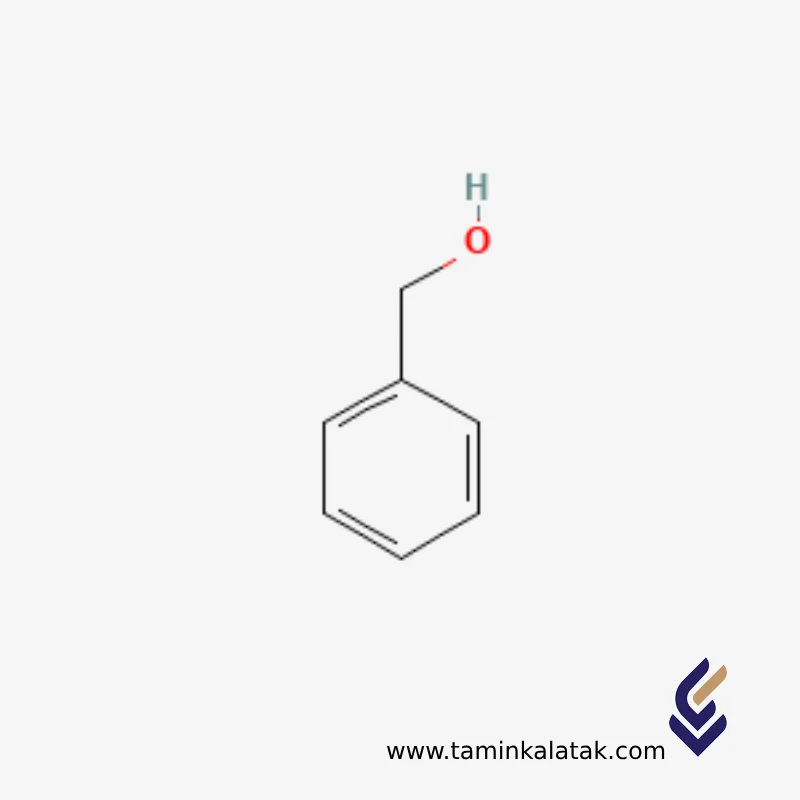
Benzyl alcohol
Benzyl Alcohol is an aromatic compound with a primary alcohol structure that occurs naturally in some essential oils such as jasmine and cinnamon oil, but is mostly produced synthetically.
Due to the presence of both a hydroxyl functional group (–OH) and a benzene ring, it exhibits solvent, bactericidal, and stabilizing properties. It is widely used across pharmaceutical, cosmetic–personal care, paint, coating, and detergent industries.
Chemical Structure of Benzyl Alcohol
-
Basic structure: An aromatic ring (C₆H₅) attached to a CH₂OH group — essentially benzene + methylene + alcohol.
-
Molecular formula: C₇H₈O
-
Molecular weight: 108.14 g/mol
-
Other names: Phenylmethanol, Benzenemethanol
-
Structural nature: An aromatic alcohol with moderate polarity, capable of forming weak hydrogen bonds and dissolving a wide range of polar and non-polar substances.
Physical and Chemical Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical state | Clear, colorless liquid |
| Odor | Mild, pleasant, aromatic |
| Boiling point | ~205 °C |
| pH (1% solution) | Approximately neutral (6–7) |
| Viscosity (25 °C) | ~5.9 mPa·s |
| Flash point | ~93 °C (flammable) |
Functional Properties
-
Polar organic solvent: Effectively dissolves resins, essential oils, dyes, and pharmaceuticals.
-
Antimicrobial: Exhibits preservative and antibacterial activity at specific concentrations.
-
Skin compatibility: Mild and relatively non-irritating at controlled levels.
-
Biodegradability: Rapidly biodegradable according to OECD guidelines.
Applications of Benzyl Alcohol
1. Pharmaceutical Industry
-
Used as a preservative in injectable formulations (e.g., lidocaine injections).
-
Serves as a solvent for poorly water-soluble active ingredients.
-
Approved and listed in USP, EP, and JP pharmacopeias.
2. Cosmetics and Personal Care
-
Functions as a mild preservative in creams, lotions, shampoos, and skin cleansers.
-
Enhances solubility of fragrances and essential oils.
-
Used in deodorants and antiperspirant formulations.
3. Paints and Coatings
-
Acts as a solvent in resin-based paints, inks, and lacquers.
-
Controls viscosity and improves film uniformity and surface appearance during drying.
4. Detergents and Industrial Cleaners
-
Used as a co-solvent in multi-purpose cleaning formulations.
-
Aids in the dissolution of oils, greases, and industrial residues.
5. Specialized Industrial Applications
-
Intermediate in the production of alkyd and polyurethane resins.
-
Used as a stabilizer in photographic chemicals.
-
Serves as a solvent softener in textile and leather processing.
Advantages of Benzyl Alcohol
-
Multi-functional solvent for cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and industrial formulations.
-
Biodegradable and relatively safe at permitted concentrations.
-
Provides mild antibacterial protection without requiring stronger preservatives.
-
Compatible with a wide range of solvents and active ingredients.
Disadvantages of Benzyl Alcohol
-
Irritating to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract at high concentrations.
-
Prolonged or repeated contact may cause dryness or allergic reactions.
-
At high doses (oral or injectable), exhibits neurotoxic effects (according to FDA and WHO data).
Safety and Handling Information
-
Chemical name: Benzyl Alcohol
-
Chemical formula: C₆H₅CH₂OH
-
CAS number: 100-51-6
Hazard Information
| Hazard Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Skin and eye irritation | May cause redness or inflammation, especially with repeated contact. |
| Central nervous system effects | High concentrations or prolonged exposure to vapors may cause drowsiness or dizziness. |
| Oral toxicity (moderate) | Harmful if swallowed in large amounts. |
| Aquatic toxicity | Potentially harmful to aquatic organisms at high concentrations. |
| Flammability | Flash point ≈ 93 °C; may ignite at elevated temperatures. |
Personal and General Safety Measures
Personal Protection
-
Wear chemical-resistant gloves (nitrile or heavy-duty latex).
-
Use laboratory safety goggles or face shields.
-
In closed or heated environments, use a half-mask respirator.
-
Wear protective lab or industrial clothing.
General Workplace Measures
-
Operate in a well-ventilated area (preferably under a fume hood).
-
Avoid prolonged skin contact.
-
Do not use or store near open flames or heat sources.
-
Keep a valid SDS (Safety Data Sheet) accessible near the work area.
Storage Conditions
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Suitable container | Tightly sealed glass or polyethylene containers resistant to organic solvents |
| Environmental conditions | Store in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and heat sources |
| Recommended storage temperature | 5 – 30 °C |
| Ventilation | Continuous ventilation, with localized exhaust in case of vapor release |
| Incompatible materials | Avoid contact with strong oxidizing agents such as peroxides, strong acids, or nitric acid |
Final Safety Recommendations
-
Personnel must be trained in HSE (Health, Safety, and Environment) procedures for handling aromatic solvents.
-
For industrial or laboratory use, an up-to-date SDS (compliant with GHS) must always be available.
-
During transport, proper hazard labeling and classification must be followed — UN No. 1990, in accordance with international chemical transport regulations.
Applications
| Applications | , , , |
|---|
Benzyl alcohol
| Products | Grade | Color and Appearance | Content(GC),% | Density | Applications | Data Sheet | MSDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benzyl alcohol | Colorless transparent liquid | ≥99% | 1.042-1.047 | Solvent, disinfectant, starting material in synthesis | |||
| Benzyl alcohol | Laboratory | Colorless and transparent | 99.50% | 1.047 g/cm³ at 20 °C | Organic synthesis, instrument calibration | ||
| Benzyl alcohol | Pharmaceutical | Colorless and transparent | 99.90% | 1.047 g/cm³ at 20 °C | Drug formulations, preservatives |