Polymers are made up of very large molecules made up of many repeating units called monomers, which ultimately form this long polymer chain
Plasticizers are chemical additives added to polymers to increase their flexibility, ductility, and processability.
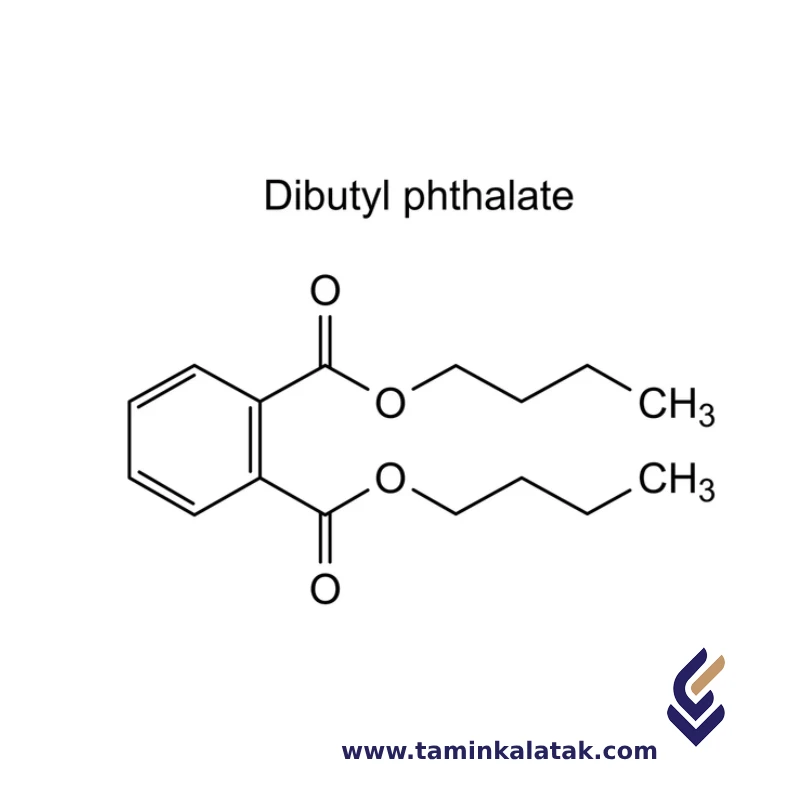
Di Butyl Phthalate (DBP)
Di Butyl Phthalate (DBP) is an organic chemical compound that belongs to the phthalate family. It is used primarily as a plasticizer to enhance the flexibility, durability, and workability of plastics. DBP is a colorless to pale yellow liquid with a characteristic odor.
Chemical Formula:
- C12H18O4 (Di-n-butyl phthalate)
Structure
Di Butyl Phthalate (DBP) is an ester compound composed of a phthalate group and two butyl groups. Its molecular structure consists of a benzene ring (C6H5) attached to a carbonyl group (C=O), which is further connected to two butyl ester groups. Each butyl group consists of a four-carbon chain (C4H9) with a terminal -CH2 group attached to the ester linkage. The two butyl groups are attached to the carbonyl group through ester bonds, making DBP a typical phthalate ester. This structure imparts the chemical its characteristic properties, including its use as a plasticizer in various industrial applications.
Properties
Di Butyl Phthalate (DBP) is a colorless, oily liquid with a faint, characteristic odor. It has a relatively high boiling point of around 340°C and a low freezing point, making it stable across a wide range of temperatures. DBP is soluble in many organic solvents but is only slightly soluble in water. It is known for its ability to act as a plasticizer, meaning it can increase the flexibility, workability, and durability of plastics, especially polyvinyl chloride (PVC). DBP is also resistant to oxidation and has a relatively low volatility, contributing to its effectiveness in various industrial applications. However, it is considered to have potential health risks, with concerns about its toxicity and environmental impact, leading to increasing regulatory scrutiny.
Applications of Di Butyl Phthalate (DBP)
- Used as a plasticizer in the production of flexible polyvinyl chloride (PVC) products such as flooring, coatings, and electrical cables.
- Commonly found in adhesives, sealants, and paints to enhance flexibility and durability.
- Employed in the manufacturing of personal care products like nail polishes, perfumes, and cosmetics.
- Used in the production of synthetic rubbers and plastics to improve workability and softness.
- Applied in the formulation of some lubricants and coatings for various industrial uses.
Advantages of Di Butyl Phthalate (DBP)
- Improves the flexibility and elongation properties of plastics and other materials.
- Enhances the durability and longevity of products by preventing them from becoming brittle.
- Acts as a stabilizer and dispersant in certain chemical formulations.
- Helps in producing smoother textures in personal care products.
- Cost-effective compared to other plasticizers for certain industrial applications.
Disadvantages of Di Butyl Phthalate (DBP)
- Potential health risks, including endocrine disruption and reproductive toxicity.
- Environmental concerns due to its persistence and potential for bioaccumulation.
- Increasing regulatory restrictions and bans in certain regions due to safety concerns.
- Can migrate out of materials over time, leading to potential exposure in consumer products.
Applications
| Applications | , , , , |
|---|
Di Butyl Phthalate (DBP)
| Products | Viscosity(Cp) | Density (g/Cm³) | Applications | Data Sheet | MSDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DBP | 88,00 | 104,00 | Plasticizer Cosmetic and Personal Care Products Rubber Manufacturing Pharmaceuticals Paints and Coatings Plastic Films and Sheets |