Polymers are made up of very large molecules made up of many repeating units called monomers, which ultimately form this long polymer chain
HDPE stands for High-Density Polyethylene, which is one of the most widely used materials in the world and is used in various industries due to its unique properties.
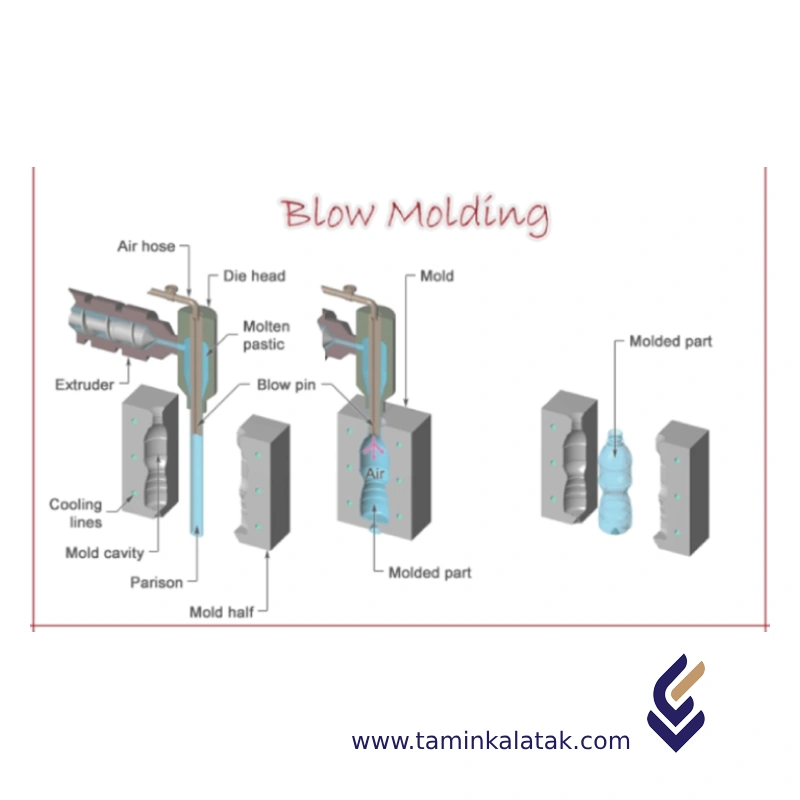
Blow Molding (BLOW)
Blow molding is a manufacturing process used to create hollow plastic parts by inflating a heated plastic tube (called a parison or preform) inside a mold cavity until it conforms to the shape of the mold. It is widely used for producing bottles, containers, and other hollow objects.
Types of blow molding
Continuous Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM)
Process:
- Molten plastic is continuously extruded in a tube-like form (parison).
- A mold clamps around the parison and inflates it with air.
- The part cools and solidifies before being ejected.
Intermittent Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM)
Types:
- Reciprocating Screw System: The screw moves back and forth to accumulate plastic before pushing it into the mold.
- Accumulator Head System: Plastic is stored in an accumulator before being discharged in a single shot.
Injection Blow Molding (IBM)
Process:
- Plastic is first injection molded into a preform (small tube-like shape with a finished neck).
- The preform is then transferred to a blow mold and inflated.
- The final shape is formed, cooled, and ejected.
injection Stretch Blow Molding (ISBM)
Process:
- Similar to IBM, but includes a stretching step before inflation to improve strength and clarity.
- The preform is reheated, stretched lengthwise, and then blown into shape.
Extrusion Stretch Blow Molding (ESBM)
Process:
- A parison is extruded and clamped in a mold.
- The parison is stretched both axially (lengthwise) and radially (outward) before being inflated.
Advantages of blow molding
- Cost-Effective Production
- High Efficiency & Fast Production
- Ability to Produce Complex Shapes
- Lightweight and Durable Products
- Versatile Material Usage
- Suitable for Large & Small Products
Disadvantages of blow molding
- Limited to Hollow Shapes
- High Initial Equipment & Mold Costs
- Inconsistent Wall Thickness
- Weak Seams & Stress Points
- Less Precision Compared to Injection Molding
- High Energy Consumption
Applications of blow molding
- packaging Industry: Bottles for beverages, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and household products.
- Automotive Industry: Fuel tanks, air ducts, washer fluid reservoirs, and coolant tanks.
- Industrial & Chemical Storage: Drums, barrels, IBCs, and spray bottles.
- Medical & Pharmaceutical: IV bottles, medicine containers, and diagnostic device housings.
- Consumer Goods: Toys, furniture components, water bottles, and detergent containers.
- Construction Industry: Water tanks, septic tanks, pipes, and conduits.
- Agriculture Industry: Pesticide and fertilizer containers, watering cans, and irrigation components.
Applications
| Applications | , , , |
|---|
MDPE / HDPE BLOW
| Prodact | Grade | MFI (190oC/ 21.6 kg) | Density (g/cm3) | Process Metod | Application / Description | Data Sheet | MSDS | Brochure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDPE | HD 0035 | ~0.30–0.40 g/10 min | ~0.953–0.955 | Blow Molding | Packaging Industry / Industrial and Chemical Containers / Agricultural and Household Products / Automotive Applications | HF-4760(BL3) is a blow molding grade resin with high density polyethylene with 1-Butene as comonomer which is manufactured by the suspension polymerization of ethylene monomer. Stiffness, good ESCR are it’s spetial properties. High rigidity and good flowablity which made it proper for usage in bottles and small blow molding goods. | ||
| HDPE | BL3 | ~0.30–0.40 g/10 min | ~0.954–0.956 | Blow Molding | Packaging Industry / Industrial and Chemical Containers / Household & Agricultural Products / Automotive Applications | |||
| HDPE | HF-4760(BL3) | ~0.30–0.40 g/10 min | ~0.954–0.956 | Blow Molding | Packaging Industry / Industrial and Chemical Containers / Household & Agricultural Products / Automotive Applications | HM-8355(BL4) is a Blow molding grade resin which is manufactured by suspension polymerization of ethylene monomer. HM-8355 (BL4) is a bi-modal high density polyethylene with Butene-1 as comonomer with general purpose of large container. | ||
| HDPE | HM-8355(BL4) | ~0.35–0.45 g/10 min | ~0.955–0.957 | Blow Molding | Industrial and Chemical Containers / Packaging Industry / Household & Agricultural Products / Automotive and Transportation Applications | |||
| HDPE | 3840 UA | ~0.40–0.50 g/10 min | ~0.954–0.958 | Extrusion Blow Molding | Industrial and Chemical Containers / Packaging Industry / Household & Agricultural Products / Automotive and Transportation Applications | HD3840UA is high density polyethylene copolymer containing butene-1(C4) as co monomer. It is suitable for use as rotational molding applications. HD3840UA has the following characteristics: good impact strength, easy to demoulding, UV stabilized, good whiteness, excellent surface finish. This grade has food contact approval. Applications: general purpose roto molded items, septic tanks, recycling tanks | ||
| HDPE | HBM 5510 | ~0.10–0.30 g/10 min | ~0.955–0.960 | Injection Blow Molding | Industrial and Chemical Containers / Packaging Industry / Household & Agricultural Products / Automotive and Transportation Applications | HBM 5510 is a high density polyethylene, specially developed for large parts blow molding. This grade, which is produced by 1-hexene as a co-monomer, offers high stiffness, good process-ability, excellent parison melt strength and good ESCR. HBM 5510 has been manufactured under Basell license | ||
| HDPE | HBM 5020 | ~0.20–0.40 g/10 min | ~0.955–0.960 | Extrusion Blow Molding / Injection Blow Molding | Industrial and Chemical Containers / Consumer Packaging / Household & Agricultural Products / Automotive and Transportation Applications | |||
| HDPE | HBM 5520 | ~0.15–0.35 g/10 min | ~0.955–0.960 | Extrusion Blow Molding / Injection Blow Molding | Industrial and Chemical Containers / Consumer & Household Packaging / Agricultural & Outdoor Products / Automotive & Industrial Applications | HBM 5020 is a high density polyethylene with broad molecular weight distribution, specially developed for small blow molded bottles. This grade which is produced by 1-hexene as a co-monomer, offer high stiffness, easy flow, very good ESCR, chemical resistance and sufficient impact strength. HBM 5020 is recommended for multipurpose blow molding process. HBM 5020 has been manufactured under Basell license. | ||
| HDPE | HBM 4265 | ~0.30–0.40 g/10 min | ~0.955–0.960 | Extrusion Blow Molding / Injection Blow Molding | Industrial and Chemical Containers / Consumer & Household Packaging / Agricultural & Outdoor Products / Automotive & Industrial Applications | |||
| HDPE | HFI 5110 | ~0.10–0.25 g/10 min | ~0.950–0.960 | Blown film extrusion | Blown film extrusion - single wall/multi-wall packaging - high quality thin films - shopping bags - high strength food sacks | MD-35504 is a UV stabilized linear medium density polyethylene grade with a narrow molecular weight distribution. It issuitable for rotational molding and some injection molding application such as technical parts and closures. Characteristics include: good impact strength, excellent external internal surface finish, and is UV stabilized. | ||
| HDPE | MFI 3713 | ~0.20–0.30 g/10 min | ~0.950–0.960 | Extrusion Blow Molding / Injection Blow Molding | Industrial and Chemical Containers / Consumer & Household Packaging / Agricultural & Outdoor Products / Automotive & Industrial Applications | |||
| Blow Molding | MD-35504 | ~0.30–0.40 g/10 min | ~0.955–0.965 | Extrusion Blow Molding / Injection Blow Molding | Industrial & Chemical Containers / Consumer & Household Packaging / Agricultural & Outdoor Products / Automotive & Industrial Applications |