Polymers are made up of very large molecules made up of many repeating units called monomers, which ultimately form this long polymer chain
A thermoplastic is a type of plastic polymer that becomes moldable or flexible at a certain temperature and solidifies upon cooling. This property allows it to be repeatedly softened by heating and hardened by cooling without significant chemical change.
Thermoplastic Copolyesters (COPE)/(TPEE)
Thermoplastic Copolyesters (COPE), also known as Thermoplastic Polyester Elastomers (TPEE), are a class of thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) that combine the mechanical properties of engineering plastics with the elasticity of rubber. They are composed of hard polyester crystalline segments and soft amorphous segments, providing a balance of strength, flexibility, and chemical resistance.
Properties
Thermoplastic Copolyesters (COPE), also known as Thermoplastic Polyester Elastomers (TPEE), combine the mechanical strength of engineering plastics with the flexibility and resilience of elastomers. They exhibit excellent elasticity, allowing them to return to their original shape after deformation, while also providing high tensile strength and durability. COPE materials offer outstanding chemical and solvent resistance, making them suitable for harsh environments. Their thermal stability enables them to maintain performance across a wide temperature range, with good low-temperature flexibility and resistance to heat aging. Additionally, they possess excellent abrasion resistance, impact strength, and fatigue resistance, ensuring longevity in demanding applications. With easy processability through injection molding, extrusion, and blow molding, COPE is widely used in automotive, industrial, consumer, and medical applications where a balance of toughness, flexibility, and chemical resistance is required.
Structure
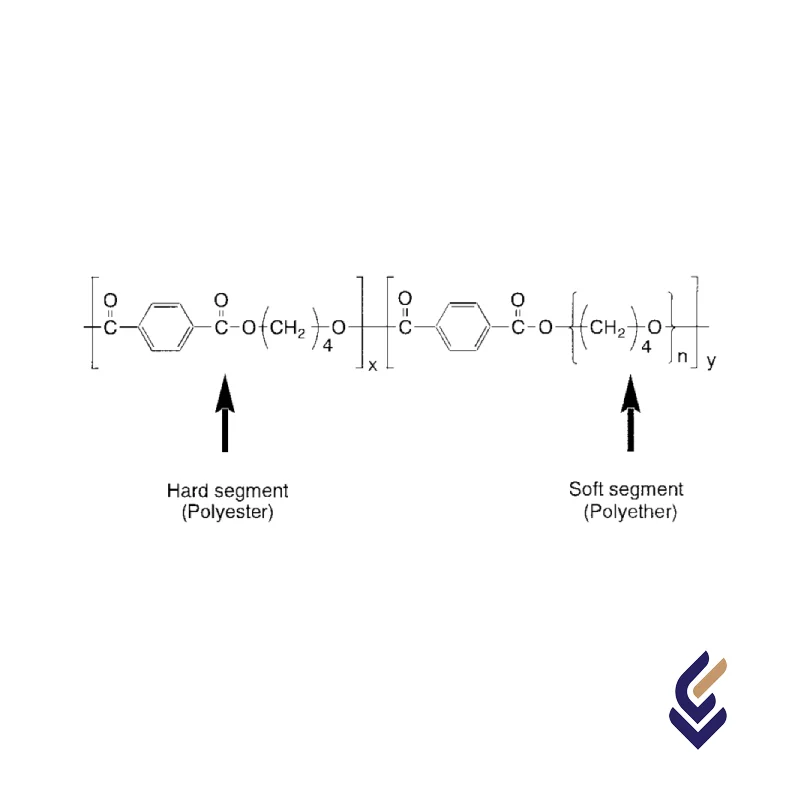
Thermoplastic Copolyesters (COPE), also known as Thermoplastic Polyester Elastomers (TPEE), are a class of high-performance elastomers that combine the characteristics of both thermoplastics and rubbers. Their structure consists of alternating soft and hard segments, where the soft segments are typically made of aliphatic polyether or polyester, providing flexibility and elasticity, while the hard segments are composed of polyester blocks, offering strength, thermal resistance, and durability. This segmented block copolymer structure enables TPEEs to exhibit excellent mechanical properties, such as high tensile strength, impact resistance, and superior fatigue endurance. The presence of ester linkages in the hard phase contributes to chemical resistance and heat stability, while the soft phase ensures flexibility even at low temperatures. Due to this unique molecular architecture, COPEs find applications in various industries, including automotive, consumer goods, electrical components, and medical devices, where both resilience and processability are essential.
Applications
- Automotive: Used in air ducts, CVJ boots, bellows, gaskets, and wire coatings due to high heat and chemical resistance.
- Industrial & Mechanical: Employed in conveyor belts, hoses, seals, and grommets for durability and flexibility.
- Consumer Goods: Found in footwear soles, sports equipment, and flexible smartphone components for comfort and toughness.
- Electrical & Electronics: Used in cable insulation, connectors, and protective coatings due to excellent dielectric properties.
- Medical Devices: Applied in tubing, catheters, and soft-touch grips because of biocompatibility and sterilization resistance.
Advantages
- High Elasticity & Flexibility: Maintains shape and flexibility even under stress.
- Excellent Heat Resistance: Performs well at elevated temperatures compared to other TPEs.
- Superior Mechanical Strength: Offers high tensile strength, impact resistance, and fatigue endurance.
- Good Chemical Resistance: Resistant to oils, solvents, and many industrial chemicals.
- Wide Processing Window: Easily processed through injection molding, extrusion, and blow molding.
- Recyclable: More environmentally friendly than thermoset elastomers.
Disadvantages
- Higher Cost: More expensive than other thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs).
- Limited Low-Temperature Flexibility: Can become less flexible at extremely low temperatures compared to TPU.
- Absorbs Moisture: May require drying before processing to prevent defects.
- Processing Challenges: Requires precise temperature control during molding and extrusion
Applications
| Applications | , , , , , |
|---|
Thermoplastic Copolyesters (COPE)(TPEE)
| Products | Melting Temperature | Density (g/Cm3) | Process Metod | Applications | Data Sheet | MSDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermoplastic Copolyesters (COPE)(TPEE) | 200 – 250°C | 1.10 – 1.35 | Injection molding, extrusion, blow molding | Automotive industry. Technical rubber articles |