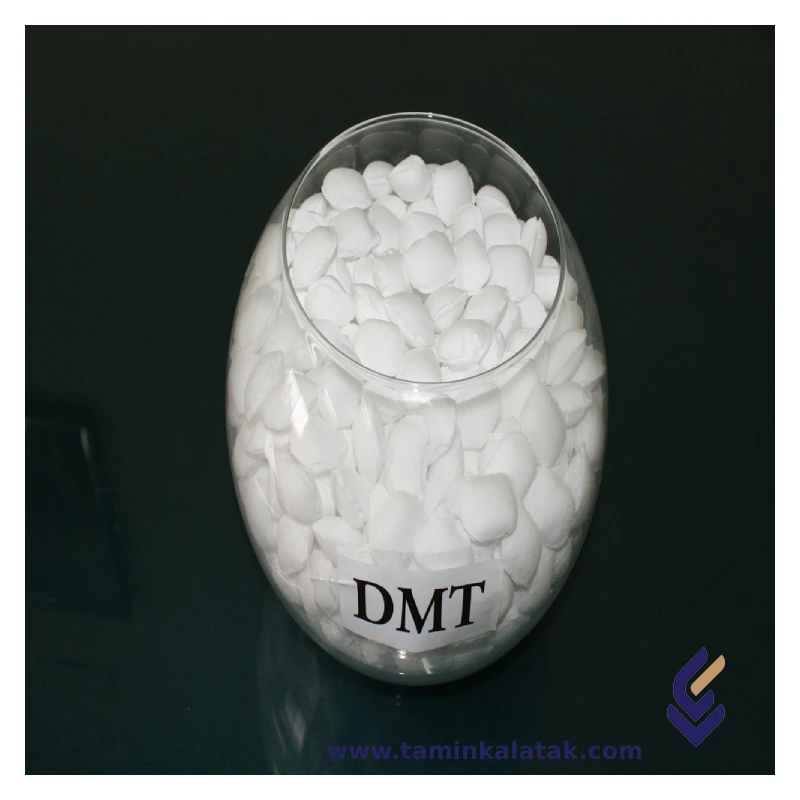
Di Methyl Terephthalate (DMT)
Dimethyl Terephthalate (DMT) is an organic compound with the chemical formula C8H10O4. It is an ester of terephthalic acid and methanol and is primarily used as a key intermediate in the production of polyester fibers and plastics. DMT plays a critical role in the production of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which is widely used in the manufacture of plastic bottles, films, and fibers.
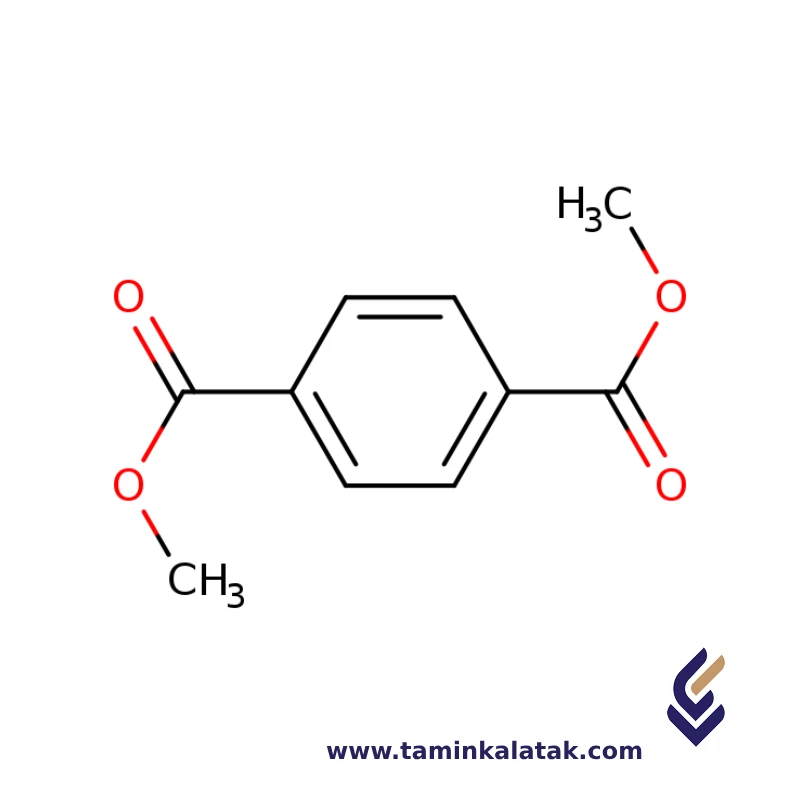
Structure
The structure of Dimethyl Terephthalate (DMT) consists of a benzene ring (C6H5) with two ester groups (-COOCH3) attached to the para positions of the ring. Each ester group is formed by the reaction of terephthalic acid and methanol, where the carboxyl group (-COOH) of the terephthalic acid is esterified with a methanol molecule to form the ester bond (-COOCH3). This gives DMT its molecular formula of C8H10O4. The structure includes a central benzene ring with two methoxy-carbonyl (-COOCH3) groups on opposite sides, making it a symmetrical compound. The ester groups contribute to the compound’s ability to polymerize, making it an important intermediate in the production of polyethylene terephthalate (PET).
Properties
Dimethyl Terephthalate (DMT) is a white crystalline solid with a slight aromatic odor. It has a melting point in the range of 140-143°C and a boiling point of approximately 284°C, making it relatively stable at high temperatures. DMT is slightly soluble in water but readily dissolves in organic solvents such as ethanol, acetone, and chloroform. Its density is around 1.305 g/cm³ at 25°C. As an ester, it has good reactivity, especially in esterification reactions, making it an essential intermediate in polyester production. DMT is stable under normal conditions but can decompose when exposed to very high temperatures or in the presence of strong acids or bases. It is also known for being flammable and should be handled with care in industrial processes. The compound has a low vapor pressure, meaning it doesn’t evaporate easily at room temperature.
Applications of Dimethyl Terephthalate (DMT)
- Polyester Production: Key precursor in the production of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), used in plastic bottles, films, and fibers.
- Textile Industry: Used in the manufacturing of polyester fibers for clothing, upholstery, and other fabric applications.
- Plastic Packaging: Important in producing plastic containers and packaging materials.
- Resins and Coatings: Used in the production of polyester resins for coatings, adhesives, and composites.
- Pharmaceutical and Agricultural Chemicals: Occasionally used in specialty chemical applications for pharmaceuticals and agricultural products.
Advantages of Dimethyl Terephthalate (DMT)
- Versatile Chemical: Acts as a key intermediate in the production of PET and other polyesters, making it highly valuable in various industries.
- Stable and Durable: Polyester products made from DMT are durable, resistant to abrasion, and possess good mechanical properties.
- Easy to Process: The esterification reaction with methanol is well-established, allowing for efficient production of DMT in large quantities.
- Recyclable: PET, produced from DMT, is widely recycled and used in new products, promoting sustainability.
Disadvantages of Dimethyl Terephthalate (DMT)
- Environmental Impact: The production of DMT can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other pollutants, requiring proper emission control measures.
- Flammability: DMT is flammable and poses a fire hazard if not handled properly during production and transportation.
- Cost: The cost of DMT can be relatively high compared to some other raw materials, especially when the demand for PET is fluctuating.
- Limited Chemical Resistance: While PET is generally durable, products made from DMT may not be as resistant to harsh chemicals and UV degradation compared to other polymers.
Applications
| Applications | , , , , , |
|---|
Dimethyl terephthalate
| Products | viscosity(cP) | Density (g/Cm³) | Applications | Data Sheet | MSDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimethyl terephthalate | 20-30 | 1.305,00 | Polyester Production Textile Industry Plastic Packaging Polyester Resins Pharmaceutical and Agricultural Chemical |