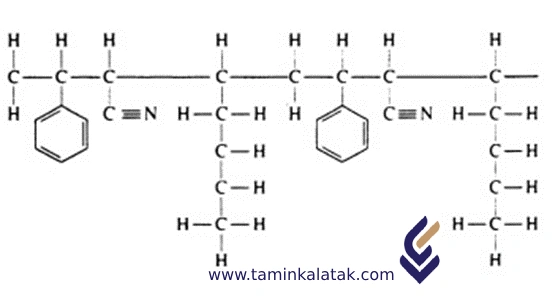
Polymers are made up of very large molecules made up of many repeating units called monomers, which ultimately form this long polymer chain
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or fomed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. As a thermoplastic polymer, polystyrene is in a solid (glassy) state at room temperature but flows if heated above about 100 °C, its glass transition temperature.and also It has wide applications in various industries including packaging, construction, and automotive.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
ABS is a terpolymer produced through the polymerization of styrene and acrylonitrile in the presence of polybutadiene.
The composition ratio typically varies between 15–35% acrylonitrile, 5–30% butadiene, and 40–60% styrene.
This material is generally manufactured through emulsion polymerization or by advanced blending techniques that combine polymers which normally do not mix, resulting in a homogeneous, high-performance product.
ABS 0150
ABS 0150 is one of the most popular and widely used grades of ABS.
Thanks to its excellent balance of strength, impact resistance, and processability, it is commonly used in a wide range of manufacturing industries.
This grade typically has a medium melt flow index (MFI), making it particularly suitable for injection molding applications.
ABS N50
ABS N50 grade offers superior mechanical performance and high impact strength, making it ideal for use in appliances, industrial parts, and electronic components.
Specially formulated for injection molding, N50 provides a smooth, glossy surface finish with excellent paintability, making it a top choice for aesthetic and functional applications across various industries.
Structure of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is an engineering thermoplastic copolymer composed of three primary monomers:
-
Acrylonitrile – provides chemical and heat resistance
-
Butadiene – imparts toughness and impact strength
-
Styrene – offers rigidity, processability, and surface gloss
This three-component structure gives ABS a well-balanced combination of toughness, mechanical strength, and processability, making it a preferred material in automotive, appliance, electronic, and consumer product manufacturing.
Due to its versatility and performance, ABS is one of the most in-demand polymers in the global supply chain.
Thermal and Mechanical Properties of ABS
The specific blend of these polymers determines the unique properties of ABS for various applications:
-
Acrylonitrile enhances chemical and heat resistance.
-
Butadiene provides impact strength and toughness.
-
Styrene contributes to rigidity, surface gloss, and ease of processing.
ABS exhibits a tensile strength ranging from 30 to 60 MPa, ensuring excellent structural integrity and load-bearing capability.
It also demonstrates good resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including acids and solvents.
Applications of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
1. Automotive Industry
ABS is widely used for both interior and exterior automotive parts.
Its impact resistance, durability, and ease of molding make it ideal for components such as dashboard panels, door trims, interior handles, and exterior body parts.
2. Consumer Goods
ABS is commonly used in the manufacture of household appliances (vacuum cleaners, kitchen devices, entertainment systems) and consumer electronics.
Its mechanical strength, impact resistance, and electrical insulation properties make it ideal for these applications.
3. Medical and Healthcare Equipment
ABS is increasingly used in medical and healthcare applications.
Its biocompatibility, ease of sterilization, and resistance to chemicals make it suitable for medical device housings, handles, and trays.
Its dimensional stability and durability allow it to withstand repeated sterilization cycles without performance degradation.
4. Industrial and Engineering Uses
ABS is also used in protective equipment, machine housings, tool handles, and industrial components.
Its high mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and impact resistance make it suitable for demanding industrial environments.
Advantages of ABS
✅ Cost-effective manufacturing
✅ Withstands multiple heating and cooling cycles
✅ Recyclable material
✅ High impact resistance
✅ Excellent chemical resistance
✅ High rigidity and mechanical strength
Disadvantages of ABS
⚠️ Flammable
⚠️ Poor weather and UV resistance
⚠️ Limited heat resistance
ABS Market in Türkiye
In recent years, the turkish polymer market has experienced strong growth in demand for ABS granules.
Due to its high impact strength, excellent mechanical properties, and easy processability, ABS has become one of the key raw materials in automotive, home appliance, and electronics industries.
For industrial customers, up-to-date ABS pricing is crucial since fluctuations in the petrochemical raw material market directly affect final production costs.
Many companies prefer to source their materials from reliable domestic producers such as Qa’ed Basir Petrochemical and Tabriz Petrochemical, both recognized for producing high-quality ABS that meets international standards.
Several factors influence ABS pricing, including grade type, producer brand, order volume, and market conditions.
Therefore, it’s important to have accurate and current price information before purchasing.
We recommend contacting our technical and sales experts for the latest ABS market updates and professional guidance.
ABS Production Process
ABS offers a balanced combination of strength, toughness, and heat resistance, which makes it a preferred polymer in automotive, appliance, electronics, and toy manufacturing.
Its production involves combining three different monomers to form a complex copolymer with unique mechanical and thermal properties.
Main Monomers – The Building Blocks of ABS
-
Acrylonitrile (C₃H₃N): Adds chemical resistance, heat stability, and hardness
-
Butadiene (C₄H₆): Provides toughness and high impact resistance
-
Styrene (C₈H₈): Offers rigidity, gloss, and processability
Primary Manufacturing Method – Emulsion Polymerization
The most efficient and widely used method for producing ABS is emulsion polymerization, which typically occurs in two main stages:
Stage 1: Production of Polybutadiene Latex
In the first stage, butadiene monomer is polymerized in water in the presence of an emulsifier (similar to soap), forming a latex of polybutadiene rubber.
This latex contains fine rubber particles that later act as impact-modifying domains in the final ABS structure.
Stage 2: Graft Polymerization
In the second stage, acrylonitrile and styrene monomers are added to the polybutadiene latex.
An initiator is then introduced to trigger polymerization.
This results in the formation of styrene-acrylonitrile (SAN) copolymer chains that graft onto the rubber particles, creating a dual-phase system — a soft rubbery phase (butadiene) dispersed within a rigid glassy matrix (SAN).
This complex morphology gives ABS its unique combination of toughness and strength.
Final Stage – From Latex to Granules
After polymerization, the ABS latex undergoes a finishing process to produce the final granulated resin:
-
Coagulation: The latex is coagulated using chemical agents, separating polymer particles from water.
-
Washing and Drying: The polymer is thoroughly washed and dried to remove residual moisture.
-
Extrusion and Pelletizing: The dried ABS powder is blended with additives (heat stabilizers, pigments, lubricants) and processed through an extruder.
The molten material is extruded into strands, cooled, and cut into uniform ABS granules, which are then ready for commercial use across industries.
Conclusion
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic offering an ideal balance of strength, impact resistance, and processability.
Its versatile properties make it indispensable in automotive, appliance, electronics, and industrial applications.
The variety of ABS grades—including 0150 and N50—caters to specific manufacturing requirements, ensuring high-quality molded products with excellent aesthetic and mechanical performance.
For updated pricing, technical consultation, or bulk purchasing, please contact our industrial specialists for expert guidance on selecting the most suitable ABS grade for your application.
Applications
ABS polymer
| Products | Grade | MFI (g/10 min) | Density (g/mm3) | Process metod | Applications | Data Sheet | MSDS | Brochure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABS polymer | D232/ M3 | 8 | 1.04 | injection molding,extrusion,thermoforming | Consumer Electronics,Consumer Electronics,Toys | |||
| ABS polymer | C442 | |||||||
| ABS polymer | B432/ E | 4.5 | 1.03-1.06 | sheet extrusion process | Foils , Multi-layer co-extruded sheets, Edges for furniture, Profiles | |||
| ABS polymer | B535/ E | |||||||
| ABS polymer | B732/ E | |||||||
| ABS polymer | F232 | |||||||
| ABS polymer | ABS 50 N | 2-6 | 1.03–1.06 | Injection Molding , Extrusion, Thermoforming | Injection Molding , Extrusion, Thermoforming | |||
| ABS polymer | ABS 40 N | |||||||
| ABS polymer | SD0150 | 1.7 | 1.04 | Injection Molding , Extrusion, Thermoforming | Automotive Parts, Home Appliances, Electrical Parts/Fittings,Telecommunication and Electronic Devices |